Recently, there has been a tendency to increase the body weight of newborn babies. Is it good or bad? Be happy or upset if your doctor tells you that you are expecting a large fetus during your pregnancy.
Everything is quite difficult. Gone are the days when the development of a large baby during pregnancy was considered a sign of the strength of the health of both mother and child. Today, both specialists and future mothers know and understand that the birth of a hero is associated with some dangers during pregnancy and childbirth. And these are real dangers for both the mother and the child.
In this article, we will figure out which baby can be considered large, why the fetus can be large, how it is determined estimated weight fetus, what dangers can lie in wait for a mother and a large baby and how to avoid them.
What kind of baby can be considered large?
Some time ago, a large fetus was considered a child who was born with a weight of 3600 g. Now a large newborn baby is called if he was born with a body weight of 4 to 5 kg. It happens that heroes are born and more than 5 kilograms. In this case, obstetrics use the concept of a giant fetus.
The growth rate for a newborn is considered to be 48-54 cm. And a height of 55-57 cm is inherent in large babies. I am a district pediatrician, and in my area I clearly see that less and less babies are born with a height of less than 55 centimeters. Moreover, long, with a height of 55-56 cm, babies are born and with relatively low weight, in the region of 3600 g.
As a rule, when defining the concept of "large fruit" we are talking only about the body weight of the child. We are not talking about growth. Many people ask: “why is the growth of the child not taken into account?”
In fact, this sign is also taken into account, but only indirectly. The fact is that the diagnosis of "large fetus" is made before the birth of the child, according to the results of ultrasound. The height of the baby, even presumably, cannot be determined at the same time due to the peculiarity of his posture. Although the length of the femur is taken into account on ultrasound, height can be accurately measured only after the birth of the baby. That is why at the stage of pregnancy, the definition of fetal growth is not indicative.
Why can the fetus be large?
According to the latest statistics, in 7-10% of cases a large child is born. Researchers explain these statistics by improving the quality of life of the population, the absence of food shortages, and improving working conditions (“light” work, maternity leave). Yes, part of the increase in the average weight of newborn babies is due to these factors.
As a rule, the development of a large child is a consequence of lifestyle characteristics. future mother, the state of her health, burdened heredity for this factor. I'll tell you about everything in detail and in order.
1. Genetic predisposition.
It seems clear that there is a high probability that large-sized parents will have large babies. But even if future parents adult life do not differ in great height and weight, then at their birth everything could be exactly the opposite. Ask your parents what height and weight you were born with. This will help to some extent assess the likelihood of having a large child.
2. Features of nutrition and lifestyle of a pregnant woman.
Risk factors are:
- lack of physical activity (physical inactivity);
- abuse of junk food (salty, fatty, smoked, fried, marinades, "fast food");
- easily digestible carbohydrates (flour and pasta, sweets, pastries).
The more risk factors you can count from those listed, the more likely it is that a large baby will develop. All this will certainly lead to excessive weight gain for the entire pregnancy. Moreover, both mother and baby will become weightier.
3. Prolongation of pregnancy.
This is possible only in case of incorrect calculation of the gestational age. Only a true gestation for 10-14 days after the fortieth week of pregnancy can have a negative impact. In such a situation, the fetus spends more time in the womb than required. And all the while it is growing. Naturally, during the period of overgestation, the child will gain more weight. In addition to increased body weight, at birth, such a child can be observed with long nails, wrinkled skin with a strongly striated pattern of skin lines, and harder, more unyielding skull bones. Cheese-like lubrication on the body of post-term children is practically absent.
4. Repeated births.
Experts have noticed that there is some (not absolute) statistical relationship between the number of births and the body weight of babies born. That is, it is highly likely that for the same woman each subsequent baby will be born with a greater weight than the previous one.
Of course, the possibility of the birth of a large first-born child and the development of events during repeated births in an inverse relationship is not excluded. But still, the likelihood of having larger children with repeated births is higher.
5. Rh-conflict pregnancy.
Rh incompatibility occurs when an Rh-negative mother has a baby who has inherited a positive Rh factor from her father.
Due to the Rh conflict, the child may develop hemolytic disease, the main manifestation of which is the destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Let me remind you that hemoglobin is “stored” and works in erythrocytes, with the help of which oxygen is delivered throughout the body to each cell of the body, and carbon dioxide is excreted back.
In turn, the destruction of red blood cells leads to anemia (oxygen starvation of the body due to insufficient amount of hemoglobin in the blood) and icteric staining of the skin, fluid retention in the child's body (edematous form), an increase in the size of the liver and spleen.
6. Metabolic pathology of a pregnant woman (hypothyroidism, obesity, diabetes mellitus).
With such diseases, a lot of excess glucose circulates in the mother's blood, which is not absorbed in time by the mother's body. This glucose then in excess then enters the blood of the fetus.
Glucose is fast energy, calories. It is clear that excess glucose will lead to a rapid weight gain of the baby.
By the way, sometimes a diagnosed or already born large fetus is the first prerequisite for examining the level of glucose in the blood of a mother or a pregnant woman. There are frequent cases of the development of gestational diabetes mellitus, whereas before pregnancy, the woman had no problems with an increase in blood glucose levels.
7. Features of the placenta.
The placenta (where mother and child come into contact) can form in the uterus at different places. Practice shows that the placenta located on the back wall of the uterus contributes to a greater intensity of metabolic processes.
It has also been noted that another reason for the development of a large child is a large, thick, with a large number of vessels, the placenta. This leads to a more active metabolism between mother and child, and the child's weight grows faster.
8. Taking certain medications.
In the special literature, there is an opinion of experts that weight gain can be provoked by prolonged uncontrolled intake of certain medicines. These drugs include drugs that improve blood flow from the uterus to the placenta (Actovegin, Pentoxifylline).
Also, some gynecologists attribute this action to the intake of complex vitamins. But so far this information has not been confirmed by scientific research.
How is the estimated weight determined?
At each appointment, the gynecologist examines a pregnant woman, measures the height of the fundus of the uterus above the pubic symphysis, abdominal circumference, compares changes in the size of the pelvis in different dates pregnancy. Based on the data obtained, we can make an assumption about the development of a weighty baby.
Next, the doctor finds out from the future mother the data on her genetic predisposition to the development of a large toddler. The card records and analyzes data on the birth weight of the future fathers and mothers themselves, on the mass of other children born to them, if any.
I will tell you more about the parameters of the uterus. In obstetric practice, there is a formula for calculating the approximate weight of the baby. The circumference of the abdomen is multiplied by the height of the fundus of the uterus in centimeters. For example, if the circumference of the abdomen is more than 100 centimeters, and the height of the fundus of the uterus above the pubic symphysis is even or more than 40 cm, then at birth the baby will weigh more than 4 kg.
