The color of feces in a newborn often changes. As a rule, parents very carefully monitor the behavior of a newborn child, look at the products of his life. And this is justified, because the baby is very vulnerable. It is very important not to miss the symptoms of developing diseases in order to take action in time. Therefore, young and inexperienced parents may be alarmed when they see drastic changes in their child's stool. They may think that something is wrong with the baby, that he is sick. Indeed, the color and consistency of feces indicate a state of health. digestive system baby. What should be the chair healthy newborn child and what changes should alert parents?
What is meconium
Immediately after birth, the baby's stool has characteristic signs. It is dark brown in color, thick and viscous in consistency, and odorless. This is meconium or original feces. It is so viscous and sticky that it is quite difficult to wipe it off the skin of the baby. Meconium is the waste products of the baby during prenatal development. Immediately after delivery, meconium passes naturally from the baby within 1-2 days. From the third day of a child's life appearance feces is changing. They become more liquid, not so sticky. The color of the stool changes to a greenish-brown hue. There may be thicker lumps in the stool.
Back to index
Normal stool color in breastfed babies
 The kid who is only on breastfeeding, defecates yellow-golden feces. If the baby has no problems in the work of the gastrointestinal tract, the stool will be a little liquid. Sometimes the color of feces in newborns can be greenish, especially in the first days after the disappearance of meconium.
The kid who is only on breastfeeding, defecates yellow-golden feces. If the baby has no problems in the work of the gastrointestinal tract, the stool will be a little liquid. Sometimes the color of feces in newborns can be greenish, especially in the first days after the disappearance of meconium.
This is a sign of the presence of bilirubin in the feces. The smell of healthy baby feces is sour. By consistency, feces often resemble liquid cottage cheese, as they contain small characteristic lumps. Lumps indicate the fat content of breast milk, which the baby's digestive system could not cope with.
Breastfed babies have more bowel movements than breastfed babies artificial feeding.
Back to index
Stool color in formula-fed babies
 If a newborn is bottle-fed, his bowel function changes. The color of feces in such a baby is not golden yellow, as when breastfeeding. The characteristics of bowel movements depend on the type of mixture that the child is fed on, on the reaction of the infant's body to it. Feces in artificial babies have more of a green tint. It is often thicker than in breastfed babies. Frequent occurrence artificial babies have very hard feces and constipation. The reason may be an unsuitable mixture for the child or improper preparation.
If a newborn is bottle-fed, his bowel function changes. The color of feces in such a baby is not golden yellow, as when breastfeeding. The characteristics of bowel movements depend on the type of mixture that the child is fed on, on the reaction of the infant's body to it. Feces in artificial babies have more of a green tint. It is often thicker than in breastfed babies. Frequent occurrence artificial babies have very hard feces and constipation. The reason may be an unsuitable mixture for the child or improper preparation.
The color of the stool varies from yellow to dark brown. Curd-like lumps in the stool occur in cases where food has not been completely digested. Perhaps the proportions were violated when preparing the mixture or the child overate. The smell of feces in artificial children is sharp and unpleasant.
Back to index
Fecal color of mixed-fed babies
Some babies are on mixed feeding, getting and breast milk, and mixture. This happens when the mother does not have enough breast milk to adequately feed the child, or if the mother works.
Feces in such children are normally not liquid and have a dense texture. Its color ranges from yellow to dark brown, as in adults. The smell of feces is quite sharp and unpleasant.
Bowel movements in artificial children and mixed-fed babies occur 1 or 2 times a day.
A healthy consistency for breastfed and formula-fed babies is a homogeneous, mushy mass.
Back to index
Why does stool turn green
![]() Sometimes your baby's stool can turn bright green. Sudden changes in the color of feces in an infant can be caused by changes in the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed or mixed. For example, if mom abuses sweet foods or foods with dyes.
Sometimes your baby's stool can turn bright green. Sudden changes in the color of feces in an infant can be caused by changes in the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed or mixed. For example, if mom abuses sweet foods or foods with dyes.
Problems with the digestion of food in a baby can occur if the mother does not allow him to drink the so-called hind milk. Hindmilk is the last portions of breast milk that the baby sucks out when the breast is almost empty. Often, mothers, guided by the desire to give the child all the best, prefer to feed him with first milk. They believe that the first milk is easier for the baby to suck. Therefore, without completely freeing one breast, they offer the child another. Thus, they deprive the baby of the necessary portion of hindmilk. It is in the back milk that enzymes are located that allow the baby to digest food. There are also many nutrients in there.
