Modern Greek culture, with all the aspirations for novelty and originality, carefully preserves three traditions.
First, antique. Existing museums receive state support ancient culture and new ones are organized. Yes, close acropolis The Museum of Ancient Performing Arts has recently been created: masks, cothurns, costumes are shown, texts of classical drama are read.
There are quite a few preserved in Greece ancient theaters under open sky. In them, and not only in them, ancient tragedies and comedies are staged - Aeschylus, Sophocles, Euripides, Aristophanes. Ancient mythology and literature are studied in schools, mainly in translation.
But in gymnasiums, humanitarian lyceums, and universities, they study the ancient Greek language and classical culture very thoroughly.
classical philology in Greece is at a decent level. ancient heritage cultures of Greece - Greek literature covers poetry, drama, philosophical and historical treatises, travel books.
Homer(9th century BC), author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, was the most famous Greek author of antiquity. The world's first travel writer was Pausanias, who in the 2nd century BC wrote the Guide to Greece. Numerous editions of this book are now available online. English language.
Sappho(who lived on the island of Lesvos in the 5th century BC) is known for his love poetry dedicated to women.
These days the most famous novelist Nikos Kazantzakis- the most widely read Greek author. And the classics of modern Greece were even awarded Nobel Prize are the writers George Seferis and Odysseus Elitis.
Culture of ancient Greece
When we talk about ancient Greece as a continuous cultural phenomenon, we must remember that, as in any culture, people's ideas about the world and its foundations are subject to evolution.
During the heyday of the Greek city-states, when democracy reigned in Athens, the ideas of the Greeks about the gods were already very different from those fabulous, semi-naive ideas that were in the time of Homer.
This can be seen from the changes that the image of Zeus underwent - from a thunderer who quarreled with other gods, was capricious and abused his power, they turned into a reasonable ruler of the world, where everything is done according to his wise instructions.
Most clearly, the changes in Greek spiritual culture are manifested in the relationship between Dionysian and Apollonian principles. This issue has been analyzed in detail Friedrich Nietzsche. According to Nietzsche, the god Dionysus symbolized for the Greeks the self-consciousness of a person living in a mysterious, enchanting, but also full of dangers world. wildlife.
This world, in principle, incomprehensible to man and chaotic, the law in it is the arbitrariness of the gods, symbolizing the forces of nature. However, not only fear caused this world in the Greek man: for him it was possible and natural to dissolve in this chaos, a feeling of happiness of belonging to this mystical world.
Tool of Dionysus- intoxication that knows no barriers, which awakens the soul from the painful sleep of the stream of forms and attracts it to the enchanting area of \u200b\u200blife, which knows no barriers and submissions.
It was precisely this kind of going beyond their own limitations and awe of the magic of the world that the Greeks achieved during the holidays dedicated to the god Dionysus, of which the best known to us are the mysteries held annually in Eleusis.
At these festivities, the Greek comprehended the nature of the Dionysian world in ecstasy, carrying the soul on the wings of sweet madness to the palace of All-consuming Love, which was apparently understood as the deepest essence of the universe. Nietzsche believes that the significance of the Dionysian orgies is in the redemption of the world and spiritual enlightenment, which allows in other days not to be crushed by the horror of the world.
World of Dionysus- the world of bodily symbolism, and not limited by masks and the severity of the ritual, but completely subjugating the dance, rhythmizing the entire body of the participant, connecting it with everyone and dissolving it in everything.
It is here that Nietzsche sees the origins of musical harmonies, rhythms and dynamics. He also believes that the origins of the great art of ancient tragedy lie in the Dionysian mysteries.
"Irrefutable tradition asserts that Greek tragedy in its most ancient form had as its theme exclusively the suffering of Dionysus, and that for quite a long time the only stage hero was precisely Dionysus."
Second nature Greek culture - harmony of order and proportion- laid down in the Apollonian beginning. His personification is a beautiful image of the young god Apollo, who sets people up to lofty feelings, he owns art, most of all - music and poetry, his gift is inspiration and talent.
Apollo- the genius of majestic harmony. From the chaos of the primordial ocean of life, he creates the universe, highlighting the parts, giving them a form, filling them with meaning, commensurate with the idea of integrity. This is the World Artist and his creative power gives the world harmony within the boundaries of stability, order, stability and peace, triumphant and continuous.
Unlike the ever-dying-reborn Dionysus, Apollo is immortal and unchanging, for he is an incarnated Spirit, while Dionysus is striving to be unincarnated.
Nietzsche believes that the Apollonian is a manifestation of an instinct as ancient as the one that manifests itself in the Dionysian, but in the opposite direction: this desire for everything to find its place means, first of all, to find a place in the world for oneself, to protect one's personality from disintegration, agreeing to limitation. , but at the same time subordinate the whole world to the idea of this limitation.
Art of Greece.
During the period of Turkish domination, art - in addition to the church and such folk and applied varieties of it as wood carving, metal forging, pottery and embroidery - practically did not develop.
After the declaration of independence, King Otto I invited many Greek artists to study in Munich, where they were influenced by the German art school 19th century
Subsequently, Greek artists trained in other countries. Western Europe especially in France. As a result, despite attempts to preserve ancient and Byzantine traditions in art, the influence of Western European trends turned out to be predominant.
The leading place among the painters of modern Greece is Kostis Parthenis, it was he who brought ideas to Greece french impressionism. Parthenis, like many other Greek artists, did not settle for any one style.
He went through hobbies of expressionism, cubism and other modern trends. Prominent Greek artists Georgos Buzianis and Nikos Hadzikyriakos-Gikas worked in the spirit of expressionism. In addition to modernists, a whole galaxy of neo-realists has developed in the country, including Yannis Tsarouchis and D. Diamantopoulos.
Another significant group of artists, among which stands out Fotis Kontoglu, successfully worked on the revival of the traditions of Byzantine art.
Modern Greek sculptors also belong to different European trends, but there remains a significant group of supporters of ancient traditions.
Of the representatives of the neoclassical school, Kostas Dimitriades stands out, who was brought up in the spirit of French naturalism. Among those who moved away from the romantic school founded by Rodin, we note A. Apartis and M. Tombas, who work in different modern directions. Abstract art represented in the cubist sculptures by A. Apergis.
Music and theater.
In the field of musical art, an ancient tradition has been preserved, manifested in folk songs. These songs are divided into dance, family, mourning and heroic songs, many of them originating in the Byzantine era or even earlier.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Greek composers, like their compatriots in literature and art, relied on folk legends and ancient stories. Creation attempts national music were undertaken by Manolis Kalomiris (1883–1963), E. Riadis (1890–1935) and Georgios Poniridis. Kalomiris used themes from Byzantine church music and set to music the poems of Palamas and Sikelianos.
Ponyridis created numerous songs, often with lyrics from lyric poems by Cavafy and other Greek poets. Modern tendencies expressed in the writings of Demetrios Skalkotas (1905–1945) and Georgios Sikelianos. Manos Hadzidakis - famous composer, which was often inspired by folk melodies.
Athens Conservatory, longtime center musical culture Greece, produced many singers and composers of international class, including composer D. Mitropoulos (1896–1960) and opera star Maria Callas.
After the revival theatrical art at the beginning of the 20th century in Greece there was a rise in dramaturgy. Opened in 1930 National Theater, and then a number of other theaters with a permanent troupe were formed.
Every year in Athens, Epidaurus and Dodona, festivals of theatrical and musical art are held right in the ancient amphitheatres, where artists National Theater ancient dramas are performed.
folk art.
AT small towns and the islands preserve centuries-old handicraft traditions. Products from gold and silver are produced in Thessaloniki, Athens, on the island of Kerkyra (Corfu) and in Ioannina; embroidery and lace - in the Ionian and Aegean islands; Crete and Epirus are famous for wool blankets and carpets handmade. Greece also produces carved wooden, ceramic and forged metal products.
Cinema is very popular in Greece.
Several Greek films, including Never on Sundays, have won awards at international film festivals. Among the Greek movie stars, Melina Mercouri has reached world fame. Film director K.Costa-Gavras, who worked in France, received awards for such films as Z and State of Siege.
Hellenic Republic.
The country is named after the ethnonym of the people - the Greeks.
Capital of Greece. Athens.
Greece square. 131957 km2.
Greece population. 10624 thousand people
Location Greece is located in the south of the Balkan Peninsula and on the adjacent 2000 islands, the Aegean and, which account for almost 20% of its territory and of which only 166 are inhabited. By land, Greece borders on, and. From west to east stretches a chain of islands - the Cyclades, and from north to south along the coast of Malaya - Sporades (Dodecanese). In the south, the Aegean Sea, as it were, closes with Crete, the largest island of Greece. Along the western coasts are ionian islands.
Administrative divisions of Greece. 51 nomes (prefecture), which are divided into 264 dimas (districts), and a special administrative unit - the region of the Holy Mountain - Athos.
Greek form of government. Republic.
Head of State of Greece. The president.
Supreme legislature of Greece. The unicameral parliament (Chamber of Deputies) is elected for a term of 4 years.
Supreme executive body of Greece. Government headed by the Prime Minister.
Major cities in Greece. Thessaloniki, Piraeus, Patras, Heraklion.
Official language of Greece. Greek.
Religion in Greece. 98% are Orthodox.
Greek currency. Euro = 100 cents.
|
|||||
| Motto: « Ἐλευθερία ἢ Θάνατος (Freedom or death)" | |||||
| Hymn: "Hymn to Freedom (Ύμνος εις την Ελευθερία)" | |||||
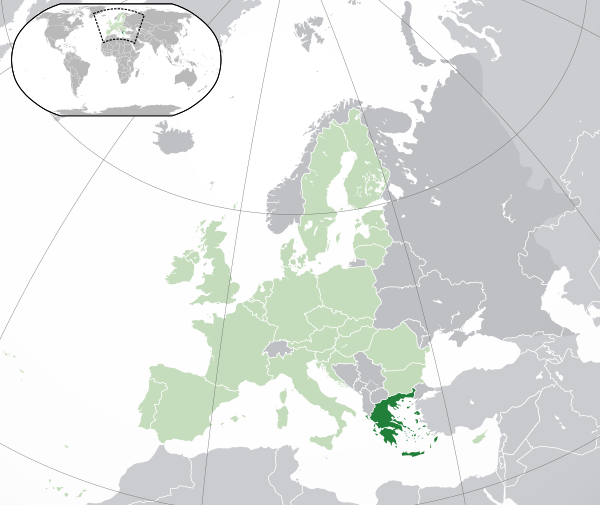 Location Greece(dark green): |
|||||
| date of independence | March 25, 1821 (from the Ottoman Empire) | ||||
| Official language | Greek | ||||
| Capital | |||||
| , | |||||
| Form of government | parliamentary republic | ||||
| The president Prime Minister |
Prokopis Pavlopoulos Alexis Tsipras |
||||
| state religion | orthodoxy | ||||
|
Territory Total % water surface |
95th in the world 131,957 km² 0,86 |
||||
|
Population Score (2013) Density |
▲ 10,955,000 people (75th) 85.3 people/km² (84th) |
||||
|
GDP(PPP) Total (2015) Per capita |
$294 billion $26,773 |
||||
|
GDP(value) Total (2015) Per capita |
$207 billion $18,863 |
||||
| HDI (2013) | ▼ 0.860 (very high) (29th) | ||||
| Names of residents | Greek, Greek, Greeks | ||||
| Currency | euro (EUR, code 978) | ||||
| Internet domains | .gr, also .eu | ||||
| ISO code | GR | ||||
| IOC code | GRE | ||||
| Telephone code | +30 | ||||
| Time Zones | EET (UTC+2, summer UTC+3) | ||||
Greece(gr. Ελλάδα , Elláda), official name - Greek Republic(gr. Ελληνική Δημοκρατία , Ellīnikī́ Dīmokratía) is a state in . The population, according to estimates for 2010, is more than 11.3 million people, the territory is 131,957 km². It occupies the seventy-third place in the world in terms of population and ninety-fifth in terms of territory.
About 98% of the population is Orthodox. Modern Greece - the heiress of culture Ancient Greece, considered the cradle of Western civilization, the birthplace of democracy and Western philosophy, the basic principles of physical and mathematical sciences, theater and the modern Olympic Games. rich cultural heritage and geographical position make Greece one of the most visited countries in the world.
An industrial-agrarian country with a dynamically developing economy. The volume of GDP at purchasing power parity for 2011 amounted to 294.339 billion US dollars (about 24,543 US dollars per capita). Monetary unit - euro.
The independence of the country was proclaimed on March 25, 1821. Prior to that, it was part of the Ottoman Caliphate.
origin of name
Hellas (gr. Ελλάδα ) - the self-name of the Greeks of their country. The word "Greece" is of Latin origin and is not used in Greek. Initially, the name of the region in southern Thessaly - gradually spread to the whole of Greece. With the adoption of the term Hellene common to all Greeks, Hellas became a collective name for all of mainland Greece, and then for all of Greece, including the archipelagos, islands and regions in Asia Minor (as opposed to the historical Magna Graecia, located in South).
Currently in Greece the word Hellas is the official self-name, and the words Greek or Greece(lat. Greco, Greek, Greece) are not recognized by the population and are used only in communication with foreigners. In other countries Hellas often serves as a synonym for the concept of Ancient Greece.
State symbols
State flag- 9 blue and white stripes with a cross - correspond to the nine syllables of the national motto - "Freedom or Death". The first national flag was created in 1821 by General Alexander Ypsilanti - red with a white cross. Since 1833, the red color has been replaced by blue.
National emblem- a blue shield with a white cross framed by two olive branches as symbols of the leading religion in Greece - Orthodoxy.
Anthem of Greece since 1860 - "Hymn to Freedom", written by the founder of modern Greek poetry Dionysios Solomos in 1823 and set to music by the first notable modern Greek composer Nikolaos Mandzaros.
Story
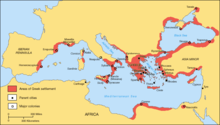
Greek territories and colonies of the Archaic period.
Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization. In the period of about 3 thousand years BC, a highly developed Minoan civilization arose on the island of Crete, the culture of which subsequently spread to the mainland. It was followed by the era of the Cretan-Mycenaean or Aegean civilization. Later, Greek policies arose, as well as ancient colonies of the Northern Black Sea region, Great Greece and Asia Minor. The cultural level of development extended to the entire Mediterranean region, which was reflected in architecture, theater, science and philosophy.
Alexander the Great
Among birds, you can most often see wild ducks, kingfishers and partridges, as well as predators - owls, eagles and kites.
There are many gulls in the coastal areas, and in the waters of Greece there is a huge variety of shellfish and fish, although the stocks of the latter have been significantly reduced in recent times.
More than 5,000 plant species are distributed in Greece. Small plants and shrubs are widespread in Greece: maquis and frigana. Pine forests are often found on the Halkidiki peninsula. Cypresses and plane trees are widespread. Some are several thousand years old. The olive is very common - one of the most valuable trees in Greece and the entire Mediterranean.
Administrative division
Previously Greece was divided into 13 administrative districts, which were divided into 54 nomes (or prefectures). Also in Greece there was one autonomous region - Aion Oros (Holy Mountain) in the region of Mount Athos - a monastic state governed by a council of representatives of 20 Athos monasteries. Real self-government existed at the level of nomes and more small formations- municipalities. The municipality was headed by the mayor, and the nome was headed by the governor.
However, from January 1, 2011, in accordance with plan of Kallikratis(Law 3852/2010), the administrative system of Greece has been radically revised. The former system of 13 regions, 54 prefectures and 1033 municipalities and communities has been replaced by 7 decentralized administrations, 13 regions and 325 municipalities. The regions and municipalities have been fully self-governing since the first elections scheduled for 7 November and 14 November 2010. The decentralized administrations are managed by a general secretary appointed by the Greek government. The Autonomous Monastic State on the Holy Mountain is exempt from these reforms.
| № | decentralized administration | Adm. Centre | Peripherals | Square, km² |
Population, people (2011) |
Density, person/km² |
Map | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Attica | 3808 | 3 827 624 | 1005,15 | 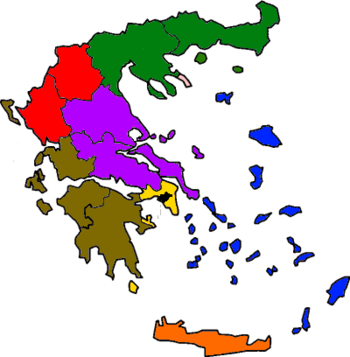 |
|||
| 2 | Macedonia and Thrace | Central Macedonia, East Macedonia and Thrace | 32 968 | 2 490 051 | 75,53 | |||
| 3 | Epirus and Western Macedonia | Epirus, West Macedonia | 18 654 | 620 545 | 33,27 | |||
| 4 | Thessaly and Central Greece | Thessaly, Central Greece | 29 586 | 1 280 152 | 43,27 | |||
| 5 | Peloponnese, Western Greece and Ionia | Peloponnese, Western Greece, Ionian Islands | 29 147 | 1 465 554 | 50,28 | |||
| 6 | Aegean | North Aegean, South Aegean | 9 122 | 508 206 | 55,71 | |||
| 7 | Crete | Crete | 8 336 | 623 065 | 74,74 | |||
| The autonomous monastic state of the Holy Mountain has a special status and its own visa regime. | 336 | |||||||
| Total | 131 957 | 10 815 197 | 81,96 |