Even to calculate the weight of the child at the time of birth, the weekly weight gain of the pregnant woman is estimated. When gaining body weight more than the weekly maximum allowable norm (more than 500 g) and with a total weight gain during pregnancy of more than 15 kg, a conclusion can be drawn about the possible development of a large child.
It is worth mentioning that such an assessment is valid only for a normal pregnancy. That is, when mommy has no concomitant pathology, no edema is observed, no increased arterial pressure and the level of glucose in the blood, there are no abnormalities in the functioning of the kidneys, which can be judged by the presence of protein in the urine.
Only an ultrasound examination will help to more accurately determine the estimated weight. On ultrasound, various parameters are evaluated: the circumference of the tummy and breast, the length of the femur and humerus, the distance between the most protruding parts of the temporal bones of the skull (biparietal size). The ratio of the length of the femur to the size of the circumference of the tummy is also determined.
The assessment and analysis of all these parameters together allows the specialist to make a conclusion about the estimated weight of the child and the compliance of its main dimensions. a certain period pregnancy. As a rule, the indicators of a large child correspond to a later gestational age, that is, an ultrasound can show a gestational age of up to two weeks more than it really is.
What are the symptoms of a large pregnancy?
The big belly of the expectant mother as a clear sign of the hero sitting in it is an erroneous opinion. Most often, the big belly of a pregnant mother makes you think about polyhydramnios.
Due to the fact that the enlarged uterus presses on nearby organs, during a large-fetal pregnancy, a pregnant woman may feel some specific symptoms more pronounced.
Various disturbances in the work of internal organs and systems can be observed (especially in the last stages of pregnancy).
Namely:
- from the side digestive system- severe heartburn, frequent constipation;
- from the urinary system - frequent urination, swelling;
- on the part of the cardiovascular system - shortness of breath, varicose veins of the lower extremities. There are frequent cases when a rather weighty uterus disrupts the blood flow through the inferior vena cava, bringing a pregnant woman lying on her back to a pre-fainting state;
- from the musculoskeletal system - pain in the joints of the legs and in the lumbar spine.
What dangers can lie in wait for a mother and a large baby in childbirth?
Obstetrician-gynecologists conduct examination and preparation for childbirth of mothers with large children more carefully. This is no accident. The birth of a hero may be associated with some complications of the process of childbearing. Let's take a closer look at some of these complications.
— Premature (before contractions) or earlier (before cervical dilatation) rupture of amniotic fluid. The cause in both cases is the high head of the fetus. Having not descended to the entrance to the pelvic ring formed by the pelvic bones, the child's head is not able to distinguish between amniotic fluid into their anterior and posterior parts. At the same time, the shape of the fetal bladder changes, which cannot adequately provoke the opening of the cervix and its readiness for childbirth.
The rapid outflow of a large amount of amniotic fluid can lead to the prolapse of the umbilical cord loops or even the limbs of the child from the uterus. This is a very dangerous condition that requires emergency surgery.
We also remind you that a long anhydrous period is a risk of infection for the fetus.
- Weakness or incoordination of labor occurs to some extent also due to the undescended fetal head. In this case, there may be a delayed opening of the cervix of the uterus. Therefore, contractions can be painful, irregular, with fading strength. All this makes it difficult for the child to move along the birth canal and lengthens the birth. Often in such situations, it is necessary to use emergency surgery (caesarean section) in order to prevent the child from developing hypoxia (hypoxia - oxygen starvation).
- Clinically narrow pelvis(revealed in childbirth). During childbirth, there is often a discrepancy between the size of the baby's head and the size of the pelvis of the expectant mother. Moreover, the pelvis can have dimensions that are quite consistent with the norm. A large head will not be able to pass through the birth canal. And here neither strong attempts, nor good contractions, nor full disclosure of the cervix will solve the problem. The solution is an emergency caesarean section.
- Dystocia (difficulty moving) of the baby's shoulders. The fact is that, due to its streamlined shape, the head of a child (even a relatively large one) passes through the birth canal, gradually pushing the soft tissues apart. But the broad shoulders of a weighty fetus can get stuck. This condition requires the midwife to provide special assistance during childbirth, which will facilitate the birth of the widest part of the body of a large child and will avoid ruptures of soft tissues and oxygen starvation of the child. But sometimes it can lead to a fracture of the collarbone in a child.
- Breaks. Often in childbirth, mothers of a large toddler have gaps. There is also a threat of uterine rupture, ligament rupture, pubic symphysis divergence. To minimize complications in the form of ruptures, an episiotomy (oblique incision of the perineum) is performed during childbirth, more often a perineotomy (dissection of the perineum towards the anus).
- Childbirth trauma. Very often, large children, due to their size, receive birth injuries during natural childbirth. Possible fractures of the baby's bones, the formation of a cephalohematoma (blood bump), up to a cerebral hemorrhage.
All of the above indicates that it is very important to know in advance that the birth of a large baby is expected. This will allow you to decide on the tactics of conducting labor in order to exclude the possibility of complications and trauma during childbirth.
What can be done to avoid complications in childbirth?
After it turned out that the baby is large, the gynecologist must comprehensively examine the woman in labor to find out the reasons for such a weight of the child. If the examination showed that the expectant mother does not have somatic diseases, and the reason is genetics and unlimited food, then the main recommendation is diet.
Compliance with the diet and a feasible increase in physical activity will help to correct the excess weight of the expectant mother until the end of pregnancy and stop the overweight in the child.
If some pathology is found that provokes weight gain in mother and baby, then inpatient treatment and hospitalization will be required long before delivery.
To determine the tactics of childbirth, the need for surgical intervention or medical assistance (prevention of bleeding, thrombosis) in childbirth can only be observed by a doctor in childbirth. And in each case, this will be decided individually.
Trust an experienced specialist and do not worry about anything. The main task of the future mother is to lead the right way of life, in the whole wide sense of this concept. After all, this is a guarantee of the health of a woman and her future children.
Good luck with your birth!
There is an opinion among the population that the large weight of the fetus speaks of health and strength, but only mothers who have given birth to "heroes" and doctors know what difficulties they have to face during childbirth and after the birth of a child. If you believe the statistics, then the birth of a large child is noted in 5 - 10% of all births.
Definition of concepts
They talk about a large fetus or macrosomia when its fetometric indicators prenatal development significantly exceed the established norm for a particular period of pregnancy, or the weight of the newborn is 4 kg or more. In addition to the weight of the child, his height is also taken into account, for example, in a normal baby, growth is in the range of 48 - 54 cm, while the length of a fetus with a large weight is 54 - 56 cm, and in some cases reaches 70 cm.
If the weight of the child at birth is 5 kg or more, then they speak of a giant fetus. The birth of giant children is less common than large ones, and has a ratio of 1/3000 births.