The baby should only be breastfed at one meal. You can give another breast only if there is no more milk in the first breast, and the baby is still hungry.
The reason for the appearance of green feces may be the mother taking medications, the presence of hormones in breast milk and replacing the usual mixture with a new one. Green color feces may indicate dysbacteriosis in infants. This is not a reason to worry, but at the appointment with the pediatrician, you need to talk about the changes that have appeared. In any case, mom needs to balance her diet, give up sweet foods and foods with dyes.
Back to index
Mucus and foam in stool
 A baby who is breastfeeding may sometimes have a stool with mucus. This is quite normal. The appearance of mucus in the feces suggests that the digestive system is not doing its job due to immaturity.
A baby who is breastfeeding may sometimes have a stool with mucus. This is quite normal. The appearance of mucus in the feces suggests that the digestive system is not doing its job due to immaturity.
Mucus may appear in the stool if the child has lactose intolerance.
This may be a reaction to a new formula or to a change in the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed or mixed.
Green stools with mucus may be a sign of developing dysbacteriosis. This condition is also characterized by skin rashes, anxiety and sleep disturbance in the baby.
If the appearance of mucus in the feces is not accompanied by other ailments in the child, and if the child looks healthy, you should not worry.
Foam in the baby's feces appears due to fermentation processes in the intestines. It may appear due to increased gas formation in a child or as a result of an allergic reaction to foods or mixtures. Gastrointestinal disorders can be accompanied by the appearance of foamy feces if the child was introduced to complementary foods too early or incorrectly.
Even in the maternity hospital, nurses and pediatricians ask mothers during rounds how the process of bowel movement occurs in a newborn. The fact is that the stool in the baby is one of key indicators the health of the child - moreover, both for those who are breastfed, and for those who are artificially fed.
Table of contents:Why is it important to control stools in babies?
Why is it so important to control the baby's stool:
- it will indicate problems in the work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- it is possible to assess the level of nutritional value of the child;
- by some changes in the stool, it is possible to determine the development of pathologies of organs and systems that are not related to the digestive tract.
A child in infancy poops daily, and even several times a day - this allows even parents without medical education to quickly respond to changes in the stool, pay attention to this moment of the pediatrician or health visitor. Of course, for this you will need to master at least minimal knowledge about what a baby’s stool should normally be, what can be considered deviations from the norm, and in what cases it is worth calling a doctor. All this information is laid out in the presented material.
Remember right away - the norm for stool in infants is a relative concept. Someone has a child pooping 3-4 times a day, and the stool is a yellowish slurry, and some children defecate 1 time in 1-2 days and this is the norm for them. How to determine how much the baby's stool fits into the normal parameters?
Bowel frequency
 On the 2nd-3rd day of life, a transitional feces begins to pass from a newborn - it has a yellow-green color, it can also be dark green of a semi-liquid consistency, which is absolutely normal.
On the 2nd-3rd day of life, a transitional feces begins to pass from a newborn - it has a yellow-green color, it can also be dark green of a semi-liquid consistency, which is absolutely normal.
On the 4th-5th day of a child's life, a bowel movement schedule is already established, and the frequency of stool in children fluctuates in a fairly large amplitude - from 10-12 times a day to 1 time in 2 days. It is noted that most newborns poop either during feeding or after eating.
Note:if a child poops once every 2 days, but at the same time behaves calmly, the act of defecation passes without screaming and strong straining, then such a rhythm of bowel movements can be considered an absolute norm.
As the child grows, the number of bowel movements also changes - for example, if in the first 1-2 months of life the baby pooped 8-10 times a day, then by 4-5 months the number of bowel movements decreases to 5-6 times a day, and by 12 months - 1-2 times a day. It is noteworthy that if a child, still in infancy, pooped 1 time in 2 days, then this frequency of stool persists in the future.
The amount of feces in a bowel movement
This indicator depends only on the diet of the child. For example, in the first 2-3 months of a baby, he will have very little feces - no more than 5 grams per bowel movement, but by 12 months this amount will be increased to 100-200 grams per day (about 60 grams per bowel movement) .