Greek wedding, Naxos
The majority of the population of Greece are Greeks (93%), although these data are disputed due to inconsistencies in data on minorities, especially linguistic ones. It is believed that Greek statistics do not keep records of the population by nationality, but this is a false conclusion. The main officially recognized religious minority of modern Greece are the Muslims of Thrace and the Dodecanese Islands, including Turks (1% of the population of Greece), Pomaks (Bulgarian-speaking Muslims, 0.3%) and Muslim gypsies (0.1%). But here Greece follows the letter of the Lausanne Accords of 1924 and demands the same from Turkey, since this part of the population remained within the borders of Greece on the same terms that they were supposed to protect the Greek minority of Constantinople and the islands of Imvros and Tenedos. The Greek minority in Istanbul is almost gone.
There are minorities that are distinguished mainly by ethnographers on linguistic grounds, but they have their own specifics: Albanians (4%; including Arvanites) are a bilingual population with Greek self-consciousness that gave the country dozens of national heroes in the fight against the Turks and Arvanites by Muslims, "Slavic-speaking Greeks" or Macedonian Slavs (1.2%), who at the beginning of the 20th century called themselves Bulgarians and were recognized as such, Aromanians (1.1%, including Meglenites) are a bilingual group with Greek self-consciousness, which gave the country national heroes and a good half of its patrons, Orthodox gypsies (another 0.8%).
Armenians, Serbs (0.3%), Arabs (0.3%), Jews (0.05%), etc. are officially recognized.
More than 4 million Greeks live abroad, of which over 2 million live in the USA, Canada and Australia.
Religion
The Greek Constitution states:
Greek constitution
entered into force 11 June 1975
[extract]
In the name of the Holy, Consubstantial
and undivided trinityPart one
Basic provisions
<. . .>
Section II
Relations between Church and StateArticle 3
- The dominant religion in Greece is the religion of the Eastern Orthodox Church of Christ. The Orthodox Church of Greece, recognizing our Lord Jesus Christ as its head, is inextricably linked in its dogmas with the Great Church of Constantinople and with every other Church of Christ of the same faith, and steadily observes, like them, the holy apostolic and conciliar canons and sacred traditions. It is autocephalous and is governed by the Holy Synod of bishops who are in church service, and the Permanent Holy Synod elected by them, which is created in the manner determined by the Charter of the Church, in compliance with the provisions of the Patriarchal Volume of June 29, 1850 and the act of the Synod of September 4, 1928.
- The church regime existing in certain regions of the state does not contradict the provisions of the previous paragraph.
- The text of Holy Scripture remains unchanged. Its official translation into any other language without the permission of the Autocephalous Church of Greece and the Great Church of Christ in Constantinople is prohibited.
Greek constitution