The reasons
Why a child is born large is explained by many reasons, which can be due to both the characteristics of the woman's body and the individual characteristics of the baby developing in the uterus. These factors include:
genetic predisposition
It is noted that heredity also plays a role in the birth of a large child. Physically developed and tall parents have a greater opportunity to produce a large baby.
Increasing the duration of pregnancy
Normally, pregnancy lasts 38 - 41 weeks (see). If the gestational age exceeds the upper limit of the norm, they talk about over-pregnancy, which can be true and false. With true overwearing, a child is born with obvious signs of overwearing: dry, without original lubrication of the skin, its wrinkling, waters have a greenish or grayish tint, and their number is reduced. Such phenomena are explained by the aging of the placenta, the formation of multiple calcifications in it, and a decrease in its functions. The lack of oxygen and nutrients leads to the development of placental insufficiency, hypoxia and even fetal hypotrophy.
Diabetes in a woman
The birth of a large baby (or on ultrasound more than the gestational age) may be due to the presence of diabetes in the mother or its development during gestation (gestational diabetes). Children are born with a number of characteristic signs, which is called diabetic fetopathy. The large weight of the fetus is the result of hormonal storms and constant jumps in the level of glucose in the woman's blood. A characteristic sign of diabetic fetopathy is excessive weight gain in the baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy against the background of developing polyhydramnios. Accordingly, the child, although born large, is initially unhealthy. Pregnant women with diabetes are hospitalized no later than 32 weeks, examined and decide on the timing and methods of delivery.
Rh-conflict pregnancy
One of the reasons that determine the size of the fetus over the term is. This complication of gestation occurs when a child with a positive Rh factor is born by a woman who has a negative Rh factor. As a result, the unborn child develops a hemolytic disease, which is characterized by anemia and jaundice, and in extremely severe forms, swelling joins them, which is called the edematous form of hemolytic disease. At the same time, fluid accumulates in the fetal cavities (abdomen, chest), and the liver and spleen increase significantly in size. Massive edema and hepatosplenomegaly determine the large weight of the child.
Features of the placenta
The structural and functional features of the placenta can also provoke the formation of a large baby (see also). Often, at the birth of a child with a large body weight, a placenta of large size and thickness (5 cm or more) is noted. A thick and massive placenta promotes an intensive exchange of nutrients and microelements, which accelerates the development of the fetus. In addition to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and intensive blood supply to the child, there are bursts of placental hormones, which indirectly affect the metabolism in the mother's body and enhance the growth and development of the baby.
Subsequent pregnancies ending in childbirth
A directly proportional relationship was noted between the number of births and the body weight of children born. After the second, third, and so on, a large fetus is formed, which is about 30% larger than the size and weight of the firstborn. Doctors explain this fact in two ways.
- Firstly, the psychological factor matters, a woman, bearing a second / third child, is familiar with the processes of pregnancy and childbirth, is more balanced and calm.
- Secondly, the large size of the baby during subsequent pregnancies is due the best conditions intrauterine nutrition due to the developed circulatory network in the uterine wall.
- Also, the conditions for intrauterine growth and development of the second child are much better due to the greater extensibility of the uterus and slight resistance of the abdominal muscles.
The nature of the nutrition of a pregnant woman
An important role in the increase in the weight of the child is played by the nutrition and lifestyle of the woman, especially after the 20th week of pregnancy (see). Hypodynamia, a growing belly, a passion for high-calorie foods (consumption of muffins, sweets, pasta) leads not only to the accumulation of fatty tissue in the expectant mother, but also provokes macrosomia in the fetus (see).
Obesity
Excessive weight of the expectant mother also plays a role. This is due not only to poor nutrition of the pregnant woman, but also to impaired lipid metabolism in her body, which provokes a violation of the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the fetus, intrauterine damage to the liver and pancreas, and activation of compensatory reactions in the placenta. All these factors contribute rapid growth and increased fetal weight. In the case of obesity of the 1st degree, a large fetus is born in 28% of pregnant women, with the 2nd degree, the probability of a large child increases to 32%, and with the 3rd degree, up to 35%.
Taking medications
Uncontrolled consumption of certain drugs by a pregnant woman, which improve uteroplacental circulation and activate anabolic processes (for example, gestagens,) also contribute to weight gain.
Other factors
The age of a woman (under 20 or over 34 years old), the presence of inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system, can also affect the size.
Large fruit: signs and diagnosis
If a woman has a large belly during pregnancy, this is not necessarily evidence of a large child. Multiple pregnancy should be excluded and (many pregnant women neglect the passage of ultrasound during such an important period of life).
By 38 weeks of pregnancy, and sometimes even earlier, the clinical manifestations of a large fetus are objective data obtained during a visit to an obstetrician. At each appearance in the antenatal clinic, a pregnant woman is measured body weight, an increase of 500 grams. weekly, against the background of absent edema and other signs of gestosis, makes the doctor suspect a large weight in the baby.
In the case of a large fetus during pregnancy, the signs are determined by the size of the woman's abdomen (circumference and height of the fundus of the uterus), evidence of this is the exceeding dimensions: The circumference of the abdomen is more than 100 cm, and the height of the fundus of the uterus is more than 40.
The estimated weight of the fetus is calculated by the formula: coolant is multiplied by VDM.
Since a baby with a large weight in utero takes up more space, the internal organs of a woman are subjected to greater compression and infringement and experience a significant load. As a result, the pregnant woman notes frequent urination, heartburn (reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus), constipation and shortness of breath. A large uterus presses on the inferior vena cava, which can provoke fainting in a horizontal position lying on your back. The load on the musculoskeletal system increases, which is manifested by pain in the legs, lower back, spine and ribs. Possible occurrence or worsening of the course of varicose veins of the legs. Also, there is a high probability of stretch marks on the abdomen and an increase in the tone of the uterus.
Ultrasound is of great importance in the diagnosis of a large fetus, with a thorough measurement of the fetal data of the fetus and the determination of its estimated weight. The circumference of the head and abdomen, the length of the femur and humerus are measured. A large head and a significant size of the abdomen, an increase in the liver and spleen, the identification of fluid in the body cavities indicates an edematous form of hemolytic disease.
The course of pregnancy
Pregnancy in women with a large fetus proceeds, as a rule, without complications. All the described complications (fainting, problems with the digestive tract and shortness of breath) develop by 38-40 weeks of pregnancy with a large fetus. There is a high probability of developing placental insufficiency and progressive hypoxia as a result of a discrepancy between the uteroplacental blood flow and the rapidly increasing weight of the child. Pregnancy features include:
- a thorough examination to exclude polyhydramnios and;
- exclude diabetes mellitus - conducting and consulting an endocrinologist;
- calculation according to ultrasound data and the size of the pregnant belly of the estimated weight of the fetus;
- physiotherapy;
- diet correction (exclude easily digestible carbohydrates and refractory fats);
- cancellation or restriction of taking drugs - anabolics.