In general, it is considered normal stool in infants, when it is a mass of soft, mushy consistency. But even this indicator can be variable - for example, feces in the form of gruel with a small amount of lumps will also be considered the norm.
As the child grows older, the consistency of feces will also change - it will become more and more dense. But keep in mind - by 6 months of a child's life, the feces will already be completely formed, but will still remain soft. 
Yellow with white lumps, dark yellow, yellow-brown, golden yellow, and in general all variations of yellow for baby feces will be the norm. But just keep in mind that as soon as the child is transferred to artificial nutrition or vegetable / fruit purees begin to be present in the diet, the color of the feces becomes darker, and by the age of 12 months the baby becomes dark brown.
Do not worry, and in the case of green feces in infants - this is also the norm, and green feces becomes due to the presence in it or biliverdin. You need to know that bilirubin with feces in infants can be excreted up to 6-9 months of age, so the green shade of the stool in this age period may be considered the absolute norm. There is no reason to worry even in case of separation yellow stool, which then turns green - this means that bilirubin is released with stool in minimal quantities, in the air it simply acquires a characteristic shade.
We recommend reading:If the baby is on artificial or mixed feeding, then his stool will have a dark yellow or brown tint, the frequency of bowel movements will become less than breastfeeding, constipation or diarrhea, flatulence with difficult gas discharge may occur periodically.
Note:if the baby is fed mixtures with iron content (this is usually practiced for anemia in newborns), then the color of the feces will be pronounced green. And if the child is fed not with special mixtures, but with cow's milk, then the feces will be different oily sheen, bright yellow color and "cheesy" smell.
![]() Complementary foods are considered a new type of food for babies, the digestive system will begin to adapt to it and produce specific enzymes for digestion. In the first days of complementary feeding, the mother may pay attention to the fact that undigested pieces of food and an increased amount of mucus appeared in the baby's feces. If such a change in the stool does not lead to a change in the well-being of the baby (the baby does not scream, the feces pass freely), then you need to continue to feed him, carefully monitoring the amount of feces excreted, the frequency of bowel movements and the nature of the stool.
Complementary foods are considered a new type of food for babies, the digestive system will begin to adapt to it and produce specific enzymes for digestion. In the first days of complementary feeding, the mother may pay attention to the fact that undigested pieces of food and an increased amount of mucus appeared in the baby's feces. If such a change in the stool does not lead to a change in the well-being of the baby (the baby does not scream, the feces pass freely), then you need to continue to feed him, carefully monitoring the amount of feces excreted, the frequency of bowel movements and the nature of the stool.
There are some foods that can cause a laxative effect - for example, boiled carrots. Moreover, it is not even digested, but comes out unchanged with liquid feces. If the parents did not have the task of correcting the stool, getting rid of constipation in the baby, then with such “feeding” it is necessary to cancel the introduction of carrots into the child’s diet and switch to more gentle vegetables - for example, potatoes, zucchini. And if you introduce into the diet of the baby rice porridge, then the chair will surely be fixed. It is necessary to take into account such features of the influence of various products on the work of the digestive system, so as not to worry and not to take any drastic measures at the slightest change in the stool.
We recommend reading:In general, it is considered normal following changes in the stool with the introduction of complementary foods:
- feces become more dense;
- stool color changes from yellow to brown;
- fecal masses become heterogeneous;
- diarrhea or constipation may occur.
Knowing which baby stool can be considered the norm, it will be easy for parents to find out how healthy the baby is. If changes are detected that can hardly be called physiological, it is necessary to call a doctor at home and describe the full clinical picture to him - this will guarantee the timely detection of pathology and appointment effective treatment if necessary.
Tsygankova Yana Alexandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category (55 voice., middle: 4,71 out of 5)
A child's stool is not just a physiological function, it reflects the state of the body. First of all, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Mothers regularly inspect their child's chair and often worry in vain. In order to know when you really need to sound the alarm and go to the doctor, you need to have an idea of what a normal stool should be.
After birth, the baby passes meconium. This is the original stool, which is formed from the amniotic fluid swallowed by the child and the desquamated intestinal epithelium. It has a putty-like consistency of black or dark green, without smell.
Normally, meconium leaves 1-2 days after birth, which indicates the patency of the gastrointestinal tract. In the early days, the baby's stool occurs only once or twice a day, since the amount of nutrition that he receives from the mother's breast in the form of colostrum is small.