Monastery of Megala Meteora
The Greek Constitution recognizes Orthodoxy as the leading religion in the country, while at the same time guaranteeing religious freedom for all citizens. The Greek government does not keep official statistics on the religious affiliation of its citizens. According to sociological research Eurostat for 2005, 81% of Greeks answered that they believe in God, which is the third indicator among EU member states, second only to Malta and Cyprus.
97% of Greek citizens identified themselves as "Greek Orthodox" according to 2006 US government data). Dominated Greek Orthodox Church, its head is Archbishop Jerome II, whose residence is in Athens. At the same time, the entire north of the country and the Dodecanese Islands are included in the canonical territory of the Church of Constantinople. Also, the monastic state on Mount Athos is subordinate to the Church of Constantinople, and the Cretan Orthodox Church is semi-autonomous.
A few inhabitants of several islands of the Aegean Sea, which at one time belonged to the Venetian Republic, are Catholics. In Thrace and on the island, in addition to the Greeks, Muslim Turks live (1.3%). Judaism has existed in Greece for over 2000 years. Sephardim once formed a large community in the city, but no more than 5,500 people were able to survive the Holocaust. The Protestant community in the country has about 3,000 people. They are Assemblies of God, Evangelicals and Baptists. There are about 30,000 Jehovah's Witnesses. There is also a non-traditional religious direction of Greek neo-paganism, its adherents number less than 2,000 people.
Science and Technology

Science Center and Technology Museum of the Aristotle University, Thessaloniki
The natural and technical sciences developed in Greece after gaining independence, although separate works on medicine were published before that time, in particular “On Diet” (Greek. Διαιτητική ) Konstantinos Michael, 1794, "History of Medical Art" (Greek. Ιστορίας Ιατρικής ) Sergio John, 1818; "Handbook of Hygiene" (gr. Υγιεινατάριον ) Spiridon Vlandis, 1820.
Founded in 1837, the University of Athens quickly became the scientific center of the country. In 1887, his departments of natural sciences were merged into a department, and later the faculty of natural sciences. The development of sciences was also facilitated by industrialization, on the path of which Greece began in the second half of the 19th century. At the end of the century, the chemist Anastasios Christomanos, the founder of a specialized laboratory, examined the Greek ores for a whole range of minerals. The general inspector of the Lavrion mines, the future first president of the Athens Academy, Fokion Negris published extensive information about the geological structure, and the physicist and mathematician Konstantinos Mitsopoulos investigated the seismicity of Greece. Biologists Theodoros Orfanidis, Theodor Heinrich Hermann von Geldreich, Spyridon Miliarakis, Ioannis H. Politis were engaged in research on the flora and fauna. The foundations of medicine in Greece were laid by Georgios Sklavunos, author of Human Anatomy (1906). At the beginning of the 20th century, the growth rate economic development contributed to the rise of technical sciences, the center of which was the Athens Polytechnic Institute.
In 1837, the Greek Archaeological Society was founded to revive archaeological science, to create conditions for the proper preservation of antiquities. For half a century, this work was also promoted by foreign archaeological schools in Athens, which operate to this day: French (1846), German (1874), American (1881), British (1886), Austrian (1898). Among the Greek archaeologists proper, Konstantinos Kourouniotis, Nikolaos Platon, Kyriakos Pittakis, Valerios Stais, Aris Poulianos and the current head of the restoration work on the Acropolis of Athens, Manolis Korres, are widely known.