The course of childbirth
“How to give birth if the fetus is large?” - expectant mothers ask a question. The answer is not the course of childbirth, which, with large sizes, have their own characteristics. Spontaneous childbirth of a child of considerable size is often complicated by the following circumstances:
Clinically narrow pelvis
This complication develops when the fetus has a large head, and even with full disclosure (10 cm) of the uterine os, it does not advance, which is called a mismatch in the size of the head to the woman's pelvis. It is characteristic that the size of the maternal pelvis may be within the normal range, but still, childbirth is difficult even with good and strong contractions. If there is also an anatomical narrowing of the pelvis (the size of the pelvis is shortened by 1-1.5 cm or more), the question of a caesarean section is raised.
Untimely outpouring of waters
Early discharge of water (before the opening of the pharynx by 8 cm) is due to the high standing of the baby's head, so due to its large size it cannot press against the entrance to the small pelvis and move forward, and there is no separation of water into the anterior (fetal bladder) and posterior ones. Early outflow of water is dangerous by prolapse of the umbilical cord or small parts of the child (leg, handle). In addition, this complication slows down the process of opening the uterine os, which lengthens the 1st period of labor and exhausts the woman in labor. If the anhydrous interval continues for 12 hours or more, the risk of the uterus is also high. If the umbilical cord or part of the fetus falls out, immediate operative delivery is indicated.
Anomalies of tribal forces
Childbirth with a fetus of large size is often complicated by anomalies of labor activity. A protracted course of childbirth leads to a decrease in the intensity and frequency of contractions (weakness of the birth forces develops, both primary and secondary). The child begins to suffer, intrauterine hypoxia increases (at first it becomes more frequent - tachycardia, then it slows down - bradycardia), which is also an indication for caesarean section.
Threat of uterine rupture
The straining period of childbirth with a large child is also fraught with danger. In the process of passing the fetal head through the birth canal, it is configured, that is, it acquires a shape that is convenient for overcoming the planes of the small pelvis (the bones of the skull "layer" on top of each other). With a disproportionate size of the baby's head and the mother's pelvis, the lower uterine segment is overstretched, which threatens to rupture it.
Fistula formation
Due to the prolonged standing of the baby's head in the same plane of the pelvis, the soft tissues of the birth canal (cervix and vagina) are compressed, but in addition to them, the bladder and urethra in front and the anus in the back are also compressed. This leads to impaired blood circulation in the tissues, ischemia, and then necrosis (necrosis). Necrotic tissues are shed after childbirth and genitourinary and/or rectovaginal fistulas are formed.
Rupture of the pubic joint
Difficult passage of the baby's head can damage the pubic articulation (rupture of the ligaments and divergence of the pubic bones), which often, especially in severe cases, requires surgical intervention after childbirth (see).
Shoulder dystocia
Childbirth with a fetus with a large weight can be complicated by difficult removal of the shoulders, which is typical for children with diabetic fetopathy (the size of the shoulder girdle is much larger than the size of the head). In this situation, special benefits are provided, which can result in fractures of the clavicle, humerus or cervical spine.
Cephalohematoma or cerebral hemorrhage in the fetus
The development of such complications is due to anomalies of the birth forces, disorder and subsequent. When the head is configured, there is an excessive displacement of the cranial bones and a sharp compression of them, which causes hemorrhage in the brain or under the periosteum.
Birth management
In the case of the diagnosis of a large fetus, what will be the delivery: operative (caesarean section) or through the natural birth canal (spontaneous birth) depends on many factors. Carrying out the planned:
- large size of the fetus in women under 18 and over 30 years of age;
- combination of breech presentation and a large child;
- prolongation of pregnancy with a large child;
- anatomical narrow pelvis, regardless of the shape and degree of narrowing, and the large weight of the child;
- anomalies in the development of the uterus, myomatous nodes and a large fetus;
- indications requiring the exclusion of the straining period (cardiovascular pathology, high myopia) and a large child;
- large fetal weight and aggravated obstetric history (birth of a dead child in the past, and the use of assisted reproductive technologies).
A caesarean section for emergency indications is performed for any complication during childbirth (threatening uterine rupture, improper insertion of the head, etc.).
In the first 2 hours after childbirth (early postpartum period), there is a high risk of developing hypotonic uterine bleeding, which is due to prolonged labor and excessive uterine distension.
When drawing up a plan for childbirth through the birth canal, take into account:
- childbirth should be carried out under the monitoring control of the child's condition and;
- in childbirth, it is obligatory to maintain a partogram (drawing up a schedule taking into account the time of each period of childbirth, disclosure of the uterine os, intensity of contractions);
- during childbirth, re-measure the size of the pelvis;
- adequate and timely anesthesia and the introduction of antispasmodics;
- in the pushing period, prophylactic administration of reducing agents in order to prevent weakness of attempts;
- early diagnosis of a clinically narrow pelvis;
- prevention of bleeding in the afterbirth period and in the first 2 hours after childbirth.
Children born with a weight of 4 kg or more are at high risk for morbidity and mortality at an early neonatal age (up to 28 days of life), the development of birth injuries (cephalohematoma, cerebral hemorrhage, fractures of the shoulder, collarbone), the development of metabolic disorders and pathology of the central nervous system.
Question answer
Is hospitalization necessary before delivery when pregnant with a large fetus?
Yes, all women diagnosed with a large baby are advised to go to the hospital in advance, at 38-39 weeks. The doctor will carefully measure the size of the pelvis and abdomen, assess the condition of the pregnant woman (the presence of extragenital diseases and complications of pregnancy), the readiness of the cervix (maturity) and draw up a plan for the management of childbirth. And if there is evidence, the decision on the issue of a planned caesarean section and preparation for it.
How can the development of a large fetus be prevented?
First of all, it is necessary from the first days of pregnancy to adhere to rational nutrition. Food should contain the necessary amount for a pregnant woman of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The expectant mother should give up overeating, excessive passion for sweets, pastries, fatty and fried foods, and if the condition allows, do special exercises for pregnant women and avoid hypodynamia (frequent and prolonged lying and sitting).
This is my first pregnancy and I have a large fetus. Will I have to have a caesarean section?
No, it is not necessary at all, especially in the first childbirth of young women. Most often, pregnancy and the birth of a large fetus in young healthy women proceed without complications and end happily.
Obstetrician-gynecologist Anna Sozinova
Pregnancy is a time of expectations, dreams of a beautiful and future baby. During pregnancy, there is a certain plan for observation by a doctor and a certain number of scheduled ultrasound examinations. And on one of the ultrasounds, any woman can hear the phrase "You are bearing a hero." This means that a large fetus is developing inside you.
