Probable conception is subject to a complex cyclic process. The female body experiences its influence throughout the entire reproductive age. You can judge how efficiently the system on which the joy of motherhood depends on the functioning of the ovaries, the maturation of the egg, and the size of the corpus luteum.
What is a corpus luteum
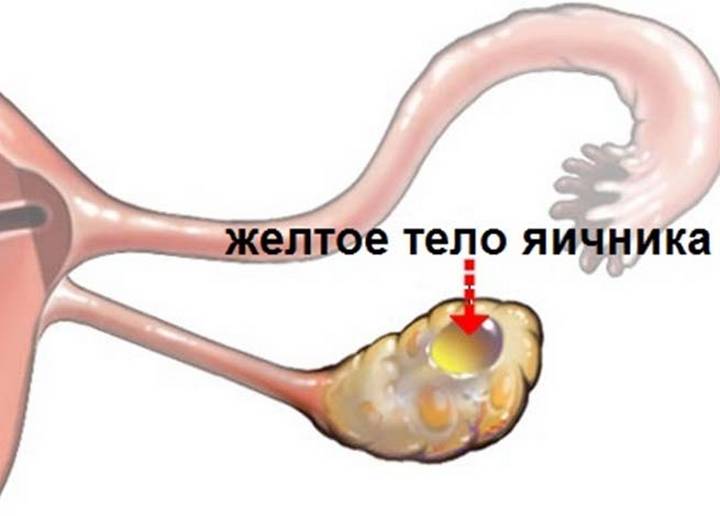
The functional process of each internal organ is different, but together they form a complex relationship so that a woman can conceive a child. If fertilization does not occur, then the body must prepare for the next period of ovulation. In this process significant role assigned to the luteal gland, which due to its color was called the "yellow body". The temporary endocrine organ synthesizes progesterone, which helps the fertilized egg to gain a foothold and promotes its further development until the placenta is formed.
Stages of development
The process of formation of the corpus luteum in the ovary (right or left) is under the control of both the organ itself and the pituitary gland with the immune system. The transient structure, which is able to periodically form, function and undergo regression, is subject to a certain cycle. As a gland that is involved in the secretion of peptides and steroids, the corpus luteum in the ovary, during the normal operation of the reproductive system, goes through the following stages of development:
- Proliferation. In place of the bursting follicle, a blood clot is formed from its vessels. Then there is a rapid replacement of the connective tissue, the cells of the granular layer of the original follicle begin to divide.
- Vascularization. When the corpus luteum is formed, blood vessels appear and the phase of glandular metamorphosis begins. Growing and increasing in size, follicular cells turn into luteocytes, the latter produce a yellow pigment. For the full-fledged work of the gland, in order not to cause developmental delay, at this stage it is important to provide the female body with iron. Experts in the field of gynecology argue that the corpus luteum in the ovary temporarily becomes the most intense organ in the entire body of a woman in terms of blood flow, and therefore needs increased care.
- Rise. The stage of maximum hormonal activity of the corpus luteum, when it slightly rises above the ovary and acquires a purple hue. The duration of the flowering of the gland does not exceed 12 days, if fertilization has not occurred during this time, then the activity of a small endocrine organ begins to decline.
- Regression (extinction). The absence of pregnancy starts the process of changing cells, which begin to decrease, a scar area appears, a white body is formed. The concentration of sex hormones decreases, the corpus luteum begins to disappear, while at the same time a new cycle of follicle maturation starts in the ovaries.
How is an ultrasound scan performed?
If a corpus luteum is found in the ovary during an ultrasound examination, the doctor can state either an early pregnancy or the completion of the menstrual cycle. While the temporary gland will produce progesterone, the woman's reproductive system will stop the development of the next follicle. If fertilization of the egg occurs, then the hormone activates the development of the uterine mucosa and reduces the influence of the immune system of the female body, giving the fetus a chance to develop.
When examining female organs, two methods of ultrasound are practiced: transabdominally (on the surface of the abdomen) and transvaginally (through the vagina). In the first case, before the procedure, you will have to drink a lot of liquid without gas to fill the bladder. For the second procedure, in order to see the corpus luteum on ultrasound, you will have to empty the bladder, undress from the waist down. The doctor will then insert one thin vaginal probe wrapped in a condom without any pain.
