Jaundice is the coloration of yellow skin, sclera of the eyes and visible mucous membranes. All this is a consequence and visible manifestations of an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. How are neonatal jaundice and bilirubin levels related? What does the critical level of bilirubin in the blood mean for the health of the baby, and what is the norm of bilirubin in the baby?
NEWBORN JAUNDICE AND BILIRUBIN
When in full-term newborns the level of bilirubin in the blood is higher than 35-50 µmol / l, jaundice develops. The same applies to the level of bilirubin in the blood exceeding 85 µmol / l in premature babies.
It should be said that the severity of jaundice is determined not only by the concentration of bilirubin in the blood, but also by the individual characteristics of the baby's skin (initial color, capillary tone, depth, etc.). Therefore, jaundice itself cannot be considered an objective indicator of the “bilirubin level”. But exceeding the norm of bilirubin in an infant clearly indicates jaundice of various degrees of severity and types. The sclera of the eyes, the skin of the face, the palate and the lower surface of the tongue are most easily stained yellow. When the rate of breakdown of erythrocytes in the blood outstrips the ability of the liver to bind bilirubin (make it direct), indirect bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream and causes the corresponding staining.
- Types of jaundice in newborns
 Diagnose different types jaundice in newborns, in particular:
Diagnose different types jaundice in newborns, in particular:
- 1. conjugative jaundice of newborns (associated with the immaturity of the enzymatic systems of the liver or with its low binding capacity),
- 2. hemolytic jaundice of newborns (due to hemolysis - increased destruction of red blood cells in the blood),
- 3. parenchymal jaundice of newborns (associated with infectious or toxic lesions of the baby's liver cells),
- 4. obstructive jaundice of newborns (due to a mechanical obstruction in the body of the outflow of bile in children).
In addition, jaundice is distinguished by the degree of flow and manifestations, into physiological, nuclear jaundice and other forms.
PHYSIOLOGICAL JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
Physiological neonatal jaundice occurs in about 60–70% of all children. By its nature, physiological jaundice of newborns is conjugative jaundice. At the heart of its process, conjugative jaundice implies a restructuring of the hemoglobin system that occurs in the body after the birth of a baby.
- How does physiological neonatal jaundice occur?
Fetal hemoglobin differs significantly from adult hemoglobin: in the body during intrauterine development, special fetal hemoglobin F (HbF) predominates (this hemoglobin binds oxygen better), which ensures the transfer of oxygen from maternal erythrocytes to fetal erythrocytes. When the baby is born, this hemoglobin is no longer needed, and shortly after birth, the child's body begins to intensively destroy HbF, and then synthesize hemoglobin HbA. The process of hemoglobin decay results in the formation of indirect bilirubin, and its concentration in the blood increases, and if the body does not have time to remove it, jaundice appears.
Most often, physiological jaundice of newborns manifests itself on the 3-4th day of the baby's life. Up to 5-6 days, the intensity of yellow staining may increase for some reason. But by the end of the first week, the activity of liver enzymes finally increases, and the level of bilirubin gradually begins to decrease, approaching normal. As a rule, by the end of the second week of a baby's life, the symptoms of jaundice disappear without treatment and without causing any harm to health.
But with immaturity, prematurity of the fetus, asphyxia and / or hypoxia, defects in liver enzyme systems due to heredity, due to the use of drugs that displace bilirubin from its connection with glucuronic acid (in particular, vitamin K, sulfonamides, levomycetin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, oxytocin, cephalosporins ) the content of bilirubin can increase to dangerous numbers - a critical level of bilirubin in the blood.
Accordingly, the types of jaundice in newborns are distinguished into the disease of prematurity, children with asphyxia, drug-induced jaundice, and so on.
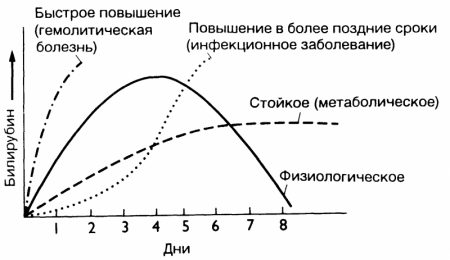
NUCLEAR JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
The critical level of bilirubin in the blood of full-term newborns is 324 µmol/l. The critical level of bilirubin in the blood of premature infants is 150-250 µmol/L.
As you noticed, the difference is significant, it is connected, first of all, with the fact that premature babies have an increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier. The main danger of this is that the still immature brain cells of the baby are more sensitive to the effects of indirect bilirubin. Nuclear jaundice of newborns is the defeat of toxins in the subcortical nuclei of the child's brain by indirect bilirubin. Also, kernicterus is called bilirubin encephalopathy.
Nuclear jaundice in newborns is manifested by the following symptoms: severe drowsiness, decreased sucking reflex, convulsions, piercing cry, sometimes stiff neck (their tension).
That is why the rate of bilirubin in a baby in maternity hospitals is carefully monitored, monitored by doctors in absolutely all newborn babies. In the event of jaundice, this analysis is prescribed 2-3 times during the time that the baby is in the hospital.
- Treatment of kernicterus of newborns
Previously, hyperbilirubinemia (increased levels of bilirubin) was treated with intravenous transfusions of 5% glucose solution, phenobarbital (to increase the activity of liver enzymes) and ascorbic acid, cholagogues (to accelerate the excretion of bilirubin in the bile), and giving adsorbents to bind bilirubin in the intestine and preventing its reabsorption.