There are certain norms for the weight and height of the baby at the time of birth. It is considered normal when a child with a height of 48 - 54 cm has a weight of up to 4,000 kg. If the baby weighs from 4 to 5 kg at the time of birth, then they talk about a large fetus during pregnancy. But it is strange that in this case they do not take into account the growth of children. After all, large kids are always taller than children, which, as they say, are normal. The growth of large babies is usually 54 - 56 cm.
According to statistics, today the number of large children is 5-10% of all pregnancies. Doctors believe that this is due to improved working conditions, good and healthy nutrition, as well as the living conditions of pregnant women.
There are also cases of the birth of giant babies: weight over 5 kg. But such cases are recorded much less frequently.
How to identify a large fruit?
Starting from the 12th week of pregnancy, the doctor at each examination listens to the baby's heartbeat, measures the circumference of the hips and abdomen of the pregnant woman, and the weight and pressure of the pregnant woman is also measured in the pre-medical office. All these measurements are not made in order to indicate to the woman how she has recovered and to offend her. All this is done in order to clearly draw a picture of the course of pregnancy and monitor the health of the baby and expectant mother.
Diagnosis of a large fetus during pregnancy is made not only on the basis of an examination of a woman. An experienced doctor always takes into account heredity and disease. The doctor should ask about the physique of the father, about the weight with which the future parents themselves were born. If, from all the data of the examination and interview, a suspicion of a large fetus is diagnosed, only then a referral for an ultrasound is issued. Only on the basis of ultrasound can you calculate the estimated weight of the baby.
On such an unscheduled study, the size of the fetal head, the diameter and circumference of the abdomen, the length of the femur and humerus of the baby are determined. And based on these data, it becomes possible to calculate the estimated weight of the fetus.
Causes of a large fetus
There can be many reasons why you are carrying a hero. Some of them are associated only with heredity, some are a reflection of the mother's lifestyle or an echo of her state of health. Let us dwell in more detail on the reasons that the fetus is overweight during pregnancy.
1. Increase in duration of pregnancy. There are two terms that are associated with a long gestation period: the prolongation of a physiological pregnancy and the prolongation of a pregnancy. Prolongation is due to the fact that the timing of childbirth was incorrectly set. In this case, it is born healthy baby but for 10-14 days late established by doctors. The health of the baby is determined by the absence of signs of overbearing and aging of the placenta. With a true prolongation of pregnancy, a baby is born with the following signs:
- wrinkling of the skin;
- greenish or grayish tint of amniotic fluid;
- lack of original lubrication; dryness.
2. A disease such as diabetes, can lead to a large fetus during pregnancy. A pregnant woman with diabetes mellitus should be examined more carefully than the others. Among such women, the statistics of the birth of large children is much higher.
Such pregnant women should be hospitalized no later than 32 weeks of pregnancy. In the hospital, they undergo a thorough examination, after which a decision is made on the timing of childbirth. If a patient with diabetes bears a large fetus, then the issue of artificial stimulation of labor is decided not earlier than 36 weeks. This decision is also made when the woman's health deteriorates (preeclampsia, decreased blood sugar,). Childbirth in this case takes place under the close supervision of a therapist. Insulin is administered during all births. Insulin treatment continues after delivery, depending on test results.
3. Hemolytic disease of the fetus- a serious reason for the development of a large fetus during pregnancy. This disease is caused by Rh-conflict mother and child. It occurs in Rh-negative women when the baby inherits an Rh-positive father. As a result of this disease, the baby not only has a decrease in hemoglobin levels and jaundice appears, but also overweight due to the accumulation of fluid in the body cavities (swelling appears), the spleen and liver increase.
4. Heredity in the development of a large fetus plays an important role. If the mother or father of the baby is tall and large in this moment, then there is a high probability that the child will be large. Also today, small parents could be born large. Then the baby can inherit this very fact and will also be a hero.
5. There is also a tendency for large fetuses to develop in subsequent pregnancies. According to statistics, the second and subsequent children are born with a weight of 30% more than their older brothers and sisters. This is primarily due to the psychological factor (during the second pregnancy, the mother no longer experiences such great stress and fear). The second reason is the readiness and training of the woman's body to bear a baby (now the metabolism between mother and baby is improving due to better blood circulation).
6. Nutrition of a pregnant woman can also affect the excess size of the baby. A large amount of food containing carbohydrates (bakery, sweets) contributes to obesity of the mother and child. In this case, the baby's body begins to work like a mother's and gains excess weight. Already in the womb, obesity can develop.
Danger with a large fetus
The final stage of pregnancy - childbirth, is one of the most responsible and difficult moments of expecting a baby. Carrying a large child can cause certain difficulties in the process of delivery. These difficulties can affect both the health of the mother and the health of the newborn.
First of all, with a large fetus during pregnancy, there may be discrepancy between the size of the baby's head and the mother's pelvis . Even if the pelvis is not narrow, the head of a large baby may not pass through the birth canal. In this case, even a good, strong labor activity will not be able to provide natural delivery.

The head of a large fetus stands high in the pelvic cavity, this is the reason for the lack of distinction between the anterior and posterior amniotic fluid. This difference from normal physiological childbirth causes early effusion of amniotic fluid. If the fetus is large, then along with the discharge into the vagina, the umbilical cord or the baby's pen may fall out. In this case, an immediate surgical intervention is performed. Early outflow of water slows down the process of opening the uterus, and the period of contractions makes it very painful. The fact that the baby is without water for a long time can cause infection of him and the uterus.
The development of a large fetus during pregnancy can cause labor disorders . Such a violation is characterized by good and strong activity in the first stage and a decrease in labor activity in the later stages of childbirth. As a result, the woman in labor gets tired and cannot push. Also, cases of violations of the activity of the nervous, cardiovascular system are not uncommon. large fruit in this situation, it suffers from a lack of oxygen - hypoxia. Such a violation may be characterized by very weak contractions in the first stage of labor.
During attempts, when the baby's head takes the form of a woman's small pelvis, uterine rupture problem . This happens, again, due to the discrepancy between the size of the small pelvis and the head of a large fetus.
emergence urinary or rectovaginal fistulas not uncommon at birth of large children. This is due to the long standing of the baby's head in the pelvic area of a woman. In this case, necrosis of the tissues of the bladder, rectum and urethra occurs. Dead tissue is then torn off, forming fistulas. The problem is solved only by surgical intervention after childbirth.
With a long period of childbirth, pinched nerve in leg , there is also a possibility of damage to the articulation of the pubic bones. This is reflected in the gait of a young mother, limping appears and pain when moving the foot. If the degree of nerve damage is high, then surgery is required to solve the problem. With a mild degree of paresis, bed rest and a bandage are recommended. At the discretion of the doctor, pain medication may be prescribed.
All of the above can occur even before the birth of the baby's head, which was considered large during pregnancy. But even when, it would seem, the most difficult thing is behind, problems can arise. After the birth of the head of a large fetus, difficulties may arise in removing the baby's shoulder girdle. If the child is large, then, first of all, the neonatologist pays attention to the condition of his clavicles and arms.