What is the normal size of the luteal gland

There is no single standard regarding the correct parameters of the corpus luteum. The concept of the norm is conditional, but the size of the transient structure helps to find out how efficiently and smoothly the reproductive system works. Normal sizes vary in a conditional range, if the indicators do not go beyond the boundaries, then the specialist diagnoses the absence of pathology.
The size of the corpus luteum by day of the cycle
The transvaginal ultrasound sensor helps to determine the parameters of a small gland with an accuracy of up to a millimeter, and during a standard menstrual cycle they can be visualized on the screen or look like in a photo. following sizes:
If after the 14th day of the monthly cycle, which accounts for the peak of ovulation, the corpus luteum continues to grow, reaching 30 mm, then this may indicate the onset of pregnancy or that a cyst has begun to form. In the case of a decrease in the diameter of the follicle in the third week of the menstrual cycle, the luteal gland leaves to appear again after a while.
What is the danger of a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
Hormonal restructuring of the body when it comes " interesting period", can provoke the appearance of a benign formation. Cystic corpus luteum is not rare, but rather frequent occurrence, which does not cause serious complications and does not require treatment. In this way, the luteal gland makes itself felt, continuing to produce progesterone and maintain pregnancy. In non-pregnant women, hyperactivity of progesterone leads to the appearance of persistence, and the corpus luteum, existing longer than the prescribed period, turns into a cyst.
Medical recommendations include limiting physical activity and maintaining normal bowel function. Urgent seeking medical help is necessary only with severe pain in the lower abdomen and a significant deterioration in well-being, which is not necessarily associated with a rupture of the cyst. Serious symptoms may be due to other causes and indicate serious complications.
Video: what does an ovarian corpus luteum cyst mean
If a corpus luteum has formed in the ovary, what is it? This is an endocrine gland, the name of which is associated with its color.
This structure appears only in the second period of the menstrual cycle, when it begins to function.
The job is to inhibit the following follicles due to the production of progesterone. When does iron disappear? The duration of her work depends on the outcome of ovulation.
The ovary with a corpus luteum are representatives of the female genital organs. The only difference is that the ovary is a permanent organ that functions for almost a lifetime.
The corpus luteum is referred to as temporary formations. His work is episodic.
The formation of the corpus luteum is cyclic in nature and is ensured by the correct, coordinated work of the endocrine system.
What are the functions of the corpus luteum? This gland is designed to prepare the inner lining of the uterus for the future attachment of the embryo.
All changes that occur in the body during pregnancy are largely provided by progesterone.
The main zone of its production is the gland in question, which synthesizes a number of other hormonal substances:
- androgenic;
- estrogen and its derivatives;
- oxytocins;
- relaxin;
- inhibins.
Iron often produces a number of other biocompounds for correct operation healthy female body.
The yellow body of the ovary has a relatively small size - 10 - 27 mm. Its growth occurs gradually, depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
The start of development begins with the luteal phase. With strong deviations from these parameters of the organ, it is important to be examined for the presence of pathological changes in the body.
Often, such changes occur during cyst formation. The diagnosis of a corpus luteum cyst does not indicate a serious disease, so it should not cause much panic. The disease worsens when a corpus luteum appears, but is treatable.
The development of the corpus luteum on ultrasound goes through 4 main stages. Proliferation is a sharp increase in the concentration of the hormone lutein in the blood.
As a result, the egg is released into abdominal cavity. This stage of development is observed without ovulation.
This happens when lutein concentrations are too high. This condition greatly affects the development of two corpus luteum in different ovaries.
Vascularization is accompanied by a significant germination of blood vessels into the cells of the follicle.
Thanks to this, the iron receives all the necessary substances and fully develops.
It has been proven that during pregnancy, the corpus luteum in the ovary receives the maximum possible blood supply among all organs.
Rise and fall
The heyday is characterized by the maximum hormonal activity of the gland. The organ itself acquires a bright color, slightly rises above the surface of the ovary.
If pregnancy has not occurred, the phase lasts a relatively short time (about 12 days). The activity of gland production gradually fades away.
This process indicates whether pregnancy has occurred. If it is absent, the strength of hormonal activity decreases, and dystrophic changes in the elements of the organ occur.
The gland decreases in size, turning into a scar. The color becomes whitish. Education disappears.
These processes occur against the background of a reduced concentration of hormones. After ovulation, the organ stops functioning.
This leads to rejection of the endometrium and the development of menstruation. In parallel, processes begin to occur in the body that affect the formation of new follicles. Some changes occur in the uterus.