If the child does not have a stool within two days of birth, the doctor must be informed.
From 2-5 days of life, the baby's intestines begin to be populated by microflora due to microorganisms that live in breast milk, air and surrounding objects. Especially importance for the microflora of the newborn, they have the first drops of colostrum, so it is necessary to attach the baby to the chest immediately after birth.
In response to the settlement of the flora, an inflammatory reaction of the intestinal mucosa occurs - transient intestinal catarrh. The chair becomes yellow-green in color, an admixture of white undigested lumps, mucus, leaving watery spots on the diaper, is possible. This is a physiological condition that does not require treatment. From 1-2 weeks, the "mature" stool of the newborn is formed.
There are significant differences between the stools of breast-fed children and the feces of formula-fed children.
 Babies who are lucky enough to eat their mother's milk have stools from birth almost after each feeding (from 8 to 10 times).
Babies who are lucky enough to eat their mother's milk have stools from birth almost after each feeding (from 8 to 10 times).
A normal stool in a baby is yellow, of a homogeneous mushy consistency, with a sour-milk smell.
With artificial feeding of a newborn, defecation is less common - from 4 to 6 times a day. At the same time, the consistency of the stool is thicker, it is mushy, with a brown or greenish tinge.
Chair 2 month old baby may be irregular. Each baby is individual. For some, daily, for others - with regularity once every 1-2 days.
Do not panic if your child has a stool frequency of once every 2 days. If at the same time he is active, does not worry, he has a good appetite, there is no vomiting and bloating, there is nothing to worry about.
The stool of a child at 1 month of small volume, about 10-15 g. In the future, the frequency of stool becomes less, and the volume of feces increases to 40-50 g per bowel movement.
With the introduction of complementary foods, the baby's stool changes. The frequency of stool becomes less frequent - once or twice a day. The nature of the feces will depend on the input nutrition. If the child has rare and dense feces, it is better to start introducing complementary foods with fruit and vegetable puree. If the baby, on the contrary, had a liquefied stool, it is better to start with cereals.
Learn more about the diet baby, read the article by a children's doctor.
Learn more about when you need a child's diet in the pediatrician's material.

Since the baby is just beginning to learn to chew, fragments of undigested food may be visualized in the stool, and its color may match the color of the food eaten.
If, when adding a new product to the diet, in addition to changes in the stool, the baby has anxiety, bloating, skin rashes, you should stop eating this food. An intolerance to this food product may be caused by an allergy.
If, when semolina or millet porridge is introduced into the child’s diet, a liquid, frothy, light stool appears, a decrease in body weight is noted, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. This clinical picture is typical for celiac disease - gluten intolerance.
Child's stool disorders
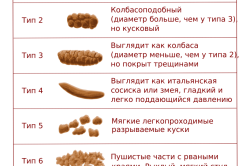
Changes in the stool in a baby can be both qualitative - changes in the color, nature of the stool, the appearance of pathological impurities, and quantitative - a delay or increase in defecation.
Characteristics of bowel movements, the appearance of the stool is directly related to the food consumed. At the same time, you should not compare the stool of two different children on the same diet, each baby has an individual character of the stool. The mother of the child will notice even the most minor changes and impurities in the stool. They can be both a variant of the norm and a sign of the onset of the disease.
If a newborn child once had a small admixture of mucus, undigested lumps, greenery in the feces, and at the same time the general condition of the baby does not suffer - he is vigorous, mobile, does not worry, sucks actively, assimilates the amount of food completely, there is a positive increase in body weight, no you should panic, call an ambulance and even more so self-medicate. It is necessary to monitor the dynamics for further changes in the stool.
What changes in the stool should you pay attention to and what can they say?
- The admixture of white curdled lumps in the feces with a positive increase in body weight may indicate overfeeding of the child, when the newborn is very often applied to the breast or the age-related amount of feeding is exceeded. If at the same time there is a decrease in body weight, anxiety of the child, there may be a dysfunction or insufficiency of enzymes that are secreted by the digestive glands.
- Rapid stools with a liquid consistency, frothy with a sour smell, which leaves a watery stain on the diaper, is a sign of insufficient digestion of carbohydrates. This may simply be lactose intolerance associated with improper organization of breastfeeding, or lactase deficiency - a disease in which there is a lack of an enzyme in the intestines.