A mismatch between the mother's pelvis and the baby's head can cause hemorrhage in the brain in a child or cephalohematoma. If there are no complications, then after 6-8 weeks the hematoma subsides without affecting the health of the child. Hemorrhage can also remain without consequences for the development and health of the baby. It all depends on its size and zone of outpouring.
We must not forget that a woman who gave birth to a large baby may have inadequate contraction of the uterus . As a result, bleeding may occur after the baby is born. The causes of bleeding are both retained placenta in the uterus, and ruptures of the tissues of the genital tract.
What to do?
If, after another examination by a doctor, you were told that you have a large fetus, you should not panic. A large fetus during pregnancy is the need for more careful monitoring in the future and during childbirth. Having learned that the baby is large, the doctor, first of all, will try to find out the reason.

If the cause is any pathology of the development of the fetus or the health of the woman, treatment in a hospital will be prescribed. In this case, in most situations, the woman is under observation until the very birth, as there is a need for constant teaching of drug treatment.
If the cause of a large fetus is heredity or mommy's overeating, then a diet is prescribed. According to the diet, the mother should receive only healthy food that will not contribute to the set excess weight.
It is also not worth being afraid of childbirth with the development of a large fetus. The only thing you need to do in advance is to talk to your doctor about the progress of your labor. In some cases, a caesarean section is immediately prescribed, in others they take expectant tactics.
Indicators for caesarean section already in the process of labor is the presence of signs of discrepancy between the head of the child and the pelvis of the mother within 4 hours. That is, if the birth is scheduled for natural, then subject to the spontaneous course of labor and the departed waters, the doctor can decide on the operation if the life of the mother or child is threatened.
Also, during childbirth, a caesarean section can be used if symptoms of uterine rupture appear.
Large fetus during pregnancy: how mom can help
Having considered the reasons for the development of a large fetus, it can be understood that the mother's first aid is to healthy eating even before conception (that is, getting rid of overweight that a child can inherit) and proper nutrition during pregnancy. It is not for nothing that at each scheduled examination, the gynecologist gives recommendations on the amount of certain nutrients in each trimester of pregnancy. So, for example, the amount of carbohydrates per day in the last trimester should be only 300-400 g.
If the reason lies in heredity, then it is worth relying on the experience of doctors who will give competent advice, provide information about possible diets and successfully carry out delivery. AT this case diet comes first. Yes, even during pregnancy, sometimes you need to sacrifice something. But you should be driven by the heartbeat of your child, it is for the sake of it that you need to deny yourself some pleasures.
Help with pathologies of a large fetus is mother's consent to receive medical care. It is impossible to hope for a miracle with the swelling of the baby, enlargement of the spleen and liver. All these symptoms are perfectly visible on ultrasound and, with proper treatment during childbirth and after, they may not affect the health and development of the child.
Remember, pregnancy is great time when a woman is already responsible not only for herself, but also for a new little life. A hero is a baby who, while still living in the womb of his mother, already demands special attention, not a reason to worry and be afraid.
A good video about a large fetus and caesarean section
I like!
Many believe that if the unborn child has a large weight, then this indicates that he will be born strong and healthy, but only doctors and "mothers" who gave birth to such heroes know how dangerous such childbirth can be and what difficulties can arise. in the process of the birth of large fruits. According to statistics, the birth of a large child occurs in 5-10% of all cases of childbirth.
Definition of concepts
They say about macrosomia or a large fetus when there is a significant excess of its fetometric indicators, compared with the norms for each specific period of pregnancy, or when the mass born child is over 4 kilograms. In addition to the weight of the newborn, their height is also taken into account. So growth normal child is in the range from 48 to 54 centimeters, while the length of the fetus, which has a large weight, is 54-56 centimeters, in some cases children are born with a height of 70 centimeters.
If the mass of a newborn child is 5 or more kilograms, then we are talking about a giant fetus. The birth of giant children is much less common than large children and accounts for 1/3000 cases.
The reasons
The birth of a large child can be explained by many reasons, among which an important role is played by the characteristics of the mother's body, as well as the individual characteristics of the child developing in the mother's uterus. Among these factors are:
genetic predisposition.
It is noted that essential role in the birth of a large child, heredity plays. Parents who are tall and physically well developed are more likely to reproduce a large baby.
Increase in the duration of pregnancy.
Pregnancy normally lasts from 38 to 41 weeks. Subject to an increase in the gestational age relative to the upper limit of the norm, doctors talk about overwearing, which can be both false and true. With a true prolongation of pregnancy, the child after birth has characteristic signs: wrinkling and dryness of the skin (lack of original lubrication), the amount of water is reduced, and their hue ranges from grayish to greenish. Such manifestations can be explained by the aging of the placenta, its multiple calcification, and decreased functions. Lack of nutrients and oxygen leads to the development of hypoxia, placental insufficiency, and in some cases even fetal hypotrophy.
The presence of diabetes in the mother.

The birth of a large baby (or the reflection of a larger fetus from the estimated gestational age during an ultrasound examination) may be caused by the presence of diabetes in the expectant mother or the development of diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes). In women diagnosed with diabetes, children are born with characteristic signs, which in gynecology is called diabetic fetopathy. The large weight of the child comes from the presence of constant jumps in glucose levels and hormonal storms in the mother's body. A characteristic symptom of diabetic fetopathy is excess weight gain in the baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy, which occurs against the background of developing polyhydramnios. As is clear from the above, the child, although born large, is already unhealthy. Pregnant women with diabetes are hospitalized up to 32 weeks and after the examination they decide on the methods and timing of delivery.
Rh-conflict pregnancy.
One of the reasons for the appearance of a large fetus is the presence of an Rh-conflict pregnancy. Such a complication of pregnancy occurs when a child who has a Rh positive is born by a woman with a negative Rh. As a result, the child gets a hemolytic disease, with anemia, jaundice, characteristic of the pathology, and in especially severe cases, swelling also joins these symptoms. This is called the edematous form of hemolytic disease. In the cavities of the fetus (thorax, abdomen) there is an accumulation of fluid, and the spleen and liver of such children have a significant increase in size. Hepatosplenomegaly and massive edema determine the presence of a large weight in a child.
features of the placenta.

The presence of functional and structural features of the placenta can become the cause of the formation and birth of a large child. Often the birth of a baby with a large weight coincides with the presence of a thick (more than 5 centimeters) and large placenta. A massive and thick placenta increases the intensity of the metabolism of microelements and nutrients, which leads to accelerated development of the fetus. In addition to an increase in the intensity of the child's blood supply and the volume of circulating blood, there are bursts of placental hormones that indirectly affect the metabolism in the mother's body and enhance the development and growth of the baby.
Subsequent pregnancies that end in childbirth.