What is a corpus luteum? With successful fertilization, this organ continues its work. The duration of its productivity increases mainly up to the 12th week of pregnancy.
Why does the body fail?
Menstrual irregularities can often be caused by hormonal changes in the corpus luteum.

But little is known about the pathology of this organ. The corpus luteum is often remembered when infertility is suspected, when, during a normal sexual life, a woman does not become pregnant for a long time or the embryo often freezes.
These situations directly point to a problematic persistent corpus luteum. The gland produces little progesterone, and this causes the termination of pregnancy.
To make such a diagnosis, it is important to conduct a comprehensive, comprehensive examination. A disturbed corpus luteum after ovulation is diagnosed using:
- ultrasound;
- hormonal blood tests;
- biopsy.
When the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient receives special hormone replacement therapy.
It allows you to restore the persistent corpus luteum, to resume its work. Drugs for treatment usually contain various concentrations of synthetic progesterone.
Even with the onset of pregnancy, the prescribed medications continue to be taken. The course of such therapy usually lasts up to 12 weeks of pregnancy.
This duration reduces the risk of sudden abortions. If the pathological persistent corpus luteum is severely damaged, treatment may take much longer.
Often, when various anomalies in the functioning of the gland are detected, doctors prescribe special medications to restore the functioning of the organ. Most often used Bromocriptine, Dostinex.
cyst formation
Often another disease of the gland is diagnosed. We are talking about cysts of the corpus luteum. A neoplasm is often detected with a delay in menstruation.
For this, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is used. Education itself occurs with sharp hormonal changes, failures in the female body.
At the same time, the size of the corpus luteum increases significantly, a woman may feel some soreness and discomfort in the abdomen and ovaries. Pathology equally often affects the corpus luteum in the right ovary and in the left.
The disease appears suddenly. Often this condition does not require medical treatment. The affected corpus luteum in the right ovary or in the left heals itself.
This can happen for no apparent reason or during pregnancy. Often it takes time to heal.
The altered corpus luteum in the left ovary recovers after several menstrual cycles. The only requirement is that they must be in the correct order.
The corpus luteum in the left ovary does not harm the health of the woman, and even more so - the fetus. But when unpleasant symptoms appear, it is better to immediately see a specialist.
Rarely, but there are episodes of malignant degeneration of the neoplasm, which struck the corpus luteum in the left ovary or in the right.
About the work of the ovary
The ovary is a paired element of the female reproductive system. He is responsible for the development, formation of the body for the subsequent function of reproduction.
Here the eggs are stored and mature, the corpus luteum is formed. We can say that the ovary produces most of the sex hormones.
The ovaries function cyclically, from one ovulation to the next. The ovulatory period in gynecology includes:
- the release of the egg;
- moving into the fallopian tubes;
- gland formation.
The ovaries regulate the maturation of follicular elements in the second period of the menstrual cycle.
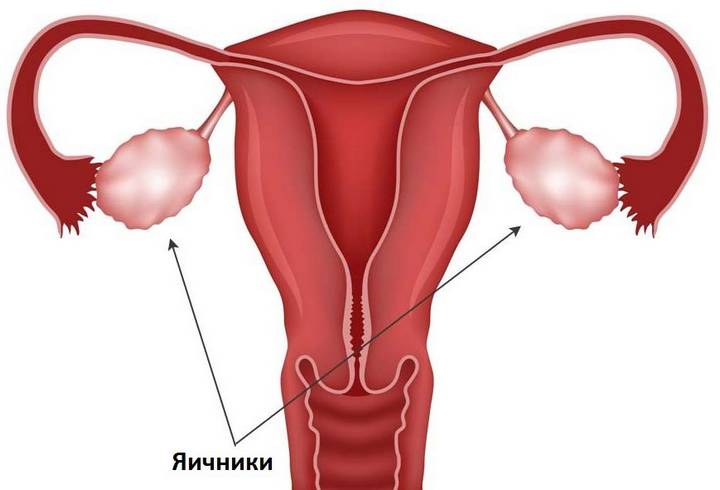
That is, 2 yellow bodies in one ovary cannot appear. As long as one gland functions, the maturation of the other is excluded.
progesterone plays essential role in a woman's body. This hormone is produced mainly by the gland and ensures reproductive health. Experts have identified the main functions of this substance:
- preservation of the fetus and prolongation of pregnancy;
- delayed development of other follicles;
- increase in the nutrition of the uterus with increased blood flow;
- build-up of the uterine mucosa for fertilization;
- participation in the development of the mammary glands;
- reducing the influence of immunity, due to which involuntary miscarriages are not able to occur.