- Fat shiny stools, leaving oily marks on the diaper, accompanied by constipation or diarrhea, indicates a violation of the digestion of fats.
- A small admixture of blood in the stool of a formula-fed baby, especially in combination with skin rashes, may be a sign of an allergy to cow's milk protein.
If there is an admixture of scarlet blood in the feces, you should immediately consult a doctor.
There can be many reasons for the appearance of blood in the diaper - from a small crack in the anus to a more serious surgical disease.

When changing the stool of a newborn, it is necessary certain actions.
- It is necessary to clarify whether changes in the stool are related to the child's nutrition. When breastfeeding, the nurse must follow a strict diet, as changes in the stool may be associated with an error in the mother's diet. In children of the second half of the year, it is necessary to exclude the influence of complementary foods on the nature of the stool.
- It is necessary to evaluate the weight gain of the child.
- Contact your doctor for additional examinations. The scatological examination includes microscopic, chemical examination of feces, examination of feces for occult blood, analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis.
Violations can occur in connection not only with a change in the nature of the stool, but also with the frequency of defecation. These include constipation and the opposite condition - diarrhea.
Constipation - the absence of an independent stool for more than two days, accompanied by bloating, anxiety of the child, decreased appetite.
One of the most common problems in the first year of life is constipation. Most often, this is faced by children receiving mixtures.
For more information about why it occurs and how to deal with this problem, read the article by a children's doctor.
First you need to install possible cause the occurrence of constipation. In children, constipation is most often functional in nature due to impaired intestinal motility.
Possible two development options motor activity intestines.
- Atonic constipation. Occurs with insufficient motor function of the intestine. At the same time, there are long delays in stool, bloating, and when emptying, the volume of feces is very large.
- Spasmodic constipation. Associated with increased contractile function of the intestine. The act of defecation is accompanied by anxiety of the child, the stool is very dense, in small portions, looks like sheep's feces.

When constipation occurs certain actions are required.
- Compliance with the diet of the child. When breastfeeding, strict adherence to the diet is necessary. With artificial feeding, the child should receive a sufficient amount of liquid. From the second half of life, the chair can be corrected by the introduction of complementary foods. With constipation, you can try to introduce a decoction or mashed prunes into the diet.
- Tummy massage and gymnastics help to increase peristalsis and improve digestion.
- With spastic constipation, the child will be helped to empty candles with glycerin.
- If an independent stool is delayed for more than two days, the child must be helped to poop with the help of cleansing enema, with bloating and flatulence - use a vent tube.
If you are not sure that you can do these procedures yourself, you need to contact a specialist. But also do not forget that stool delays can be associated with organic congenital changes in the intestine.
If constipation persists for a long time, you should consult a doctor. Do not self-medicate and use laxatives without the appointment of a specialist.
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
Frequent loose stools of a greenish hue with an admixture of mucus, a streak of blood, combined with vomiting, are a sign of an acute infection.
In children in the first year of life, intestinal infections are common, since the protective immune functions of the intestine are not fully formed. Non-dangerous pathogens that are not clinically manifested in an adult can lead to a serious condition in a newborn.
Diarrhea in a child is dangerous because, in addition to a large loss of fluid from the body, absorption in the intestine is disturbed. This leads to dehydration of the body.
When a child becomes ill, a doctor's consultation is necessary to prescribe treatment. Despite the reduced appetite, it is necessary to continue to feed the child, especially breastfeeding. The protective factors of mother's milk will help to improve bowel function.
For any violations of the stool, first of all, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps your fears are unfounded, and unreasonable treatment can only aggravate the situation.
Very often, the condition of a small child is assessed by the nature of the stool. Many problems can be solved at the initial stage. To do this, you need to know the norm and deviations for the main indicators: stool frequency, color, consistency. All these characteristics may differ depending on what kind of feeding the baby is on.
The chair of children who are on breast milk has its own characteristics.
- The number and frequency of stools fluctuate frequently.
- Stools up to 12 times a day are not considered a digestive disorder, and the absence of a stool for three days is not constipation.
- After the introduction of complementary foods (not earlier than the sixth month), the baby's stool depends on the foods eaten, but not on what the mother ate. The diet of a nursing woman does not affect feces.