Celebrate right proportional dependence on the number of births and the weight of children born. After the second and third births, as well as further, the formation of a large fetus occurs, which is approximately 30% larger than the weight and size of the firstborn. Doctors explain this fact by the presence of such moments:
firstly, there is a psychological factor, a woman who is carrying a second, third, and so on child is already well acquainted with all the features of pregnancy and, accordingly, is more calm and balanced;
secondly, the large size of the fetus during subsequent pregnancies may be due to improved intrauterine nutrition, since the circulatory network of the uterus after the first birth is more developed;
also, more favorable conditions for the development of a second child can be explained by the fact that the uterus is in a more stretched state, and the abdominal muscles have little resistance.
The nature of the nutrition of a woman in position.

A significant role in the process of increasing the weight of the child is also played by the lifestyle of a woman and the nature of her diet, this is especially true after the 20th week of gestation. Hypodynamia, abdominal growth and the use of a large number of high-calorie foods (pasta, sweets, muffins) leads to the accumulation of fatty tissue, and also provokes the development of macrosomia in an unborn child.
Obesity.
Excessive weight of a woman during and before pregnancy also plays a role. This may be due not only to the lack proper nutrition, but also caused by a violation of lipid metabolism in the body, respectively, this leads to a violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the fetus, intrauterine damage to the pancreas and liver occurs, and the compensatory functions of the placenta are activated. These factors together contribute to weight gain and fetal growth. If a woman has obesity of the first degree, then the birth of a large fetus is observed in 28%, in the presence of a second degree of obesity, this figure rises to 32%, and if there is obesity of the third degree, the probability of having a large child is 35%.
Taking medications.
![]()
Uncontrolled use of certain drugs by a pregnant woman, which activate anabolic processes and improve uteroplacental circulation (for example, Actovegin, Gestagens) can cause an increase in fetal weight.
Other factors.
The age of the expectant mother (under 20 years old or over 34 years old), cycle disorders, the presence of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system and genital organs can also cause an increase in the size and weight of the fetus.
Large fetus: diagnosis and signs
If a woman has a large belly during pregnancy, this is not necessarily evidence of a large fetus. In such cases, it is necessary to exclude the presence of multiple pregnancy and such a feature of gestation as polyhydramnios (a large percentage of women neglect ultrasound even in such an important period of their lives).
By the beginning of the 38th week of pregnancy, and in some cases even earlier, signs of the presence of a fetus big size are objective data that are recorded during regular visits to the antenatal clinic. The main indicators include weight measurement, weight gain of 500 grams per week; in the absence of edema and other manifestations of gestosis, they are a reason for suspicion of the presence of a large fetus.
With a large fetus during pregnancy, the signs are determined on the basis of measurements of the woman's abdomen (bottom height and uterine circumference), confirmation of suspicions for a large fetus are indicators: the height of the fundus of the uterus is more than 40 and the abdominal circumference is more than 100 cm.
Since a fetus with a large weight in utero takes up much more space (compared to a normal fetus), the internal organs of a woman are subjected to infringement and compression, and the load on these organs increases. This leads to the occurrence of such phenomena as shortness of breath, constipation, heartburn (due to the reflux of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus), and frequent urination. Due to the increase in the size of the uterus, additional pressure appears on the inferior vena cava, as a result, the likelihood of developing fainting conditions while lying on your back in a horizontal position increases. The load on the musculoskeletal system increases, this load is manifested by pain in the ribs, spine, lower back, legs. The course of varicose veins of the lower extremities may occur or be aggravated. There is also a high probability of an increase in the tone of the uterus and the appearance of stretch marks on the abdomen.
A huge role in diagnosing the presence of a large fetus in a woman is played by ultrasound diagnostics, which allows you to carefully measure the fetometric data of the embryo and establish its estimated weight. Measure the length of the humerus and femur, the circumference of the abdomen and head. The significant size of the abdomen and a large head, enlargement of the spleen and liver, the presence of fluid in the body cavities of the child indicate the presence of an edematous form of hemolytic disease in the fetus.

The course of pregnancy
The course of pregnancy in women with a large fetus usually passes without significant complications. The complications described above (shortness of breath, problems with the digestive tract, fainting) occur at 38-40 weeks during pregnancy with a large fetus. There is also a high probability of progressive hypoxia and placental insufficiency against the background of a discrepancy between the rapidly increasing fetal weight and the rate of uteroplacental blood flow. Features of conducting such a pregnancy include:
limiting or canceling the use of anabolic drugs;
diet correction (exclusion of refractory fats and easily digestible carbohydrates);
physiotherapy;
calculation according to the size of the belly of the pregnant woman and the ultrasound data of the estimated weight of the child;
consultations with an endocrinologist and a glucose tolerance test to exclude diabetes mellitus;
a thorough examination to exclude multiple pregnancy and polyhydramnios.
The course of childbirth
Many expectant mothers ask themselves: “But how to give birth if the fetus is large?”. The answer to this question is the nature of the course of childbirth, which, in the presence of a large fetus, has its own characteristics. Spontaneous childbirth in the presence of a large fetus is often complicated by such circumstances:
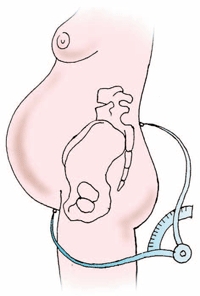
Clinically narrow pelvis.
Such a complication occurs when the fetus has a large head, and even if the cervix is fully opened (10 cm), it does not advance. This complication is called a discrepancy between the size of the baby's head and the pelvis of the expectant mother. characteristic feature is that the parameters of the mother's pelvis may be normal, but childbirth is significantly hampered even if there are strong and good contractions. If there is an anatomically narrowed pelvis (the dimensions of the pelvis are shortened by 1-1.5 or more centimeters), then the issue of performing a caesarean section is discussed.
Untimely outpouring of water.
The discharge of amniotic fluid before the opening of the pharynx by 8 cm (early) may be due to the high position of the head of the child, due to its large size, it cannot normally press against the entrance of the small pelvis and move forward, respectively, there is no differentiation of the amnion into the posterior and anterior. Early discharge of amniotic fluid threatens to fall out of small parts of the child (handle, leg) or umbilical cord. In addition, a complication can slow down the process of opening the cervix of the uterus, which leads to a lengthening of the first stage of labor and significantly weakens the woman in labor. In case of loss of part of the fetus or umbilical cord, immediate delivery through surgery is indicated.
Anomalies of tribal forces.
The birth of a large fetus is quite often complicated by anomalies of the birth forces. A protracted labor process leads to a decrease in the frequency and intensity of contractions (weak labor activity appears, primary or secondary). The child suffers in such cases, as intrauterine hypoxia increases (first, tachycardia is heard in the fetal heartbeat, and then slowing down - bradycardia). Such signs are also an indication for operative delivery.