A hormone may appear in the right amount only in a healthy structure. Normally, there is one gonad in the body.
But there are exceptions. For various reasons (due to chronic ailments, genetic abnormalities or environmental problems), the corpus luteum appears, but it is defective, it does not work correctly.
Since the follicles are not held back, a new ovulation occurs. A new gland matures.
A corpus luteum always forms during pregnancy, and we are talking about its full function.
Only a sufficient amount of progesterone during and after conception will allow you to safely endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
The corpus luteum is an indicator of a woman's reproductive health. It is he who is often searched for with ultrasound of the reproductive system.
The absence of the corpus luteum indicates that there was no ovulation. This can be a sign of infertility.
If these glands appear, a woman can be calm: her body is working normally, ovulatory processes are taking place in it.
Sometimes doctors can identify two corpus luteum in different ovaries. This phenomenon indicates the maturation of 2 eggs. This confirms a multiple pregnancy.
Every month, a woman's body undergoes cyclical processes aimed at the development, maturation and preparation of the egg for release from the ovary, where it must be fertilized and give rise to a new life. Through these processes, a woman is able to become a mother. If pregnancy does not occur, the egg dies, but if fertilization occurs, then a change in the hormonal background begins in the woman's body, aimed at preserving developing fetus.
Unfortunately, not every doctor considers it necessary to explain the results of an ultrasound scan to patients, not thinking that many entries in the study sheet simply frighten women and make them nervous. The corpus luteum during pregnancy is often perceived by women as a kind of deviation, especially in cases where the entry is accompanied by the word "cyst".
Ovulation in a woman of childbearing age occurs every month, on average every 21–35 days, when a mature egg leaves the follicle. If fertilization does not occur, then next month a new egg matures and the cycle repeats. But ovulation is not the only preparatory stage for the possible development of a new life in a woman's body.
After the mature follicle ruptures and the egg begins to move from the ovary to the uterus, a body begins to form from the cells of the follicle, which have a granular texture, called yellow because of the color of the substance inside it.
The corpus luteum during pregnancy is formed in the body of every woman, and is a temporary gland related to the endocrine system, the main function of which is the production of the necessary hormones - progesterone and estrogen.
The value of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
Progesterone is often referred to as the hormone of pregnancy because it is essential for the proper formation of gestational sac, its attachment to the wall of the uterus and further development child. It is the normal level of progesterone that creates favorable conditions for the onset of pregnancy and its development.
In addition, progesterone prepares the endometrium in the uterus for further growth, and also inhibits the contractile functions of the uterine muscles and the formation of new eggs.
It is progesterone that further stimulates the preparatory processes and the very production of milk by the mammary glands and prepares the woman for the process of bearing and giving birth to a baby, exerting the necessary influence on her nervous system.
A lack of progesterone in the body usually leads to some form of female infertility, since even a successfully fertilized egg cannot attach itself to the wall of the uterus. Decrease in hormone levels after pregnancy can lead to miscarriage early dates.
The production of progesterone is carried out precisely by the corpus luteum, and for this it is formed every month in the woman's body after the release of the egg from the ovary. The adrenal glands are also capable of synthesizing a small amount of the hormone, but it is not enough for the onset and development of pregnancy.
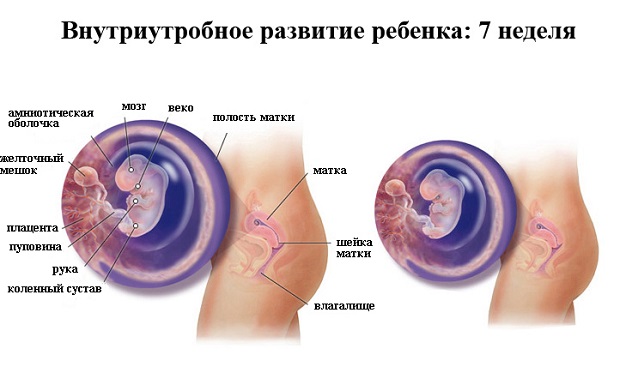
After formation, the corpus luteum develops rapidly, but its fate depends entirely on whether the egg is fertilized or not:
- If fertilization does not occur, then the corpus luteum continues to function for about two weeks, after which it dies and it is at this time that the woman begins her next menstruation.