Headquarters of the telecommunications company OTE.
At the present stage, the leading scientific institution in the field of physical sciences is the Democritus Center for Nuclear Research, founded in 1961 in Aya-Paraskevi. It has a nuclear reactor, a subcritical reactor and a Van de Graaff generator. Research in astronomy, atmospheric physics, seismology and meteorology is carried out by the Athens National Observatory. Scientific research in applied mathematics is carried out by the specialized bureau and computing center of the Athens Academy of Sciences. Major works in the field of electronics, artificial intelligence, electrochemistry, aerodynamics are held at the Aristotle University and the Technical University of Athens.
Ioannis Argyris - Greek mathematician and engineer, one of the authors of the finite element method and the direct stiffness method. The mathematician Constantine Carathéodory worked in the field of real analysis, calculus of variations and measure theory in the early 20th century, his teachings helped Albert Einstein in the mathematical part of his theory of relativity. Biologist Fotis Kafatos is a pioneer in molecular cloning and genomics. Dimitris Nanopoulos is a renowned theoretical physicist who has made significant contributions to the fields of particle physics and physical cosmology. Georgios Papanikolaou - pioneer of cytology and early diagnosis Cancer, inventor of the pap test. Greek car designer Alec Issigonis created the "Mini" car design, while Michalis Dertouzos was one of the pioneers of the internet. Greek informatics Christos Papadimitriou, Diomidis Spinellis, Joseph Sifakis, Michalis Yannakakis are widely known in the world. Nicholas Negroponte founded the MIT Media Lab and the One Laptop Per Child program.
Education
Education in Greece is compulsory for all children aged 6 to 15 years. It includes the initial (Greek. Δημοτικό Σχολείο ) - 6 classes, and incomplete secondary (Greek. Γυμνάσιο ) - gymnasium, 3rd grade, education. Exist preschool institutions: nursery-gardens (gr. Παιδικός σταθμός ) for children from 2.5 years old, working separately or as part of kindergartens (Greek. Νηπιαγωγείο ).
culture
The culture of Greece was formed over many thousands of years, starting from the time Minoan civilization, the formation took place during Classical Greece and Greece during the Roman domination. The Ottoman yoke also influenced the culture of the Greeks. But even during the Greek Revolution, great works of literature, music, and painting were created. Orthodox Christianity had a huge impact on the entire culture of modern Greece. Some researchers, such as Robert Kagan, believe that modern culture Greece is much more connected with cultural heritage Byzantine and Ottoman Empires than with culture ancient Hellas. At the same time, as the historian of Haverford College A. Kitroff notes: "The idea that modern Greeks descend directly from the ancient Greeks is one of the fundamental moments of self-awareness of the modern Greek nation."
Greek language

Map of the distribution of languages in the country (with the exception of Greek). Today the Greek language has a dominant position among others in Greece.
The Greek language is one of the oldest among modern languages peace. It has been in use for over 4,000 years, and Greek writing has been around for 3,000 years. Today, the Greek language is the basis of the vocabulary of any Indo-European language, most of the basic concepts of scientific vocabulary are also partly Greek in origin. The modern Greek language - Dimotika - is a South Greek dialect adapted as a standard variant of the language. It is significantly different from kafarevusa, which, in fact, was artificially created on the basis of the ancient Greek Koine and planted on the initiative of Adamantios Korais, a Greek writer, educator and active public figure of the era of the national liberation movement of the 19th century.
Greece has always been a relatively homogeneous country linguistically. At the beginning of the 20th century, the Greek-Turkish population exchange took place, which further intensified the process of assimilation of ethnic minorities. Now Greek as the first or even the only language is used by about 99% of the population of the country. The main dialects of the Greek language are: Pontic dialect, Cappadocian dialect, Tsakonian dialect, Hebrew-Greek dialect. In the last decade, the spread of Internet services and mobile communications caused the Latinization of Greek writing. This phenomenon is known as Greeklish, it is common throughout the Greek diaspora and even in countries with a majority of the Greek population - in Greece and Cyprus.
Philosophy

Platonic Academy, Raphael
The Western philosophical tradition originated in ancient Greece as early as the 6th century BC. e. First ancient Greek philosophers commonly referred to as "pre-Socratics", most of their works have not survived even in fragments. Among the pre-Socratics, seven ancient sages occupy a separate place. One of them - Thales of Miletus, since the time of Aristotle is considered the first philosopher of Greece, who belonged to the so-called Milesian school. It was followed by the Eleatic school, which dealt with the philosophy of being.

Prominent representatives of the Greek Renaissance (15th-18th centuries) are the cleric Theophilos Koridalleus, Nikolai Mavrokordat, Vikentios Damodos, Mefodios Anthrakitis. The modern Greek Enlightenment is characterized by a return to the ancient Greek heritage, its leaders are Evgeny Bulgaris, Josipos Misiodakas, Benjamin of Lesbos, and the revolutionary Rigas Fereos. In the first years of independence from the Ottoman Empire, religious philosophy (Philippos Ioannou, Petros Brailas-Armenis) and Hegelianism became widespread.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the main motive of philosophical works was an attempt to substantiate the Great Idea (Yannis Kambisis, Ioannis Zervos, Ion Dragoumis), the political conductor of which was Eleftherios Venizelos, and the ideas of positivism spread in philosophy (Theophilos Voreas and Panagiotis Agiosofitis). AT postwar period neo-Kantianism (Ioannis Theodorakopoulos, Panagiotis Kanellopoulos, Konstantinos Tsatsos), phenomenology (Konstantinos Georgoulis and Leandros Vranousis), as well as irrationalism and intuitionism became influential philosophical trends. Existentialism is represented by Yorgos Sarandaris, Dimitrios Kapetanakis, Christos Yannaras.
Literature
![]()
Dionysios Solomos, composer of the Greek national anthem.
Greek literature is divided into three periods: Ancient Greek, Byzantine and Modern Greek. In ancient Greece, literature flourished before classical science, education, and art. Around the 8th century BC. e. created the "Iliad" and "Odyssey" - poems associated with heroic epic dedicated to the Trojan War. Hesiod continued the tradition of Homer in Theogony. Fragmentarily, the verses of Sappho and Anacreon have come down to us, whose names gave the name to the Sapphic stanza and Anacreontics. how independent genre developed ancient Greek drama, among its prominent representatives Aeschylus, Sophocles, Euripides, Aristophanes.

Adamantios Korais
The period of Byzantine literature covers the 4th-15th centuries, it is written in the Middle Greek language. Until now, literature has been preserved, created mainly by the church, which played an important economic and political role in Byzantium. At the same time, the latter inherited the traditions of Hellenistic prose. The famous story "Alexandria" of the XI-XII centuries is full of fabulous episodes from the life of Alexander the Great, Christianized in different editions. The poetry of Roman the Melodist stands out especially, out of more than a thousand hymns written by him, about 80 have survived. The chronicles of George Amartol are of great historiographical significance.
The birth of modern Greek literature was marked by the Cretan Renaissance poem "Erotokritos", written by Vitsendzos Kornaros in the vernacular. The poem consists of ten thousand verses and sings of the valor, patience and love of the hero Erotokritos. However, the Greek Revolution gave a real impetus to the development of modern Greek literature. The Athenian school of purists appeared, the ideological leader of which was Adamantios Korais, the creator of the kafarevusa, and the Ionian school, headed by Dionysios Solomos, the author of the “Hymn to Freedom” (became the anthem of Greece), which promoted the living vernacular- dimotic.
The literature of the 20th century is represented by the talents of many writers and poets, including Andreas Kalvos, Yiannis Psycharis, Alexandros Pallis, Angelos Sikelianos, Kostis Palamas, storyteller Penelope Delta, Yiannis Ritsos, Alexandros Papadiamandis, Kostas Kariotakis, Kostas Varnalis, Konstantinos Cavafy, Demetrius Vikelas, Nikos Kazantzakis, and Nobel laureates Yorgos Seferis and Odyseas Elytis.
Theatre
Architecture
![]()
Academy of Athens building