But today, doctors prefer to use phototherapy: the baby's skin is irradiated with special lamps. Under the influence of light of a certain wavelength, a transition occurs, the “transformation” of bilirubin into its own photoisomer (lumirubin). This isomer is devoid of toxic properties and is highly soluble in water, due to which it is excreted from the body with bile and urine, without requiring preliminary transformation in the liver. Phototherapy is carried out in the hospital. The indication for prescribing the treatment of jaundice with phototherapy is the bilirubin concentration in the blood exceeding 250 µmol/l in full-term newborns or 85-200 µmol/l in premature babies.
ARIES SYNDROME OR "MAILK JAUNDICE OF BABIES"
The group of conjugative jaundice also includes Aries syndrome - the so-called jaundice in children, which appears due to breastfeeding by the mother. During the first week of life, breast-fed babies develop transient jaundice 3 times more often than formula-fed babies. It is believed that the cause of Aries syndrome is the content of certain fatty acids in the mother's milk, and an increased level of hormones. These substances are able to suppress liver function, while inhibiting the conversion of indirect bilirubin to direct.
When breastfeeding is stopped for this type of jaundice, the blood bilirubin level drops to 85 µmol/L (the upper limit of normal bilirubin in a preterm infant) in less than 48-72 hours. Thus, a test for "milk" jaundice is carried out. However, for its implementation it is not at all necessary to transfer the child to artificial nutrition, it is sufficient to feed the baby with expressed milk, pre-treated in the following way: milk is heated to 55-60 ° C and cooled to body temperature - approximately 36-37 ° C. This treatment significantly reduces the biological activity of estrogens and other substances in mother's milk that can compete with the baby's body for liver enzymes.
- Treatment of Aries syndrome
The course of this condition is generally benign, against the background of "milk" jaundice, cases of bilirubin encephalopathy are not described, so usually no treatment is required, and the baby can be breastfed. Moreover: a child with such jaundice is often recommended to breastfeed even more often than usual, so that the baby’s body releases bilirubin faster with stool.
HEMOLYTIC JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
 Hemolytic jaundice occurs in case of increased hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells). Hemolytic jaundice of newborns may be one of the manifestations in newborns of hemolytic disease that develops in Rh-positive babies born by an Rh-negative mother. In this case, antibodies can be produced in the mother's body that destroy the fetal red blood cells.
Hemolytic jaundice occurs in case of increased hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells). Hemolytic jaundice of newborns may be one of the manifestations in newborns of hemolytic disease that develops in Rh-positive babies born by an Rh-negative mother. In this case, antibodies can be produced in the mother's body that destroy the fetal red blood cells.
The main signs of hemolytic disease of the newborn are:
- 1. hyperbilirubinemia,
- 2. anemia (decreased levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells),
- 3. enlargement of the spleen and liver,
- 4. in severe cases - general swelling of tissues, skin, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal and chest cavities of the body, severe anemia, inhibition of reflexes, a sharp decrease in muscle tone.
The mildest form of hemolytic disease is congenital anemia of newborns, which is manifested by pallor of the skin in combination with a low amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells. As a rule, the disease proceeds favorably and, in case of timely treatment, ends with a complete recovery.
Hemolytic jaundice can develop with hereditary diseases that are accompanied by defects in either the structure of membranes, or hemoglobin molecules, or erythrocyte enzymes. Jaundice is noted from the very first days of life. Its accompanying symptoms are anemia, an enlarged spleen.
- Treatment of hemolytic jaundice
Hemolytic jaundice of newborns appears on the very first day of life, while the level of bilirubin in the blood quickly rises to a critical one.
For its treatment, surgical methods are often used, in particular: hemosorption and exchange transfusion. During a blood transfusion, blood is taken from the baby, which contains an increased level of bilirubin and a reduced number of red blood cells, and is replaced with normal donor blood. One procedure replaces up to 70% of the total blood volume of a newborn. This approach reduces the concentration of bilirubin and prevents brain damage, and restore the required number of red blood cells. In the case when a critical level of bilirubin in the blood is reached, the procedure is required to be repeated.
Hemosorption is a procedure for cleaning the blood from bilirubin by precipitation of maternal antibodies.
In the case of a mild course of the disease, treatment methods that are used for transient jaundice can be used.
PARENCHYMATOUS JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
 Parenchymal jaundice of newborns develops as a result of damage to liver cells by toxic or infectious substances. Such damage leads to a decrease in the ability of these cells to bind bilirubin. Parenchymal jaundice of newborns often develops against the background of intrauterine infections, in particular: cytomegalovirus (about 60% is the cause of all cases of prolonged jaundice in infants), rubella, toxoplasmosis, viral hepatitis, listeriosis.
Parenchymal jaundice of newborns develops as a result of damage to liver cells by toxic or infectious substances. Such damage leads to a decrease in the ability of these cells to bind bilirubin. Parenchymal jaundice of newborns often develops against the background of intrauterine infections, in particular: cytomegalovirus (about 60% is the cause of all cases of prolonged jaundice in infants), rubella, toxoplasmosis, viral hepatitis, listeriosis.
The following signs indicate the presence of intrauterine infection of the fetus:
- 1) prolonged jaundice of newborns (the duration of prolonged jaundice is longer than 2-3 weeks in full-term babies and 4-5 weeks in premature babies);
- 2) anemia;
- 3) enlargement of the liver, peripheral lymph nodes and spleen;
- 4) discoloration of feces and darkening of urine;
- 5) inflammatory signs in the general blood test (increased ESR, an increase in the number of leukocytes);
- 6) an increase in the level of liver enzymes in the blood test.