What stool test result is considered normal?
- Stool from yellow to green.
- The presence of bilirubin can be traced up to the 8th month.
- Sour smell.
- White blood cells, streaks of blood, mucus, and milk clots may be present.
- Unformed intestinal microflora.
Key metrics: what you need to know
Stool standards may change. It depends on the general condition of the baby, what kind of food it receives (formula or breast milk), whether complementary foods are introduced into the diet. If the child is breastfed, then the feces have the following rate.
Color can vary from light yellow to brown. For a child who eats breast milk, a greenish tint to the stool will also be the norm.
Feces can change color for several reasons:

Normal stools can vary in consistency from thick to runny. It is important to distinguish the state of diarrhea from the norm.
Worrying points:
- the stool becomes watery;
- bowel movements frequent;
- an unpleasant odor appears;
- pronounced green color;
- high body temperature;
- the appearance of vomiting;
- mucus, blood, foam can be observed in the feces;
- the child looks lethargic, drowsy, apathetic.
Parents need to know that with an increase in body temperature, a change in the behavior of the baby, loss of appetite and poor weight gain, an urgent need to see a doctor.

Baby feces always have various impurities
- A large number of white lumps may indicate overeating of the baby. Not enough enzymes to digest all the milk.
- A small amount of mucus is always found in the stool. In the case when it becomes larger, we can talk about the beginning of the inflammatory process. There are several more reasons for the appearance of mucus in the stool in a breast-fed child: improper attachment to the breast, early introduction complementary foods, infections.
- Foam may indicate dysbacteriosis, food allergies, abdominal colic. The appearance of abundant foam indicates an intestinal infection.
- The appearance of blood in the feces may be the result of anal fissures, inflammation in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, vitamin K deficiency, and helminthiasis.
Changes from birth to year
If the child is breastfed, then the composition of the feces will depend on what the mother ate, and on the characteristics of the development of the digestive sphere of the child. If mom eats foods that weaken, then the stool will liquefy. And vice versa.
As soon as the baby is born, within three days he has a first-born stool - meconium comes out. It has a black color and a viscous composition. After that, the baby will begin to poop with ordinary feces, which have a mustard color and a medium liquid consistency. There may not be a chair for several days, since the child has completely freed the intestines from the contents.
When breastfeeding a child, his feces acquire a greenish tint, liquefy and acquire a sour smell.
Around the second week of life, transitional milk changes to mature milk. The child's digestive organs begin to get used to these changes. Often there are colic, regurgitation. By the end of the first month, milk acquires its final composition.
At 1 month, the baby defecates after almost every feeding. At 2 months, the frequency of stool decreases up to 4 times. The norm is considered yellow, liquid consistency, milky smell.
The third month is characterized by the fact that the child can poop every other day. During this period, there is a change in the composition of breast milk and enzymes in the intestines of the child. If the child rarely poops, but does not experience discomfort, you just need to wait out this period.
After the 6th month, changes in the stool can be observed. It acquires a more pronounced pungent odor, the consistency thickens. These changes can occur even if complementary foods have not been introduced. This is due to the fact that the child's body is preparing for a new food and began to produce more enzymes.
It is very important to ensure that the baby sucks out not only foremilk, which is a thirst quencher for the baby. Back milk has all the nutrients, which is more difficult for a baby to reach.
The advent of green liquid stool says that the child eats only foremilk. Mom should keep the baby at one breast longer during feeding.

Important points: how to recognize the problem
Problems with stools during breastfeeding can occur for the following reasons:
- feeding the child according to the regimen;
- lack of milk;
- supplementation with water;
- early feeding with mixtures;
- early introduction of complementary foods.
If the following symptoms appear, you should seek medical help:
- Stool more than 12 times a day.
- Rare urination.
- Copious, frequent regurgitation.
- Stomach ache.
- Bad breath.
How to fix the situation: tips for solving the problem
Constipation in a child can be suspected in the following cases:
- the child has not pooped for more than three days;
- the behavior of the baby becomes capricious, there is constant crying;
- the child has a hard stomach;
- feces become dry and very hard;
- suspicion of abdominal pain in a child (he often bends his legs to his tummy).