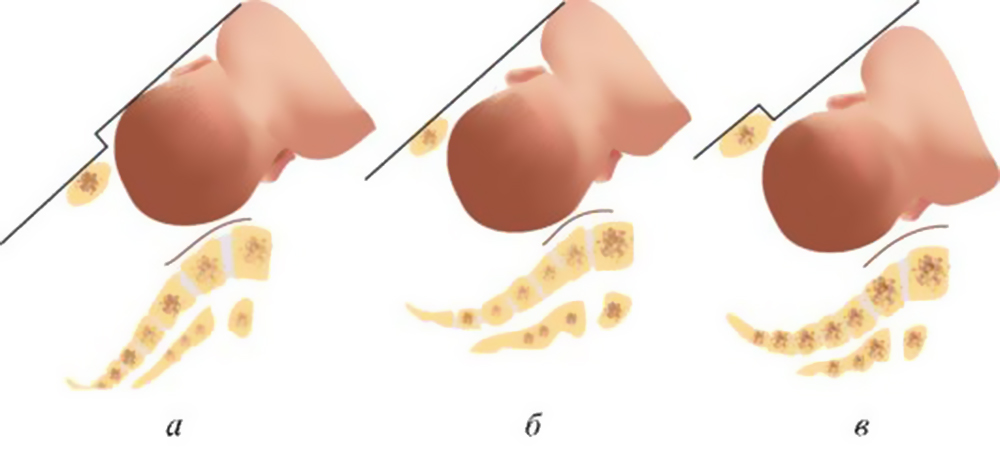
Threat of uterine rupture.
The pushing period at the birth of a large child is also dangerous. During the passage of the fetal head through the birth canal, it changes shape, acquiring the most suitable configuration for overcoming the planes of the small pelvis (the bones of the skull seem to overlap one another). If the size of the baby's head and the mother's pelvis are disproportionate, overstretching of the lower segment of the uterus occurs, which can cause it to rupture.
Fistula formation.
Prolonged standing of the baby's head in one of the planes of the pelvis leads to compression of the soft tissues of the birth canal (vagina and cervix), the bladder is also compressed in a pair with the urethra in front and the anus, respectively, in the back. Such pressure leads to a violation of blood circulation in the tissues, ischemia occurs, followed by the death of fiber (tissue necrosis). Dead tissues after childbirth are rejected by the body, which leads to the appearance of rectovaginal and genitourinary fistulas.
Rupture of the articulation of the womb.
Severe passage of the baby's head can cause damage to the pubic joint (divergence of the pubic bones, rupture of the ligaments), often such injuries, especially severe ones, require exclusively surgical treatment.
Shoulder dystocia.
Childbirth with large sizes can be complicated during the passage of the shoulders, this complication is especially typical for children with diabetic phenopathy (the size of the head is much smaller than the size of the shoulder girdle). In such situations, additional assistance is provided during the passage, which often ends in fractures of the cervical spine, humerus or collarbone.
Cerebral hemorrhage or cephalohematoma in the fetus.
The development of such a complication occurs against the background of a disorder of the uteroplacental blood flow, followed by hypoxia of the child, anomalies of the birth forces. During a change in the configuration of the head, there is a strong displacement of the bones and their excessive compression, which ends in hemorrhage into the periosteum or brain.
Birth management
If a woman is diagnosed with a large fetus, then the nature of delivery: through the natural birth canal (normal birth) or through surgery (caesarean section) depends on many factors. Planned operative delivery is required for the following indications:
large fetus in women over 30 and under 18;
myomatous nodes and a large fetus, anomalies in the development of the uterus;
anatomically narrow pelvis with a large weight of the child;
a large child and re-carrying of pregnancy;
the totality of a large fetus and its breech presentation;
large fetal weight with an aggravating obstetric history (use of assisted reproductive technologies for infertility, recurrent miscarriage, stillbirth in the past);
indications that require the exclusion of a tight period (high myopia, cardiovascular pathology) in combination with a large child.
Cesarean section in the event of emergency indications is performed in any case of complications in childbirth (incorrect insertion of the head, the threat of uterine rupture, weakness of contractions).
In the first couple of hours after delivery (early postpartum period) there is a high risk of developing hypotonic uterine bleeding, which is caused by excessive distension of the uterus and prolonged labor.
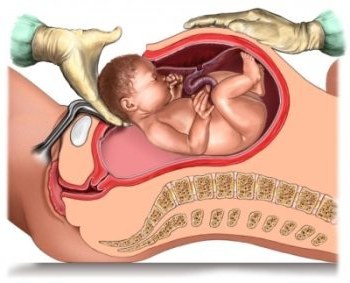
In the course of drawing up a plan for delivery through the natural birth canal, it is necessary to take into account:
childbirth should take place under the monitor control of contractions and the condition of the child;
it is obligatory to maintain a partogram (a schedule taking into account the time of each of the periods of labor, the intensity of contractions, the opening of the uterine os);
in childbirth, a re-measurement of the parameters of the pelvis should be carried out;
timely and adequate pain relief, as well as the introduction of antispasmodics;
prophylactic administration of reducing agents in the pushing period in order to prevent weakness of attempts;
early diagnosis of a narrow (clinically) pelvis;
prevention of possible bleeding in the first 2 hours after childbirth and in the postpartum period.
Children who are born weighing four or more kilograms are at high risk of pathologies of the central nervous system, the development of metabolic disorders, asphyxia, the development of birth injuries (fractures of the collarbone, shoulder, cerebral hemorrhages, cephalohematomas), general morbidity and mortality in early neonatal age (first 28 days of life).
Question answer
Is hospitalization required before childbirth, in case of pregnancy with a large fetus?
Yes, all women diagnosed with a large fetus should go to the hospital a little earlier than the due date, at about 38-39 weeks. During this time, the doctor will perform a thorough diagnosis, assess the condition of the expectant mother (presence of pregnancy complications, extragenital diseases), carefully measure the size of the abdomen and pelvis of the woman in labor, draw up a plan for conducting the birth process. If there are indications for a planned caesarean section, then an operation plan will be drawn up.
How to prevent the development of a large fetus?
First of all, from the moment of pregnancy, you need to adhere to proper nutrition. The diet should consist of food rich in carbohydrates, fats and proteins. You should give up the habit of overeating, as well as the passion for fried, fatty foods and pastries with sweets. If the state of health allows, it is necessary to perform exercises for pregnant women in order to avoid hypodynamia (prolonged sitting or lying down).

During my first pregnancy, I was diagnosed with a large fetus. Is it necessary to perform a caesarean section?
No, operative delivery is not a mandatory algorithm for childbirth, especially in the first childbirth in young women. In most cases, in young healthy women, the process of pregnancy and childbirth takes place without significant complications and with a favorable outcome.