Protracted neonatal jaundice, parenchymal jaundice is diagnosed using the PCR method (detection of antibodies to viruses in the blood or bacteria), serological reactions.
OBTURATIONAL JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
This type of disease is associated with problems with the outflow of bile in the body. Obstructive jaundice of newborns occurs against the background of blockage of the biliary tract, impaired bile outflow. It develops with defects in the development of the bile ducts (aplasia, atresia), intrauterine gallstone disease, intrahepatic hypoplasia, tumor compression of the bile ducts, bile thickening syndromes and other pathologies.
Obstructive jaundice of newborns has characteristic symptoms, in particular: a yellow-green hue of the skin, induration and enlargement of the liver, periodic or permanent discoloration of the feces. Obstructive jaundice of newborns appears, as a rule, not immediately, but only at the 2-3rd week of life. To diagnose it, a biopsy and radiological methods are used. Treatment is supposed to be through surgery.
A little more about what is neonatal jaundice and bilirubin levels in babies:
The topic of today's article, bilirubin in newborns, is extremely relevant, since an increase in its level is becoming more common.
"Your child has elevated bilirubin." Today, 70% of mothers of newborns hear this phrase from a doctor in the maternity hospital. Of course, in this way, the joyful event of the birth of a long-awaited baby is noticeably overshadowed. And for many, this sounds like a sentence.
Of course, finding out that your child has neonatal jaundice is an unpleasant event. And an increase in bilirubin in a child means exactly this diagnosis.
But there is no need to panic. We'll fix everything. Parents are only required to figure out what depends on them in this condition and what needs to be done (or NOT done) for the speedy recovery of the baby.
Firstly, in no case should you ignore the increase in bilirubin in a newborn or interfere with the examination and treatment of the baby. A pathological increase in bilirubin is dangerous for the child's nervous system. In this case, it is easier to prevent than to treat the consequences of the disease.
What is bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a yellow-olive pigment, a by-product of the breakdown of erythrocytes (red blood cells). Erythrocytes are found in the blood and are responsible for normal gas exchange in the body.
Red blood cells contain the protein hemoglobin, which brings the oxygen necessary for life to each cell of the body, and on the way back it takes and removes the carbon dioxide formed in the cells.
It is normal for red blood cells to break down. There is nothing eternal. So are erythrocytes. They have served their time - they must be disposed of. New ones are formed in their place.
The blood of the fetus contains the so-called fetal hemoglobin, which provides oxygen transport to the organs and tissues of an unborn child in the womb, while his lungs are not yet functioning. After the baby is born and the lungs are activated, fetal fetal hemoglobin begins to be replaced by normal hemoglobin A.
By itself, hemoglobin outside the erythrocyte is toxic. To neutralize it, the body launches a series of transformations, as a result of which, at one of the stages, bilirubin is formed as a by-product.
Causes of increased bilirubin
There is direct and indirect bilirubin.
First, when hemoglobin breaks down, indirect hemoglobin is formed. It cannot dissolve in water, so it is not excreted from the body. As a result of the connection with the blood protein albumin, indirect hemoglobin enters the liver through the bloodstream. There it is transformed into direct bilirubin, which is easily excreted in the urine from the body.
Since the enzymatic system of the liver in a newborn is not yet complete, it cannot quickly cope with a large amount of unclaimed fetal hemoglobin. And for some time, indirect hemoglobin cannot be excreted from the baby's body. That is why the rate of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn is much higher than that of a child at the age of one month.
If the liver does not improve for a long time, bilirubin has time to color the skin and mucous membranes yellow. And this condition is considered physiological jaundice of newborns.
Necessary examination for a child with jaundice
Even in the delivery room, the level of bilirubin in the umbilical cord blood is measured in the baby. Then, in full-term children, bilirubin is controlled again after two days. Premature babies are re-measured the level of pigment in the blood 24 hours after birth. In the future, control it every 12-24 hours.
Premature babies or babies with thin, brittle blood vessels often take blood from the parietotemporal vein, which is located on the baby's head. This is very scary for parents. But there is no need to worry, as this is a large vein. The skin in this place is thin, the procedure is safe and less painful for the child than elsewhere. And the staff in children's departments is always recruited by experienced.
Thanks to modern technologies, it became possible to measure the level of bilirubin by a bloodless method (bili-test). That is, with the help of a special apparatus that is applied to the forehead of the child, the amount of this yellow pigment is determined by the color of the skin. More often this method is used in children who do not have clear signs of jaundice.
The advantages of the beat test method are that it is non-invasive (without skin damage), which means that the study is painless and safe, and the result becomes known instantly. The disadvantage is that only total bilirubin is determined, without dividing it into direct and indirect, which is very important in the diagnosis of pathological jaundice.
Throughout the entire period of treatment of jaundice in the hospital, regular monitoring of bilirubin levels is carried out until it normalizes. At the outpatient stage, a control measurement is carried out during a dispensary observation of one month.
The norm of bilirubin for a newborn
After the baby is born, the numbers of bilirubin are constantly changing depending on age. For full-term and premature babies, the norms differ.