Typical Greek houses with balconies and terraces, Neos Kosmos district of Athens

Parthenon, Acropolis of Athens
In the conditions of democracy of Ancient Greece, for the first time, an integral environment of city-states - policies is being created. A system of regular city planning is developing with a rectangular grid of streets and the main square - the agora - the center of trade and public life. A type of residential building with rooms facing the inner spatial core was developed - the peristyle.
The cult and architectural and compositional center of the ancient Greek city was the acropolis with a temple dedicated to the deity - the patron of the city. The peripter became the classically completed type of temple. The most striking example of it is the main temple Athenian acropolis- Parthenon. Based on the aesthetic understanding of the stable-beam structure in ancient Greece, an order system is being created. architectural composition, which harmoniously combines high artistry architectural forms with the perfection of design and material. The rapid development of the public life of the ancient Greek polis gave rise to such types of structures as a theater, a stadium, a palestra, etc. Thus, the Theater of Dionysus appeared in Ancient Athens, and later the Odeon of Herodes Atticus, the unique marble stadium of Panathinaikos.
In the Middle Ages, mainly monastic architecture developed in Greece, Greek cities fell into decay. People's housing was built of various types, depending on the shape of the relief. Fully architecture begins to develop from the 1830s, when they became the capital. Their building plan was created by Greek architects Stamatios Kleantis and Lysandros Kavtanzoglou. At the same time, the architects Theophil von Hansen and Ernst Ziller were invited, who are building public buildings contributing to the flourishing architectural style neo-Greek. Church architecture of the 19th century gravitated towards Byzantine.
Starting from the 1920s, the port cities -, - begin to grow rapidly, at present, a type of apartment building with numerous balconies and terraces, proposed by Kostas Kitsikis, is being formed, which is typical for Greece. In the future, Greek architecture perceives the influence of functionalism and neoclassicism. During the 1950s and 1960s, park-like suburbs sprang up around Athens with neighborhoods built up with villas and mansions of wealthy Greeks with elements of vernacular architecture (architect Dimitris Pikionis). Much less cheap apartment buildings were built (architect Aris Konstantinidis), but the need for the construction of new hotels and museum premises grew (architects Charalambos Sfaellos, Prokopios Vasiliadis). Industrial and office construction was developed by Takis Zenetos.
Music
The folklore music of Greece is in many ways similar to the music of other Balkan countries - the former Yugoslav. They traced similar rhythms and emotional coloring of the songs.

Dancing to traditional music
Rebetika is a Greek city song. It was formed at the beginning of the 20th century, when, after the Asia Minor catastrophe, many destitute refugees poured into Greece and the music of Ionia, that is, the west of Asia Minor, merged with the tavern music of the portside Greek lumpen proletariat. The rebetika style was persecuted by the Greek authorities, so this music came out of the “underground” only in the 1950s with the support of composers such as Manos Hadzidakis and Theodorakis, who supported the rebetika as a musical trend that carries elements of ancient Byzantine music.
One of the most famous Greek singers in the world is Demis Roussos, who started solo career in 1971.
Contemporary popular music is heavily influenced by the West. But even in it, traditional Greek melodies and the use of national instruments such as bouzouki are often traced.
In 2005 Greek singer Elena Paparizou won the Eurovision Song Contest with the song "Number One" - a first for Greece.
Modern Greece has given the world many composers close to the New Age direction. Among them are the world famous Vangelis and Yanni and the lesser known Chris Spheeris and Stamatis Spanoudakis.
Rock is very popular among young people, the black metal scene in Greece is one of the strongest in the world along with the Scandinavian countries. Rotting Christ is a Greek dark/black/gothic metal band, formed in Athens in 1987, known far beyond the borders of the country. The second cult rock band from Greece is the occult black metal band Necromantia. The third most important rock band from Greece is the doom/death band Septic Flesh.
Opera singer Maria Callas, a contemporary and long time lover of Aristotle Onassis, is rightfully considered a phenomenon in music world. From modern opera singers Greece stands out Marios Frangoulis.
One of the best modern world guitarists is Antigoni Goni.
By right, Sakis Rouvas can be called a recognized and successful performer. Success at Eurovision 2004 in Istanbul with the song "Shake It" brought Greece third place.
The relatively young dance "Sirtaki" in the modern world acts as one of the symbols of Greece.
Sports in Greece

Spyros Louis Olympic Stadium in Athens - Opening of the 2004 Paralympic Games

Angelos Charisteas winning goal in Euro 2004 final
Greece, as the birthplace of the Olympic competition, has the oldest sporting tradition in the world. She is three times new history hosted Olympic Games modernity: the first Olympics in 1896, the first Extraordinary Olympic Games in 1906 and in 2004 the next Summer Olympic Games in Athens. The Greek National Olympic Committee was established in 1894 and recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) in 1895. The Greek businessman and poet Demetrios Vikelas became the first President of the IOC.
The most popular sports in Greece are football and basketball. Basketball gained popularity in Greece after the 1968 Cup Winners' Cup was won by the AEK club. The second wave of growth was caused by victories in the European Basketball Championship in 1987 and especially in 2005. The most successful basketball clubs in the Greek Championship are Panathinaikos (31 wins), Aris (10 wins), Olympiakos (9 wins), AEK (8 wins) and Panellinios (6 wins).
Similarly, the rise of football took place after the victory of the Greek national team at the European Football Championship in 2004. This event has been called one of the biggest surprises in modern history sports. The most successful football clubs in the Greek Super League are Olympiakos (37 wins), Panathinaikos (19 wins) and AEK (13 wins).
In recent decades, volleyball, water polo, and athletics have also gained popularity in Greece. The national teams adequately represent Greece in international competitions in weightlifting, gymnastics, sailing, rowing and canoeing, diving, swimming, rowing, wrestling, cycling, boxing, shooting, tennis, archery, triathlon. Rugby, cricket, golf, hockey, equestrian sport have a certain fame. In 1952, the Rally of Greece was launched, which in 1973 became a stage of the World Rally Championship and is now considered one of the most difficult, oldest and most prestigious rally events in the world. Since 1972, the Athens Classic Marathon has been held annually.
In 1991, Athens, the capital of Greece, hosted the 11th Mediterranean Games. sports event Mediterranean countries. On October 28, 2007, during a vote in Italy, Greece again won the right to host the XVII Mediterranean Games. They were supposed to take place in the cities in 2013 as well. However, the organizers did not build sports facilities on time, and on January 28, 2011, the International Committee of the Games deprived Greece of the right to host the Games. But on January 27, 2011, the Association of International Marathons and Runs signed an agreement with the Greek Ministry of Culture and Tourism, according to which the association moves its headquarters to Athens.
Mass media