- When pregnancy occurs, the active development of the corpus luteum and the production of the hormone continues until the period of 12-15 weeks, after which all the functions of this gland are transferred to the already formed placenta. Gradually, the activity of the corpus luteum ceases, and after the end of its existence, a small scar is formed in its place in the ovary, which has a whitish color.
Some women during ultrasound, having heard about the presence of a corpus luteum in the right or left ovary, perceive this as a kind of sign of pregnancy, believing that its formation is possible only in this case.
But the fact that there is a corpus luteum in the ovary only indicates that the maturation of the egg has occurred and the body is ready for conception and I am carrying a child. If there is no corpus luteum in the ovary, this is an indicator that there was no egg maturation in this cycle, which means that pregnancy is impossible.
The presence of a corpus luteum can become a sign of pregnancy only if, during an ultrasound scan before the start of the next menstruation, this gland is clearly visible in a certain one, for example, in the right ovary, and has pronounced dimensions that do not decrease.
The size of the corpus luteum during pregnancy is different, in the early stages its diameter does not exceed 15–20 mm, but gradually it increases to 27–28 mm, maintaining this indicator during normal pregnancy up to 15 weeks. After that, a gradual cessation of the main function and a decrease in size begin.
Pathologies in the development of the corpus luteum
There is also the concept of a corpus luteum cyst, when the size of the gland during pregnancy exceeds 30 mm, which is a pathology. But do not worry if, during an ultrasound scan, the doctor reports that there is a corpus luteum cyst in the ovarian cavity. Its presence will not affect the course of pregnancy and the health of a woman, since even with an increased size of iron, it produces progesterone.
The appearance of a cyst can be caused by various reasons, which most often include:
- constant stress;
- Availability bad habits or harmful working conditions of the expectant mother;
- extreme diets;
- diseases of the genital organs of an infectious type;
- taking hormonal drugs before pregnancy;
- the presence of functional disorders of the circulatory or lymphatic system of the ovaries.
As a rule, a corpus luteum cyst does not require special treatment, but a pregnant woman who has it will need additional monitoring of the condition of the gland and a strict limitation of physical activity.
You should not be afraid that a cyst can degenerate into a malignant formation, since such cases have never been seen in medical practice. The cyst usually does not cause discomfort and does not hurt.

However, if the doctor's requirements regarding the restriction of physical activity and sexual contacts are not followed, a rupture of the corpus luteum cyst may occur, which will require urgent surgical intervention to remove it. The rupture of the cyst is always accompanied by severe pain and severe bleeding, and if it is not removed, this can lead to infection of the internal organs.
Surgical intervention will also require torsion of the cyst stem, since this causes strong compression of the tissues, which can lead to their necrosis.
In some cases, when performing an ultrasound scan on a woman with an established pregnancy, doctors do not detect the presence of a corpus luteum. This happens when outdated equipment is used for early ultrasound, or when the study is performed by a doctor who does not have the necessary qualifications.
In this case, the woman needs to undergo an additional ultrasound in another clinic and, if the diagnosis is confirmed, the pregnant woman will need urgent medical care in the form of hormonal correction.
Another pathology is the insufficiency of the corpus luteum, which often leads to spontaneous abortion (miscarriage). With insufficient development of iron, it cannot produce progesterone in the amount necessary for the normal course of pregnancy, and in this case, the uterus does not allow the fertilized egg to implant and rejects it.
With an already onset pregnancy, insufficient progesterone levels greatly increase the risk of rejection of the developing fetus, as well as the appearance of placental insufficiency in the future.
Today, doctors successfully solve the problem of insufficient development and functioning of the corpus luteum, replenishing the missing amount of the hormone with special preparations, which allows saving many pregnancies. It is important to remember that going to the doctor in the earliest stages of pregnancy is the key to bearing a healthy baby.
Useful video about the corpus luteum cyst
I like!
Many women ask why they could have found a corpus luteum on an ultrasound scan, whether it is pregnancy or not, and how they should be with such a diagnosis. Let's figure it out.
What does the term itself mean?