For clarity, I will give the figures for the normal content of bilirubin in the blood for full-term and premature babies in the form of a table.
| Child's age | Norm of bilirubin for full-term babies, µmol/l | Norm of bilirubin for premature babies, µmol/l |
| 24 hours | up to 85 | up to 97 |
| 36 hours | up to 150 | up to 120 |
| 48 hours | up to 180 | up to 150 |
| 3-5 days | up to 256 | up to 171 |
| 6–7 days | up to 145 | up to 145 |
| 8–9 days | up to 110 | up to 97 |
| 10–11 days | up to 80 | up to 50 |
| 12–13 days | up to 45 | up to 35 |
| More than 14 days | up to 20.5 | before 18 |
Signs of physiological jaundice
She appears by the third or fourth day of the baby's life. It resolves on its own by the end of the third week.
The skin is moderately yellowish, while bilirubin reaches the upper limit of normal, not exceeding 256 µmol/l. This condition absolutely does not affect the general well-being of the baby (there is no decrease in appetite, no lethargy and excessive drowsiness, the baby sucks well).
The reasons for its occurrence are different:
- pathology of the mother during pregnancy and the associated use of various medications;
- multiple pregnancy;
- maternal alcohol or tobacco abuse during pregnancy;
- prematurity;
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen) of the fetus during pregnancy or childbirth.
Physiological jaundice is not yet a pathology. Such children need to control the level of bilirubin, including for the timely diagnosis of the transition physiological jaundice into pathology.
Jaundice from breast milk. Truth or fiction?
Sometimes jaundice in a child does not appear until a week after birth. More often, such “belated” jaundice is typical for babies with a good weight gain.
The mothers of these children usually produce a lot of milk, and due to the characteristics of the body, their milk contains an increased amount of estrogens (female sex hormones). And they, in turn, prevent the natural excretion of excess bilirubin from the body of the baby.
If the bilirubin in the newborn does not decrease, the mother should express milk and warm it up to a temperature of 60-70 ° C. It is necessary to give milk to a child in a state cooled to 36-37 ° C. When heated, the structure of the hormone is destroyed, and the composition of milk does not fundamentally change. In this way, it is possible to cope with the negative effect of the mother's female sex hormones on the baby's body, while maintaining the ability to breastfeeding.
Knowing the features and capabilities of our maternity hospitals, I understand that in most cases they will not bother with pumping and warming up milk. It is immediately recommended to transfer the child to artificial feeding. It is not right. I am against such measures.
As an ardent supporter of breastfeeding, I want to clarify that the hormonal changes in the mother will end in a couple of weeks, and save breast milk Until then, not everyone can. Especially if the mother was told that her milk is not suitable for the baby. So the baby will remain without the most useful product preserving and increasing his health.
Signs of pathological jaundice
Unlike physiological, pathological jaundice is a dangerous condition for the baby. It is diagnosed when the level of bilirubin in the blood is higher than normal.
The causes of pathological jaundice in newborns can be:
- infectious lesions of the liver (viral hepatitis);
- hormonal disorders;
- Rhesus conflict or incompatibility of blood groups of mother and child;
- intestinal obstruction in a child;
- genetic diseases in which the destruction of red blood cells occurs;
- mechanical jaundice (impaired outflow of bile);
- cephalohematoma in a baby;
- liver dysfunction (fermentopathy).
Signs of pathological jaundice:
- appears almost immediately after birth (1st day);
- elevated bilirubin, approaching critical levels or above normal;
- the skin is intensely colored yellow, including the feet and palms;
- in case of violation of the liver, dark urine and colorless feces appear;
- there is a confirmed fact of immunoconflict between the mother and the newborn child;
- jaundice is prolonged or has an undulating course.
The final diagnosis is made only by the doctor, analyzing the history of the pregnant woman, the clinic and the results of the examination.
What is the danger of pathological jaundice?
The fact is that a newborn baby has an incomplete blood-brain barrier, which should retain all toxic and dangerous substances and prevent their penetration to the brain. In this regard, excess bilirubin also passes through this barrier and enters the brain with blood flow and into nervous system baby.
The toxic effect of bilirubin (usually at a level of more than 300 µmol / l) on the state of the nervous system is manifested by the so-called bilirubin encephalopathy (nuclear jaundice).
Already on the first day after birth, a child with bilirubin encephalopathy can observe the following manifestations:
- an increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
- a decrease in the sucking reflex up to its absence and, as a result, a lack of body weight;
- decline blood pressure(hypotension);
- excessive physical activity or, conversely, lethargy and drowsiness;
- convulsive muscle contraction.
This form of jaundice must be treated without fail and immediately. This condition is very dangerous, including for all centers of the brain. If the child is not helped in time, then by six months the child will lag behind in physical and mental development. There will be hearing loss. Often these children develop paralysis.
Therapeutic measures for jaundice
Of course, the treatment of newborns is carried out in a hospital and is prescribed exclusively by a doctor. The prescribed treatment will depend on the cause that caused the increase in bilirubin. The following information is provided for informational purposes only.
- Phototherapy is one of the main and most effective methods treatment of jaundice in a newborn. The baby is placed under special lamps. Under the influence of their light, bilirubin is transformed into lumirubin - non-toxic soluble bilirubin, which is freely excreted from the body with urine and feces within 12 hours.
The baby's eyes are protected with a special bandage or a cap is tied, since the light of lamps is harmful to vision. Possible side effects of this procedure: dryness and flaking of the skin, loose stools, excessive sleepiness. All these effects disappear after discontinuation of phototherapy.