Front page of the Kathimerini newspaper, August 10, 2005.
A 2009 study published by the British public broadcaster BBC showed that 78% of Greeks turn to television for news, 41% to print media, 35% to electronic publications and 32% to radio. According to the Press Freedom Index, published in 2009 by the international organization Reporters Without Borders, Greece ranks 35th out of 175 countries in the world. Some international analysts define the Greek media as highly politicized, while less politicized than in the late 1980s, and also recognize the mutual influence of the authorities and the press.
Press
The Athens-Macedonian News Agency is considered the largest, oldest and most authoritative news agency in Greece. The main daily newspapers have a clear political affiliation: the newspapers "Katemerini" and "Acropolis" (circulations of 35,500 and 50,800 copies respectively) are center-right publications; "Eleftheros Typos" (circulation 135,500 copies) - a publication that gravitates towards a more conservative right wing; the newspaper "Avgi" (circulation 55,000 copies) is positioned as a left-wing publication, the publications of the center-left direction include Avriani, Ta Nea and Eleftherotype (circulations 51,000, 133,000 and 108,000 copies, respectively) ; finally, the newspaper Rizospastis (circulation 40,000 copies) is the official print organ of the Communist Party of Greece. Also available in Athens wide circle magazines, among them the popular ones: Economics, Ependitis, Prin, Status, and To Vima. 2% of Greek newspapers and magazines are exported to, to, and. In Greece, German and English-language publications are in the greatest demand.
Broadcasting
The first broadcaster in Greece (YRE) appeared in 1938, in the same year it launched the first radio station in Greece, in 1952 radio broadcasting in Greece became two-program, in 1954 - three-program, in 1966 - the first two TV channels in Greece were launched and a fourth radio station, in 1987 television in Greece became three-program. In 1989, the monopoly of public broadcasters on broadcasting was abolished, the first commercial broadcasters in Greece were established and the first commercial radio stations and TV channels in Greece were launched. In 1999 the first NOVA satellite platform in Greece was launched, in 2006 the first digital platform ΕΡΤ Ψηφιακή, in 2008 the Conn-x TV IPTV platform, in 2009 the second Digea digital platform, in 2011 the second OTE satellite platform . On August 17, 2012, on-air analog television broadcasting ceased. On February 12, 2016, licensing of commercial broadcasters was introduced. Depending on the form of financing, television and radio broadcasting in Greece is divided into public and commercial, and there are also elements of state television and radio broadcasting in the form of a satellite TV channel Βουλή - Τηλεόραση, municipal radio stations (Athena 98.4 FM, Channels 1, etc.), as well as radio stations educational institutions(Ράδιο Χώρος 94.2, Yellow Radio, etc.), and broadcasting public organizations in the form of party (αρτ FM 90.6 (People's Orthodox appeal), στο κόκκινο 105.5 (siriza), 904 αριστερά (CPG)) and church radio stations (εκκλησία της ελλάδος, πειραϊκή εκλησία and others).
A television
Greek television, depending on the form of signal distribution, is divided into terrestrial, satellite and IPTV. Greek public television is represented by the broadcaster ERT, broadcasting on the 1st (ERT1), 2nd (ERT2) and 3rd (ERT3) channels. Commercial broadcasting is represented by broadcasters Mega TV (4th TV channel and radio station), ANT1 (4th TV channel, radio stations Easy 97.2 and Ρυθμός 94.9), Alpha TV (6th TV channel, radio stations Alpha 98.9 and Alpha 96.5) and Skai TV (8 TV channel, Skai 100.3, Μelodia 99.2, Red FM 96.3 radio stations), Star Channel (TV channel 7, Star FM 107.7 radio station), Epsilon TV (TV channel 9), as well as regional commercial broadcasters (up to 15 per region) , broadcast based on temporary permissions. There are two digital television operators in Greece - Digea, owned by the commercial broadcasters, and ΕΡΤnet, owned by the public broadcaster ERT. The main operator of IPTV is OTE (it is also the main operator of fixed and mobile telephony and the Internet), which has an IPTV platform OTE TV, satellite TV operators OTE and NOVA, the latter has a satellite platform NOVA Greece.
Broadcasting
Broadcasting in Greece, depending on the form of distribution, exists only in the form of terrestrial broadcasting, public radio stations are also included in common multiplexes with terrestrial, satellite and IPTV versions of public television channels, in addition, there are Internet radio stations. Over-the-air broadcasting in Greece is carried out in an analogue format in the VHF band, VHF CCIR version, some public radio stations are also available in the medium wave band. Public Radio presents broadcaster ERT broadcast via radio Πρώτο Πρόγραμμα, Δεύτερο Πρόγραμμα, Τρίτο Πρόγραμμα, ΕΡΑ Σπορ, ERT Περιφέρεια and Kosmos 93.6, commercial radio shows nationwide radio stations: 261 Athens, Εν Λευκώ, Παραπολιτικά 90.1 FM, Best Radio, Kiss FM 92.9, Σπορ fm 94.6, ρυθμός 94.9, Athens Deejay, Flash 96, Easy 97.2, Love Radio 97.5, Real FM 97.8, αθήνα 9.84 (municipal radio station Athens), μελωδία 99.2, ήήμα FM 99.5, σκαϊ 100.3, Sfera 102.2, Nitro Radio, Mad Radio 106.2, in addition, in the regions there may be from one to several dozen regional commercial radio stations. The country also has Internet radio, in particular ArionRadio.
Greek Armed Forces
 Tank Leopard 2A6 HEL |
 Ship MEKO-200 HN |
 Fighter Mirage 2000 |
Greek Armed Forces - state structures, united armed military formations and structural organizations, which, in accordance with the Greek Constitution, are intended to protect the freedom, independence and territorial integrity of the state and include the ground forces, naval forces and air forces of the Hellenic Republic. The Greek armed forces are recruited on the basis of the law on universal conscription, their number is 177,600 people.

The Greek Presidential Guard (Evzones) at the parade on June 2, 2007
The supreme governing body of the Armed Forces is the Greek Ministry of Defense, the military command and control body is the General Staff of the National Defense of Greece (Greek. Γενικό Επιτελείο Εθνικής Άμυνας - ΓΕΕΘΑ ). Greece is a member of NATO and participates in operations in Afghanistan, Bosnia, Chad and Kosovo and Metohija.