Do not resort to self-treatment and use people's councils(thermometer, soap). All these methods can lead to disruption of the intestinal microflora and inflammatory processes. Constipation is rare in breastfed babies. A symptom can be not only a long absence of feces. It becomes hard and dry.
What foods are weak? Help change the situation following products: cereals, fruits, boiled vegetables, kefir. Prunes will help to establish the process of digestion. To do this, a woman should eat about 4 pieces of this dried fruit on an empty stomach in the morning.
Thick stools may occur due to preparations that contain iron. They are usually prescribed to mothers in the first months after childbirth to raise hemoglobin.
Another reason that the feces are thick is a violation of intestinal motility.
To adjust the chair will help:
- laying the baby on the stomach before feeding;
- a sufficient amount of liquid;
- belly massage;
- gymnastics.
If all these methods do not help, they resort to laxative drugs. What medicines are allowed for babies with constipation? Glycerin suppositories or Microlax preparation instantly weaken and lead to the desired result.
From the diet it is better to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation and worsen the situation. What foods should not be consumed? These are peas, grapes, cucumbers, cabbage. If there are white lumps in the feces, then this indicates poor digestion of breast milk. Enzyme preparations, which should be prescribed only by a doctor, help to normalize the situation.
Frequent loose stools can occur due to infection in the body.

Dangerous symptoms:
- temperature rise;
- the stool becomes very liquid;
- the appearance of copious amounts of blood, mucus;
- lack of weight gain;
- regurgitation, vomiting.
In this case, only medicines will help to improve the chair: antibiotics, antiviral drugs, prebiotics. Mom should not eat foods that weaken and lead to increased gas formation.
Do not worry and stop breastfeeding. The main thing is to recognize the problem in time and consult a doctor. Self-medication can lead to serious health problems for the baby.
Frequent stools in a newborn baby are a sign of health. As a rule, the child poops with mushy masses, while the color of the feces is yellow or green, you can observe the presence of particles of processed milk or a mixture. Such a picture is a common occurrence and parents should not worry. If the baby poops with increased frequency or does it very rarely, experiencing discomfort from bloating or colic, gaining weight poorly and eating without appetite, this is a signal to go to the pediatrician for a consultation.
Age norms for stool frequency
For breastfed babies
Let's talk about what are the norms of defecation in a newborn. New parents should be aware that the color, texture, and amount of breastfeeding baby's stools are not always the same.
The quality of the chair is influenced by many factors: the amount of water and the type of food, the time of day and the characteristics of the child's body. The emotional background and physical condition of a nursing mother also affect the number of bowel movements.
Features of the chair of children up to 2 months
Let's list age-related changes stool frequencies:
- 1 day. Meconium - the original stool, tarry and black, is characteristic of all newborns. Children on the first day of life may defecate one or even more than six times a day.
- 2-7 days. Meconium may have already stopped, but its presence is also quite normal. The original feces accumulate in the children's intestines during the period of prenatal development. He needs to completely go out in order to be replaced by ordinary feces. For this age, stools in the amount of one to three per day are characteristic.
- 2 weeks (we recommend reading:). For a newborn during this period, irregular bowel movements are quite acceptable. The number of bowel movements for each baby will be individual, depending on the lactation of the mother. The constant change in the composition of breast milk during the first month due to the establishment of lactation affects the quality and quantity of the baby's stool. At this age, the baby may begin increased gas formation and colic may appear.
- 3-5 weeks. Mom's milk acts as a laxative, so frequent stools are often observed - up to 10 bowel movements per day. The number of bowel movements directly depends on the number of feedings. A small number of bowel movements in 1 month (less than 4 times) indicates that the young mother does not have enough milk.
- Starting from the sixth week. During this period, parents may notice a sharp decrease in the number of bowel movements. Lack of bowel movements can be observed for a day, two or even three. What is the reason? The enzyme crisis is to blame. The renewal of breast milk provokes the appearance of new enzymes, to which the small organism is now getting used. The process of adaptation can take up to several weeks - during this period, you can notice both an increase in the desire to suck on the breast, and the rejection of mother's milk.