Light treatment results in a drop in bilirubin levels of 30–35 µmol/L over 4–6 hours of therapy. Light therapy can be prescribed both for 48 hours in a row with breaks for feeding, and carried out in several approaches at intervals of 3 hours. With a decrease in bilirubin to 220 µmol / l and below, the procedure is usually stopped.
- Intravenous administration (infusion) of detoxifying agents or glucose to facilitate the removal of bilirubin. This is an emergency measure.
- Drugs that improve the rheological properties of bile (fluidity), which contributes to a better outflow of it through the biliary tract. Relevant for problems associated with the passage of bile through the biliary tract.
- Frequent and as early as possible application of the baby to the breast allows you to achieve a laxative effect from colostrum, so that the original feces, which contain a lot of bilirubin, quickly come out of the intestines of the baby.
In most cases, the level of bilirubin in the blood can be reduced quickly. It is important not to waste time. Even pathological jaundice in infants can be treated in an average of 4-5 days.
Believe me, the health of the child is more important than any inconvenience associated with treatment in a hospital.
Health to you and your children!
A practicing pediatrician, twice mother Elena Borisova-Tsarenok told you about bilirubin in a newborn.
Many young mothers, seeing their newborn baby for the first time, are very puzzled. yellow its mucous membranes and skin. Neonatologists say that this phenomenon is transient. This is due to the fact that in some cases the rate of bilirubin in newborns can only be balanced over time. What do the values of bilirubin indicate, what are the symptoms and consequences of its increase in infants?
Types of bilirubin
To begin with, you need to understand the concepts that in question. So, bilirubin is a bright green-brown bile pigment. It is produced due to the breakdown of red blood cells - hemoglobin - as they age. Hemoglobin consists of two components: heme - protein and globin - iron. The organism “takes” these elements, and the decay products take on two forms.
Read also:
One type of component - direct - binds to liver albumin and is excreted from the body with urine and feces. And the second - indirect - does not dissolve in water, but easily penetrates the liver and "supplies" the body with toxins. A special protein is responsible for the transformation of indirect bilirubin into direct bilirubin. The ratio of direct and indirect components - bilirubin - is measured in a ratio of 1:4. Any deviations can be associated with problems in the liver.
The norm of bilirubin in infants
Babies are born with two types of red blood cells: their own and fetal, which were needed for prenatal development. Having been born, the child's body gets rid of fetal erythrocytes, so there are much more decay products in the blood than in an adult. On the third or fourth day after birth on time, the baby should have 205 µmol / l. Bilirubin levels in premature babies can be in the range of 171 µmol/L. The table of the norm of bilirubin in newborns looks like this:
Thus, by the second or third week of life, the rate of bilirubin in infants stabilizes and approaches the indicators of an adult.
Jaundice in newborns
Elevated bilirubin in newborns causes a yellowish tint to the mucous membranes and skin. These are external manifestations of infantile jaundice, which are observed in 65% of infants. As a rule, it does not require treatment and passes on its own. However, some of its features still need to be known. Jaundice in newborns is of several types:
- physiological (caused by the breakdown of fetal erythrocytes);
- pathological (which is a symptom of certain diseases).
To determine the type and determine the tactics of treatment, you should donate blood for bilirubin.
Causes and manifestations of physiological jaundice

The causes of physiological jaundice are:
- fetal hypoxia;
- asphyxia;
- infection that aggravated uterine development;
- a combination of mother's 1st blood group and 2nd (sometimes 3rd) baby blood group.
Manifestations of physiological jaundice usually look like this:
- yellow tint skin on the chest, neck, face;
- yellowness appears for the first time 36 hours of life;
At the same time, the child is active, and all indicators of the body's work are normal. Jaundice passes by the second or third week of life, and in premature babies - by a month.
Symptoms and causes of pathological jaundice
The causes of pathological jaundice are:
- different Rh factors of mother and child;
- genetic disorders;
- diseases associated with the circulatory system;
- problems with the liver or biliary tract;
- hormonal disruptions;
- problems with the intestines (when bilirubin is not excreted, but is absorbed back into the bloodstream).
As a rule, pathological jaundice manifests itself as follows:
- yellow color of the skin below the navel, as well as the palms and feet;
- lethargy or overexcitation;
- white stool, very dark urine.
If the symptoms worsen and do not go away by the third or fourth week of life, then you should consult a doctor and take the necessary tests.
Complications that pathological jaundice can cause
Due to the increased level of bilirubin, which does not decrease for a long time, certain complications may occur:
- kernicterus (the level of bilirubin is so high - over 290 µmol / l that it penetrates the brain and causes destabilization of gray matter cells);
- obstructive jaundice (associated with a delay in the outflow of bile due to a cyst of the bile duct or features of the development of the bile ducts).
Symptoms of complications are:
- lethargy;
- breast rejection;
- constant crying;
- uncontrollable head shaking.
Tests prescribed for prolonged jaundice
If the symptoms of infantile jaundice do not go away for a long time or there are suspicions of complications, diagnosis is necessary:
- blood test (to determine the indicators of bilirubin);
- determining the proportion of bilirubin types;
- study of the liver (in particular, the production of albumin);
- ultrasound abdominal cavity(to exclude problems with the intestines);
- consultation with an endocrinologist, a surgeon if necessary.