Soldiers of the Greek army from the peacekeeping contingent in Bosnia and Herzegovina
During the war of independence against the Ottoman Empire in 1821, the Greek land forces and navy were created. In September 1912, the Air Force was formed as the third branch of the armed forces. The Greek Armed Forces participated in the Balkan Wars against the Turkish and Bulgarian armies. During World War I military establishment Greece took part on the side of the allies. The Greco-Turkish war of 1919-1922 ended in defeat, turned into the loss of territories and the “Asia Minor catastrophe”.
During World War II, Greece, under the leadership of dictator Ioannis Metaxas, rejected the Italian surrender ultimatum on 28 October 1940 and was able to repulse the Italian forces and push them back to the Albanian border. The Greek armed forces were only defeated by the military intervention of the German Wehrmacht and the Bulgarian armed forces in April and May 1941.
The Greek armed forces participated in the Korean War in the 1950s. In April 1967, as a result of the rebellion, the military regime led by Georgios Papadopoulos seized power in Greece. The Cyprus conflict and the subsequent Turkish invasion in 1974 led to the fall of the military dictatorship and the return to democracy through the efforts of Prime Minister Konstantinos Karamanlis.
Greece spends the largest percentage of gross domestic product (4.3% of GDP) on defense among NATO member states. The main reason for the cost is the perceived threat from Turkey.
Greece - general information about the country
Greece map
Greece
Greece (self-name - Hellas (Greek Ελλάδα), official name - Hellenic Republic - a state in southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula.
The current Greek Constitution came into force on June 11, 1975. According to the form of government, Greece is a parliamentary republic. The political regime is democratic.
The recognized cradle of Western civilization, the place where the first democratic states known in history appeared. A member of the EU since 1981, NATO - since 1952 (in 1973-1981 the country left the organization).
Geography
Greece is located in the southern part of the Balkan Peninsula and on the islands adjacent to it and to the coast of Asia Minor and covers an area of 131,994 km². It borders with Albania, the former Yugoslav Macedonia, Bulgaria and Turkey. It is washed by the Mediterranean Sea, including: the Ionian, Aegean Seas, and the southern coast of Crete - the Libyan Sea. Greece consists of about 2 thousand islands, which account for almost 20% of the entire country.
The territory of Greece can be divided into three parts:
mainland Greece, which includes Macedonia (Florina, Slavic name Lerins, Pella Kavala, Kastoria, Halkidiki, etc.), Thrace (Rhodopi, Xanthi and Evros), Epirus (Thesprotia, Preveza Janina, etc.), Thessaly (Larisa, Magnesia, etc.) ) and Central Greece (Phthiotis, Phokis, Attica, etc.). Also geographically, the Ionian Islands can be attributed to this region;
Peloponnese - the largest peninsula of Greece and the center of ancient civilization Europe, includes the nomes of Arcadia, Laconia, Messinia, etc. The famous Corinth Canal is also located here, dug by a French company for the Greek state in the 19th century;
islands of the Aegean Sea, the largest of which are Crete - largest island Greece and the eighth in Europe (8259 km²) and Euboea - the second largest, after Crete, the island of Greece (3654 km²), connected to the continent by a bridge thrown across the Evrip Strait, as well as Lesbos (1630 km²), located off the coast of Turkey. There are also many groups of small islands - Northern Sporades, Cyclades, Dodecanese.
Climate
The climate of Greece can be divided into three types: Mediterranean, Alpine and temperate, each of which affects a strictly defined area. The Pindus mountain range strongly influences the climate of the mainland: the regions located to the west of the slopes of Pindus (Epirus) receive more rainfall than the regions located on the eastern side of the range (Thessaly).
The Mediterranean type of climate is characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The Cyclades, Dodecanese, Crete, the eastern part of the Peloponnese and part of Central Greece are located in this type of climate. Temperatures here don't often hit record highs, and in winter, even in the Cyclades and Dodecanese, snow can occasionally fall during the winter months.
The Alpine type of climate is more typical for the mountainous regions of the country: Epirus, Central Greece, Western Macedonia, part of Thessaly, as well as the nomes of Achaea, Arcadia and Laconia.
Eastern Macedonia and Thrace can be classified as regions with a temperate climate type, with relatively cold and wet winters and hot, dry summers.
Athens is located in a transitional zone where two types of climate are combined: Mediterranean and temperate. In the northern part of Athens, a temperate climate prevails, while in the central and southern regions there are features of the Mediterranean climate.
Story
The history of Greece is very rich and has more than 5 millennia. By 2000 B.C. e. one of the most ancient civilizations, the Cretan-Mycenaean, was born on its territory. At this time, luxurious palaces are being built, science and art are developing, writing is taking shape. In subsequent centuries, the country reaches unprecedented heights in development: city-polises with a well-developed political system, trade, crafts. The cultural, political and social achievements of this era became the basis for the formation of many European civilizations. But against the background of this prosperity, a fierce struggle for supremacy was waged between the city-states, which over the years weakened the forces of the state. As a result, in 146 BC. Greece was subject to Rome. Fortunately, the Romans were the successors of Greek culture and brought it to modern world. During this period, Christianity was born. Like any civilization, the Roman did not escape the decline. The collapse of the empire formally took place in 1054 due to the division of the church into Orthodox (Eastern) and Catholic (Western). But the reasons for the collapse were deeper - the slave system has become obsolete, the uprisings of slaves and the poor led to the creation of a new feudal system. After the fall of the Roman Empire, Greece was ceded to Byzantium. In 1453, the country was conquered by the Turks, and from that time on, decline began in all areas of activity. Liberation from the Ottoman yoke occurred only in 1821 as a result of the victory of the national liberation movement. The end of the 19th - the beginning of the 20th century became a period of military cataclysms. There were national unrest in Greece, she became a participant in the Balkan, First and Second World Wars. In 1974, as a result of a referendum, the monarchy was abolished and Greece became a republic. A new republican constitution was adopted in 1975. Greece is a member of the UN, GATT, IMF, WHO, ILO, Council of Europe, NATO, CFE, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, EU.
Population
The majority of the population of Greece are Greeks (95%), although these data are disputed due to inconsistencies in data on minorities, especially linguistic ones. It is believed that Greek statistics do not keep records of the population by nationality, but this is a false conclusion. The main officially recognized religious minority of modern Greece are the Muslims of Thrace and the Dodecanese Islands, including Turks (1% of the population of Greece), Pomaks (Bulgarian-speaking Muslims, 0.3%) and Muslim gypsies (0.1%). But here Greece follows the letter of the Lausanne Accords of 1924 and demands the same from Turkey, since this part of the population remained within Greece on the same terms that they were supposed to protect the Greek minority of Constantinople and the islands of Imvros and Tenedos. But only the Greek side follows the agreements - there is practically no Greek minority in Constantinople anymore.
There are minorities that are distinguished mainly by ethnographers on linguistic grounds, but they have their own specifics: Albanians (4%; including Arvanites) are a bilingual population with Greek self-consciousness, which gave the country dozens of national heroes in the fight against the Turks and Muslim Arvanites, “Slavic-speaking Greeks” or Macedonian Slavs (1.2%), who at the beginning of the 20th century called themselves Bulgarians and were recognized as such, Aromunians (1.1%, including Meglenites) are a bilingual group with Greek self-consciousness, which gave the country national heroes and good half of its patrons are Orthodox gypsies (another 0.8%).
Armenians, Serbs (0.3%), Arabs (0.3%), Jews (0.05%), etc. are officially recognized
Religion
Almost the entire population of Greece professes Orthodoxy. According to the Constitution, Orthodox Christianity is the state religion.
culture
The culture of Greece was formed over many thousands of years, starting from the time of the Minoan civilization, the formation took place during Classical Greece and Greece during the Roman domination. The Ottoman yoke also had an impact on the culture of the Greeks, mainly by slowing down the active development of ancient Greek culture. But even during the Greek Revolution, great works of literature, music, and painting were created. Orthodox Christianity had a huge impact on the entire culture of modern Greece. Some researchers believe that the modern culture of Greece is much more connected with the cultural heritage of the Byzantine and Ottoman empires than with the culture of ancient Hellas.
Tourism
Greece is visited by more than 19 million tourists annually, bringing, thereby, about 15% of the gross domestic product of the entire country. Greece attracts foreign visitors with its rich history and traditions from ancient times. But in recent decades, beach tourism has grown significantly. In 2005, only the capital of Greece - Athens, was visited by more than 6 million tourists.
Crete, Peloponnese, Rhodes - are corners of extraordinary beauty and are well suited for a vacation. On Crete, not far from the village of Hersonissos, there is a beautiful cape, from which the view opens up to the entire island, it is here that you can have a great time, because there is everything. On Rhodes, you can feel all the hospitality of Greece, if you relax near Kallithea. The island of Peloponnese in the town of Pyrgos (Tower gr.) has the longest sandy beach in the entire Mediterranean.
Mykonos and Santorini have long been among the most popular island tourist destinations in the world. In 2006, about 16.5 million tourists arrived in Greece. The number of jobs provided by the tourism and related industries was 659,719 in 2006. This is 16% of all workers employed in the Greek economy.
Transport
In Greece, all types of transport are represented.
Metro (Athens). It operates from 5:30 to 23:50, the interval between trains is 5 minutes during the day, 10 minutes in the morning and evening. A trip on new lines costs 0.73 euros, on old ground lines - 0.59 euros.
Bus and trolleybus. Most buses and trolleybuses operate from 05:30 to 00:00. The fare is 0.44 euros. The ticket must be purchased in advance at the stall of the city transport company at the end station or at the stall from a street vendor. To stop the bus, you need to raise your hand, to exit you need to press the button on the handrail.
Taxi. There are many taxis and this is a relatively inexpensive way to travel. It should be noted that a taxi driver may turn out to be not very decent and take you through the night counter during the day or, using your ignorance, circle around the city. You need to be prepared for the fact that the taxi driver will pick up passengers during the trip. The minimum fare is 1.47 euros, when traveling to the airport, railway and bus stations, an additional fee is charged in favor of a taxi driver in the amount of 0.44 euros; 0.44 euros is charged for each additional piece of baggage. Athens taxi drivers often choose to take a longer route or do not turn on the meter. Such acts are severely punished - you must write down the taxi number and report it to the tourist police.