 After 6 weeks, children have an enzyme crisis - the baby's gastrointestinal tract is completely rebuilt for mother's breast milk, in connection with which new enzymes are produced
After 6 weeks, children have an enzyme crisis - the baby's gastrointestinal tract is completely rebuilt for mother's breast milk, in connection with which new enzymes are produced Number of stools after 2 months to a year
We continue to study the change in defecation:
- 2 months. The individual rhythm of the gastrointestinal tract begins precisely from this age. Bowel movements at this age are no longer so frequent. Pediatricians note that each two-month-old child may have its own characteristics and the amount of stool: some poop once or twice a day, while others do it still intensively - up to six times. Both options are considered normal.
- 6 months. The prepared body of a 6-month-old baby and a large number of enzymes allow you to start introducing complementary foods. The quality of the stool changes even before the start of complementary foods: the appearance of a specific smell is noted, the density of the feces increases, and the number of bowel movements decreases.
- A one-year-old baby can poop one to three times a day.
There are no clear norms for the number of bowel movements for infants. The presence of a chair after each feeding is a completely normal picture. A child who poops a lot can be weighed more often, starting from the second week, since the first week of life is characterized by weight loss, and the second - the beginning of a set of treasured grams. No matter how many bowel movements a day your baby has, a weekly increase of 150 g is a sign of normality.
 By the year the child's stool is set at a frequency of about 1-3 times a day, its consistency and smell also change. This is due to a change in diet and the beginning of the use of "adult" food.
By the year the child's stool is set at a frequency of about 1-3 times a day, its consistency and smell also change. This is due to a change in diet and the beginning of the use of "adult" food. For formula-fed babies
It is noted that artificially fed babies can poop with the same intensity as babies, but still, in most cases, an artificial baby poops less often. This difference is associated with a longer absorption of the adapted mixture compared to mother's milk:
- Number of feedings = number of bowel movements. For a child on an artificial type of feeding, the same principle is characteristic as with breastfeeding. The baby receives the mixture every 3.5 hours, which means that the number of bowel movements will also decrease.
- Thickness of feces. The feces of formula-fed babies are denser, which affects the different times of bowel movements and their regularity. The long passage of feces through the intestines leads to its hardening and possible constipation.
- Stool retention. A sign of stool retention in an artificial baby is the absence of defecation during the day, which would be quite normal for a breastfed baby.
The baby may experience constipation or suffer from frequent loose stools due to an improperly selected mixture. Consulting with a pediatrician will help solve this problem. Joint choice a suitable mixture and a smooth transition to it will help to establish a chair.
Frequent change of the adapted mixture is harmful to the child's digestive system. A small body must get used to the new composition of the mixture, and a frequent or abrupt change in food provokes an increase in the frequency of stools, or vice versa - greatly reduces it.
Get rid of constipation in 4 steps
Constipation in children who eat mother's milk is a rare phenomenon. You don’t have to worry if the baby poops on its own every three days, this indicates the correct assimilation of mother’s milk. A chair even once every 5 days for babies is considered the norm by pediatricians, provided wellness child.
If a mother notices frequent whims, increased gas formation, colic or refusal to eat, it is worth resorting to auxiliary means:
- Syrup of lactulose. Milk sugar - lactulose helps the active work of the intestines. Such a safe laxative can be purchased at any pharmacy without a prescription. Pediatricians advise keeping it in an individual baby. From side effects there may be an increase in the amount of gases in the first days of taking the remedy. It is necessary to start treatment with small doses, exceeding the amount is not permissible.
- Such candles should be placed only when necessary. One candle, as a rule, solves the problem. Irregular stools and the inability of the child to poop on their own, the need to regularly resort to the help of candles is a signal to seek help from a pediatrician.
- Enema or gas tube. These procedures are not recommended to be performed regularly. They should only be used as a life-saving remedy for severe bloating and the absence of stools for several days. About that, and an enema, read our article.
- Gymnastics and tummy massage. Such physical activity will help the intestines to start working. In this case, there will be an active promotion of fecal masses and the discharge of gases.
 Glycerin suppositories are an emergency remedy that allows you to quickly solve the problem of childhood constipation. If their use becomes systematic, it is urgent to contact a pediatrician.
Glycerin suppositories are an emergency remedy that allows you to quickly solve the problem of childhood constipation. If their use becomes systematic, it is urgent to contact a pediatrician. If a three month old baby does not poop, perhaps the reason is the lack of mother's milk and the body simply has nothing to remove. To increase lactation, doctors recommend frequent attachment of the newborn to the breast.
- The average number of daily bowel movements is from 3 to 10 times.