Treatment and prevention of the disease

Modern methods of treating jaundice can normalize the level of bilirubin and eliminate possible complications. Have a positive therapeutic effect:
- phototherapy with infusion therapy (ultraviolet rays that cause active production of albumin to transport indirect bilirubin to the liver. Combined with the introduction of solutions of membrane stabilizers to prevent dehydration);
- drugs that increase the production of liver enzymes (phenobarbital, zixorin and others);
- blood transfusion in case of kernicterus;
- enterosorbents as aids to eliminate the threat of bilirubin looping between the intestines and the liver;
- vitamins, which are water-soluble fats (A, E, K);
- diet (lactose-free formulas, not breastfeeding).
The latter method of treatment is used if the baby has an increase in the level of bilirubin due to breast milk. Then the hormonal composition of milk and fatty acids prevents the synthesis of the indirect type of bilirubin in the direct one. In order not to completely refuse breastfeeding, you can heat and cool the expressed milk - it will not contain fatty acids.
The choice of a specific method of treatment depends on individual indicators of the level of bilirubin, as well as the presence or absence of concomitant diseases.
In order for a newborn to quickly adapt to new living conditions (including to stabilize its bilirubin level), there is nothing better and more effective than breast milk. Of course, it will serve in this case in good stead, only if there are no contraindications for breastfeeding. The more often the baby will eat, the faster the excess bilirubin will be excreted through urine and feces.
Bilirubin is a substance synthesized in the human body from decayed red blood cells. In an adult healthy person, it is metabolized in the liver, and then excreted along with bile through the intestines. In some pathological processes, the amount of bilirubin increases significantly, which leads to its accumulation in the surrounding tissues. At high concentrations, this substance gives a person a yellow tint. Depending on the severity of the pathological process, its intensity may vary. The rate of bilirubin in newborns varies greatly depending on the day after birth.
Child with physiological jaundice
The reasons
The main molecule involved in blood transport is hemoglobin. Few people know that there are several varieties of it. In adults, hemoglobin A predominates, and in children, fetal hemoglobin (F). During the intrauterine period, hemoglobin F is the main carrier of oxygen for the fetus. Compared to hemoglobin A, it is more efficient as an oxygen carrier, but less resistant to large pH fluctuations and other negative environmental factors that affect the body. An increase in bilirubin levels is normal for a newborn. Yellowing of the skin and visible areas of the mucous membranes indicates the active breakdown of immature erythrocytes and accumulation in the surrounding tissues.
Physiological jaundice is a normal reaction of the newborn organism to contact with environment. It develops in the predominant majority of children and is a kind of adaptation to new living conditions. Physiological jaundice can be expressed in all children in different ways, but, as a rule, it occurs on the 2-3rd day after birth, and disappears on the 8-9th day. The norm of bilirubin with physiological jaundice in newborns may increase. A similar reaction is observed in more than half of healthy children. According to some reports, the percentage of children with physiological jaundice that occurs after birth reaches 70%. Gradually, hemoglobin A begins to predominate, and bilirubin, accumulated in the skin and mucous membranes, is destroyed and excreted by the kidneys and liver.
Hemoglobin
Originally an oxygen carrier developing fetus is embryonic hemoglobin. It begins to be synthesized already at 1 week of pregnancy. Fetal hemoglobin replaces fetal hemoglobin in the middle of the 2nd month. Whatever it was, embryonic hemoglobin does not disappear completely and is contained in the blood in a small concentration throughout the entire intrauterine development.
ADVICE! Get rid of dark circles around the eyes in 2 weeks.
At the time of birth, the content of fetal hemoglobin reaches 80% percent. Over time, this indicator decreases and by the end of the first year of life it is 1.5%, which corresponds to the content in adults.
Diagnostics
Quantitative analysis of bilirubin is carried out immediately after the birth of the child. As a sample for research, blood is taken from the umbilical cord of a newborn. The next one is held on the 3rd day of life. The level of bilirubin in the blood is measured in µmol/l. Immediately after birth, this indicator ranges from 50 to 60. Within a few days, fetal hemoglobin begins to actively decompose, as a result of which the total level of bilirubin can increase to 250 μmol / l. Hyperbilirubinemia is also due to low plasma protein, underdevelopment of enzymatic systems and bile ducts of the liver. By the 8th day, this indicator begins to fall, and by the 30th it is 8-20 µmol / l.
If the bilirubin index exceeds the mark of 300 μmol / l, the child needs emergency medical care, since there is a high risk of developing complications from the central nervous system. The rate of bilirubin for premature babies is up to 250 µmol / l.
TREAT THE CAUSE, NOT THE EFFECT! Remedy from natural ingredients Nutricomplex restores the correct metabolism in 1 month.One of the latest developments that helps to quickly and reliably determine the level of bilirubin is the bilitest. With this device, it is possible to carry out percutaneous measurement of bilirubin, determine the effectiveness of treatment and predict the further course of jaundice. The norm of bilitest indicators in newborns is up to 50 µmol / l at birth. The device gives the result in figures of the transcutaneous bilirubin index. In order to determine the concentration of bilirubin in the blood, this indicator must be multiplied by 10.
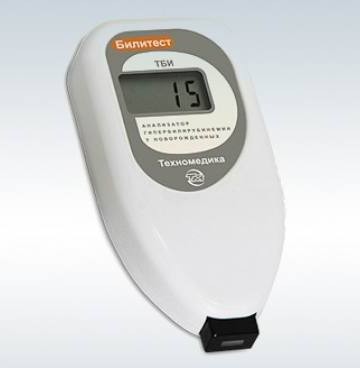
Bilitest
How to recognize physiological jaundice on your own?