Transport rental. Renting a car is not difficult. There are both international firms and local ones. When using the services of an international rental company, a car can be returned anywhere in the country, but in a local one it will be 1.5 times cheaper. The longer the period for which the car is taken, the greater the discount. For a weekly rental, a minicar like the Fiat Seicento will cost 25-30 euros per day. A variety of models are available for rent - from small-sized to minibuses.
To rent a car, you need a category "B" license, driving experience must be at least a year, and the minimum age of the driver can range from 21 to 25 years.
Kitchen
Greek cuisine is an example of a typical Mediterranean or Balkan cuisine. But in many ways the cuisine of the Greeks is different from the cuisines of its closest neighbors - Bulgaria, Albania and Italy. First of all, spices. Greeks add them to their food more often than others in Europe. However, Greek cuisine is not spicy.
Other distinguishing feature Greek cuisine is an abundance of olive oil. It is added to almost all dishes and is used not only as an aromatic seasoning, but also during the heat treatment of food. Another essential ingredient is lemon.
The special pride of the Greeks is cheese. In Greece, it is produced at least 50 varieties (each region has its own special recipe). The Greeks consume the most cheese in the world - more than 25 kg per person per year. The most popular variety is called "Feta": it is he who is used in the preparation of the famous "Greek salad". In Greece, this salad is called "horiatiki" (rustic).
No less popular in Greece is meat. Preference is given to pork, lamb and goat meat. Moussaka is one of the most famous dishes prepared with the addition of both meat and traditional Greek vegetables. Pastizio is another favorite dish of the Greeks. Fish, shellfish and other seafood are popular.
The shops
Shop opening hours:
Monday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 14:00 or 15:00
Tuesday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 14:00 or 15:00; 17:00 - 20:00 (summer 21:00)
Wednesday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 14:00 or 15:00
Thursday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 14:00 or 15:00; 17:00 - 20:00 (summer 21:00)
Friday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 14:00 or 15:00; 17:00 - 20:00 (summer 21:00)
Saturday 9:00 (summer 8:30) - 15:00
Sunday is a day off
Before Christmas and Easter, all shops are open until the evening.
Supermarkets are open daily from 8:00 to 20:00. It should be borne in mind that goods in supermarkets located in tourist areas are more expensive than in ordinary stores.
There are streets in Athens where all the shops sell one particular product.
Tips
In restaurants and cafes in Greece, it is customary to give a tip (about 10% of the order amount), they can be left on a plate on which the bill was brought. Sometimes tips are included in the bill.
Tipping can be given to a taxi driver or a hotel worker who helps carry luggage to your room (about 1 euro).
Beaches
Most beaches in Greece are municipal. Therefore, the use of sun loungers and umbrellas on them is paid. The cost is about 4 EUR per day. The vast majority of beaches are sandy.
Attractions
The main center of tourism in the country is its capital - Athens, one of the oldest cities in the world.
The National Archaeological Museum is undoubtedly the most important museum in Athens, its collections contain the brightest works of art, created in different periods of ancient Greek civilization.
There are 250 museums, galleries and more modern temple complexes in Athens.
Other attractions
Acropolis - in the ancient Greek city-states, the acropolis was called the elevated and fortified part.
Heraklion Archaeological Museum - The Heraklion Archaeological Museum is considered one of the most important museums in Europe.
Delphi - Delphi, one of the oldest cities in Greece, located on the slope of Mount Parnassus, was famous in the ancient world for its temple of Apollo and the famous Delphic oracle.
Cyclades - a group of almost 2 thousand large and small islands, forming a ring ("kyklos") around the ancient sacred island of Delos with its sanctuaries of Apollo.
Meteora is a unique medieval monastery complex. About a thousand huge rocks rise perpendicularly above the city of Kalambaka and the village of Kastraki.
Museum of Greek folk instruments- this museum houses a collection of 1200 Greek folk instruments from the 18th century to the present, they have been collected for half a century by the musicologist Fivos Anogyanakis.
Interesting Facts
The national anthem of Greece - "Hymn to Liberty" by Dionysios Solomos, has 158 quatrains. Of these, the first 18 are adopted by the National Anthem, but, as a rule, the first 4 quatrains are sung.
Souvenirs
The best purchase in Greece will undoubtedly be a fur or leather product. Moreover, leather clothes are twice cheaper in Greece than in Turkey. Especially good prices in Kastoria. However! Keep in mind, if an "escort" is attached to you, in any store, then you will pay a much larger amount for the product.
Orthodox icons made in the Byzantine style are also interesting.
Of course, as in almost any country in the world, you will find original ceramics, leather goods and colored glass.
From Greece you can bring unique, natural washcloths that are not sold anywhere else in the world. There are especially many of them on the island of Kalymnos.
A great souvenir from Greece - olive oil, with and without seasonings. No wonder Greece is considered his homeland.
Huge selection of souvenirs and products made from shells.
An interesting souvenir from Greece is ouzo - aniseed vodka, which is sold in bottles and vessels made in antique style.
Of course, Greek cognac *Metaxa*, especially Prive Reserve, is a kind that is very rarely found on sale in other countries.
In Greece, you can buy very fragrant dried herbs, goat cheese, peanuts (considered the best in the world), olives, dried fruits, honey.
Many people like wine from the island of Santorini (the island itself is of volcanic origin).
Remember the legends and myths about the exploits of the brave and strong Hercules, about the brave Jason and the Golden Fleece, about Prometheus, who made fire for people? They appeared many thousands of years ago in Ancient Greece. Greece was the cradle European culture and science. The Greek mathematician Pythagoras discovered his theorem, and the philosophers Aristotle and Plato formulated the laws of being.
Greece is located in the southeast of Europe, near the border with Asia. Its shores are washed by three seas: the Ionian, the Mediterranean and the Aegean. Greece consists of the mainland and three thousand islands. The largest island - Crete, is famous for the legend of the Minotaur - a terrible monster that lived in the labyrinths of the Knossos Palace (its ruins are preserved on the island). The total area of the country is 132 thousand square meters. km. Greece borders with Bulgaria, Macedonia, Albania, Turkey. The country is inhabited by Greeks, there are more than ten million of them (2003).
The capital of Greece - Athens - is one of the oldest cities in the world. Actually, about 950 thousand people live within the boundaries of the city, but the population of Greater Athens with its suburbs is more than three million people. Usually, tourists come to Athens to visit the ancient Acropolis with the majestic Parthenon - the temple of the patroness of the city, the goddess Athena, take a walk through the ancient Plaka quarter, and then go to the picturesque islands.
Greece is a mountainous country; mountains occupy more than half of the territory. The highest point is Mount Olympus, where the ancient Greek gods lived. The coast of Greece is heavily indented - nature has created convenient natural harbors for ships. The rivers of Greece are small. The most significant of them flow in the north of the country. In the northern regions of Epirus and Macedonia, there are many mountain lakes. The climate in Greece is Mediterranean subtropical, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Greece is an industrialized country. The most developed industries are textile and food. An important branch of the economy is shipping. The country's merchant fleet is one of the largest in the world. Greece is the main supplier of olives and olives to many countries of the world. Tourism brings significant income to the country.
The first tribes that lived on the modern territory of Greece were the Pelasgians, Lelekhs, and others. The most ancient Greek cities of Knossos and Mycenae were founded in the second millennium BC. At the same time, the tribes of the Achaeans, Ionians, Aeolians and Dorians, who lived in the south of the Balkan Peninsula and along the shores of the Aegean Sea, began to recognize themselves as one people - the Hellenes. Hellenic civilization reached outstanding ancient world heights and had a huge impact on the development of all European culture. On the basis of the Greek alphabet, Latin, Coptic, Gothic, Slavic alphabets subsequently arose. feature ancient greek civilization was the predominance of independent city-states - policies.
But scattered policies could not withstand the power of the Roman Republic. In 148 BC, Roman troops occupied the territory of Greece. In 395, the Roman Empire was divided into Western and Eastern (Byzantine). Greece became the basis of the Byzantine Empire, its state language became Greek, the Greeks occupied the main administrative posts in the empire. During this period, Christianity was established here. Churches and monasteries began to be built throughout the country. of his heyday Byzantine Empire reached under Emperor Justinian I. But already in the seventh century, with the beginning of the Arab conquests, the decline of the empire began, and in 1453 the Byzantine Empire fell under the onslaught of the Ottoman Turks. The Turkish yoke is one of the blackest pages in the history of Greece. For four hundred years the Greeks struggled to preserve their national consciousness and the Orthodox faith. Only in 1830, after many years of stubborn, bloody war, independence was proclaimed in a small part of Greece. Later, other Greek lands were also liberated from Turkish rule, but nevertheless, a significant part of the territory inhabited by Greeks since ancient times remained part of the Turkish state. Greece also experienced severe trials in the twentieth century. Its territory became the scene of hostilities during the First and Second World Wars. And in 1946, when the shots had already died down in all of Europe, a Civil War between the communists and the pro-American government regime. In 1967, a military junta of "black colonels" came to power in Greece. Only after their overthrow in 1974, the country was proclaimed a republic and began to develop along a democratic path.
According to the 1975 constitution, Greece is a parliamentary republic. The official head of state is the president, who is elected by parliament. Karolos Papoulias has been President of the Hellenic Republic since March 12, 2005. Greece is part of the European Union.
The main administrative-territorial unit of Greece is the nome (district). The country is divided into 51 nomes, but there are also larger territorial associations, which include several nomes. Greece has made an invaluable contribution to the development of world science and culture. Modern art, philosophy, science, politics, language are rooted in ancient Greek culture. The official language of the country is Greek, and currency unit- Euro.