As a rule, expectant mothers are advised about this so as not to cause concern at the birth of a child:
For the prevention and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, our readers advise Monastic tea. This is a unique remedy which includes 9 medicinal herbs useful for digestion, which not only complement, but also enhance each other's actions. Monastic tea will not only eliminate all the symptoms of the disease of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive organs, but will also permanently get rid of the cause of its occurrence.
Readers' opinions... »
- Jaundice appears 2-3 days after birth;
- The newborn does not feel bad;
- Physiological departures of normal color;
- The liver and spleen are of normal size;
- Decreased severity of jaundice by the end of the first week.
Complications
In most cases, physiological jaundice resolves without complications for the child. At high concentrations of bilirubin in the blood, a toxic effect can be exerted on the body. The first step will be damage to the central nervous system. At a low content, bilirubin is not able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and cause brain damage. In some cases, there is an increased breakdown of red blood cells, which is accompanied by a massive release of conjugated bilirubin and its accumulation in surrounding tissues.
IMPORTANT! How to remove bags and wrinkles around the eyes at 50?
A similar condition, accompanied by yellowing of the skin, high concentrations of bilirubin and damage to the central nervous system, is called kernicterus. It can occur in some pathological conditions caused by the pathology of the mother, fetus or incompatibility in blood type and / or Rh factor. Also, a special role is played by congenital diseases in which hemolysis of erythrocytes develops. It has been noted that kernicterus occurs in those newborns whose mothers took sulfa drugs during pregnancy.
In the initial stages, the disease is manifested by general weakness, increased fatigue, and a weakened sucking reflex. Gradually, the level of bilirubin in newborns increases, the brain is damaged, and the tone in the extensor muscles begins to predominate. The child straightens the upper and lower limbs, throws his head back and begins to actively scream. So far, no indicator has been established indicating the presence of nuclear jaundice. AT this moment doctors are guided by clinical manifestations, the presence of a complicated course of pregnancy and an elevated concentration of bilirubin. If on the third day after birth the total bilirubin exceeds the norm by 1.5 times, then emergency care is needed.
Treatment
By itself, physiological jaundice does not require treatment. In certain situations associated with an increased risk of developing kernicterus, light therapy is prescribed. At risk are newborns whose bilirubin level reaches 250 µmol / l and above. Treatment of elevated bilirubin in newborns with phototherapy involves placing the baby in a special box containing an ultraviolet lamp. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, bilirubin, located in the skin, begins to break down, and then is excreted from the body along with feces and urine.
This method of therapy is actively used in the treatment of premature infants suffering from Rhesus conflict, hemolytic anemia and other pathologies accompanied by excessive breakdown of red blood cells and the formation of bilirubin. To protect against radiation and prevent retinal burns, it is necessary to close the eyes and external genital eyes of the child during the procedure. Phototherapy has almost no side effects if you follow all safety recommendations. The procedure is not accompanied by overheating or intense loss of moisture. It has been noted that children during phototherapy experience general weakness, drowsiness, slight peeling and decreased mobility. All this takes place immediately after the end of the course of phototherapy. The duration of the course of therapy in most cases is 4 days.
The information given in the text may not be complete. For more detailed information about neonatal jaundice, you should seek the advice of a specialist.
Special pharmacological preparations that help reduce the concentration of bilirubin in the blood are not currently used. When applied medicines may increase the load on the liver and increase the risk of cerebral complications. The use of vitamins, sorbents, choleretic and hepatoprotectors is ineffective or useless. There is a high efficiency of early attachment to the breast of a newborn. In this case, there is a more rapid formation of feces, with which bilirubin departs. At artificial feeding the duration of physiological jaundice increases. If the child was prescribed phototherapy, then the number of attachments to the breast is recommended to be increased.
- observation by a pediatrician;
- UV irradiation for half an hour every day;
- Regular walks in the fresh air;
- Breastfeeding.
Late jaundice
If within 2-3 weeks the bilirubin in the newborn has not reached normal values, then this means that there has been a violation in the system of breakdown and excretion of bilirubin. To clarify the cause, you need to consult a doctor. In the hospital, with the help of special biochemical tests, the level and ratio of bilirubin fractions in the blood will be determined. The main causes of late jaundice.
Many mothers do not even know what bilirubin is, as well as what risk it carries for a child at an increased rate.
Approximately 70% of babies suffer physiological jaundice. Its manifestation begins immediately after birth. There are cases when physiological jaundice becomes pathological. To avoid this, this indicator must be strictly controlled.
Bilirubin in newborns is a bile pigment, an intermediate product of a yellowish-brown color, resulting from the breakdown of red blood cells due to their expiration of their due date. At an elevated level, the skin acquires a yellowish tint. Therefore, this condition is called jaundice.
Each person has a small amount of pigment in his body, only in newborns it is much more, since the liver of a small child is not yet able to fully neutralize bilirubin as in adults.
With physiological jaundice, the face and neck are first stained. Then - the skin of the hands and feet, the navel area. At the same time, no changes are observed in the condition of the baby.
Normally, the pigment in adults is in the range of 8.8 - 20.5 µmol / l, and in the blood taken from the umbilical cord of a newborn, 51-60 µmol / l. After two days, its concentration should be? 205 µmol/l. This is the norm. This figure should decrease every day. By the end of 4 weeks of life, he should reach the "adult" level.
But there are times when it does not go down, but goes up. This poses a serious threat to the health of the child. Already at 256 µmol/l, hospitalization is needed. And if the baby is premature, this threshold is 172 µmol/l.
Table.The norms of the level of bilirubin in newborns
What is bilirubin?
The delivery of a blood test makes it possible to determine the levels of bilirubin. It is general, direct and indirect. Also determine their percentage. Usually in children who have just been born, it is violated.
Part general indicator includes direct and indirect types that differ from each other.
Straight(free) - insoluble. It is not excreted from the body. It should account for no more than 25%.
Indirect- soluble. Processed by liver enzymes. Excreted naturally. Its rate is 75% of the total.
How long does jaundice last?
Gradually, the bile pigment in newborns begins to stand out and by the end of the first week of life, the baby's skin acquires a normal color. It also happens that the yellowness of the skin lasts up to 21 days. This is also considered normal. Physiological jaundice should not be afraid, as it does not bear any negative consequences. And if mom uses breastfeeding, then the removal of bilirubin will go much faster.
Nuclear jaundice
What is it? The thing is that the brain has a blood barrier that protects it from various toxic substances carried by the blood. Only thanks to him nerve cells are not damaged during physiological jaundice. But high levels of bilirubin can cause serious damage to the nervous system.
In the first stage, the child is very lethargic and refuses to breastfeed, and in the second, he throws his head back and screams monotonously.
Mechanical jaundice
Such a disease may occur due to a violation of the outflow of bile. Or rather: all kinds of cysts and underdevelopment of the bile ducts.
Causes of an increased rate in a newborn
Some factors can contribute to the transition of physiological jaundice to pathological:

- If the mother has complications during pregnancy
- Preterm or multiple pregnancy
- Hormonal disorders
- Having diseases such as diabetes
- Taking certain medications
- maternal liver infection
- Gilbert's syndrome, as well as other disorders of the child's liver
- Oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia)
- bowel obstruction
- Incompatibility of mother and child by blood types
- Fetal asphyxia
In severe disease, there is a strong increase in the level of pigment -> 85 µmol / l per day.
In addition, there are some symptoms:
- the appearance of yellowness of the skin of the palms, feet and below the navel of the child;
- severe excitability or lethargy of the baby;
- the feces become white and the urine is dark in color.
Required tests
When jaundice does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to establish the cause of this condition. For this purpose, some analyzes are carried out:
- take blood for a general analysis;
- determine the overall indicator, as well as its fractions;
- take a sample for hemolysis;
- establish indicators of liver function;
- perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- if necessary, consult the relevant specialists.
Why is high bilirubin dangerous?
An increase in the concentration of pigment in the body can cause serious damage to the baby. It seriously affects the brain and nervous system. As a result, developmental deviations, mental disorders, hearing and vision disappear.
Every parent should know exactly when the child needs to be hospitalized. The first sign is a decrease in blood pressure. There is also an increase in the liver or spleen, the sucking reflex fades, convulsions occur and the baby becomes lethargic.
Treatment Methods
Physiological jaundice is a normal condition for a newborn, so you should not panic because of this, but pathological jaundice should force parents to take appropriate measures.
One of the most simple ways treatment - phototherapy. The child is placed under special lamps for 96 hours. The entire course takes place in several sessions.
Thanks to special rays, the toxic pigment is converted into another substance - lumirubin. And it tends to be easily excreted from the body within 12 hours after the procedure. During this time, the baby may experience a deterioration in appetite, increased drowsiness, peeling of the skin, and loose stools.
But this method is effective only for the first few days of life. There are cases when the jaundice is already running. Then you just need drug therapy. Basically, when this disease is detected, choleretic drugs are prescribed. Also glucose and ascorbic acid. Phenobarbital is sometimes attributed.
Highly important role in the treatment of bilirubinemia, the nutrition of the baby with mother's milk plays. It is especially important that the baby receives colostrum. It will contribute to a good excretion of meconium (original feces). Along with it comes out unnecessary pigment. If the meconium does not come out, the yellow pigment from the intestines of the child can get back into the blood. Which will make the jaundice worse. So proper breastfeeding will serve as the best protection against many diseases.
However, there are cases that it is mother's milk that causes an increase in bile. To make sure of this, it is enough to replace mother's milk artificial nutrition. If the indicator decreases, then the cause was established correctly.
To restore water balance after phototherapy, use infusion therapy. It consists in the introduction of a glucose solution with the addition of special substances.
To stop the circulation of the pigment between the liver and intestines, apply enterosorbents. However, this is an optional method.
If there is a threat of nuclear jaundice, the child can be saved exchange transfusion.
When cholestasis occurs, they often use Ursofalkom. This suspension is completely harmless to newborns.
It is important to constantly monitor the replenishment of fat-soluble vitamins and trace elements.
If metabolic disorders occur, more loyal methods of treatment can be dispensed with. With galactosemia, mixtures are used that do not contain galactose and lactose. With tyrosinemia - a diet is observed. It should not contain tyrosine, methionine and phenylalanine.
Causes of low bilirubin
Hyperbilirubinemia is a state of low overall index. The main reason for the change in the level of this substance is the liver, however, according to recent observations, its decrease can also provoke the heart.
If the pigment in the blood is less than 3 µmol / - this is already a deviation. This happens when there are not enough red blood cells. According to statistics, this phenomenon is observed very rarely. But if it does happen, then don't panic. It is necessary to pass tests and select methods for the normalization of total bilirubin.