The corpus luteum is not a disease. This is what is formed at the site of the burst follicle, from which the egg came out for fertilization (this process is called ovulation). While the egg is in free access for sperm, the corpus luteum secretes a special hormone progesterone, which prepares the entire body (in particular the uterus and mammary glands) for pregnancy. If it does not occur, the corpus luteum ceases to function, menstruation begins. It itself is replaced by a tissue similar to scar tissue, and acquires the name "whitish body". Hence the conclusion: the corpus luteum in the right ovary (it may also be in the left) is a temporary endocrine organ.
If pregnancy occurs
If the “efforts” of the corpus luteum were not in vain, it will remain in the ovary and will continue to produce progesterone, which is now needed to maintain pregnancy up to 10-16 weeks. Then the placenta will take over this function. That is, the option when there is a delay in menstruation and the corpus luteum is determined on ultrasound, most likely indicates that you are pregnant. This can be precisely recognized by the presence of the fetus, detected by ultrasound, by the increase in the uterus.
There is a corpus luteum on ultrasound, a negative test - what can this mean?
 If the doctor who held the delay in menstruation said that he does not see the fetus, but sees the corpus luteum, take a blood test from a vein for If its amount exceeds the norm, then you are pregnant, just the gestational age is quite short to see on ultrasound Moreover, Again, the corpus luteum on ultrasound is not a child, but a sign of pregnancy. A necessary organ that, before the formation of the placenta, is responsible for maintaining pregnancy.
If the doctor who held the delay in menstruation said that he does not see the fetus, but sees the corpus luteum, take a blood test from a vein for If its amount exceeds the norm, then you are pregnant, just the gestational age is quite short to see on ultrasound Moreover, Again, the corpus luteum on ultrasound is not a child, but a sign of pregnancy. A necessary organ that, before the formation of the placenta, is responsible for maintaining pregnancy.
If the corpus luteum on ultrasound is small, there is no menstruation, there is no fetus, and the test became positive?
The first thing that is recommended in this case is to redo the ultrasound from another specialist after a second examination by the gynecologist. If the result is the same (no fetus and small corpus luteum), then there may be a complication of pregnancy such as hydatidiform mole.  It occurs in 1 in 2 thousand pregnancies, the diagnosis means that instead of forming a normal placenta, peculiar villi and vesicles form from its tissue. In this case, the fetus may not be. But it should be visible on ultrasound. It is imperative to treat it, as this situation can result in profuse bleeding.
It occurs in 1 in 2 thousand pregnancies, the diagnosis means that instead of forming a normal placenta, peculiar villi and vesicles form from its tissue. In this case, the fetus may not be. But it should be visible on ultrasound. It is imperative to treat it, as this situation can result in profuse bleeding.
Its normal size is 12-20 mm in diameter before pregnancy. Upon its onset, the corpus luteum increases to 30 mm. If there is a pregnancy, and the corpus luteum is 10 mm or less, this indicates that the woman needs to be given synthetic progesterone to maintain the pregnancy (for example, the drug "Utrozhestan"). Dimensions of more than 30 mm (this is called does not indicate that there is an excess of this hormone. Therefore, if the pregnancy is desired, it makes sense to determine its level in the blood, and then proceed from the situation. Usually, the cyst does not affect the pregnancy in any way and resolves itself. It should only avoid extremely active sex so that the cyst does not burst.
The onset of pregnancy entails many changes in a woman's body. Most of them are associated with the launch of new biochemical processes that are responsible for healthy development fetus. One of important changes in the reproductive organs - the corpus luteum during pregnancy. This temporary endocrine organ has another name - the luteal gland.
What is the corpus luteum
Many mistakenly believe that the corpus luteum is a sign of pregnancy. In fact, this additional gland appears every month at the site of a burst follicle, from which a full-fledged egg was released. With the onset of menstruation, the corpus luteum in the ovary completely ceases to function and dies. The gland got its main name due to its characteristic color, and the second - due to the content of the hormone luteotropin.
If fertilization occurs during ovulation, the luteal gland continues to produce the hormones progesterone and estrogen necessary for the full development of pregnancy. They are released for 13-15 weeks until a fully formed placenta takes over this function. The development of the gland occurs in four successive stages:
- After ovulation, the cells of the burst follicle begin to multiply intensively.
- There is a germination of blood vessels in the tissue of the uterus.
- Stage of hormonal activity and growth of the gland.
- Phase of reverse development, gradual death and formation of a whitish body (scar).
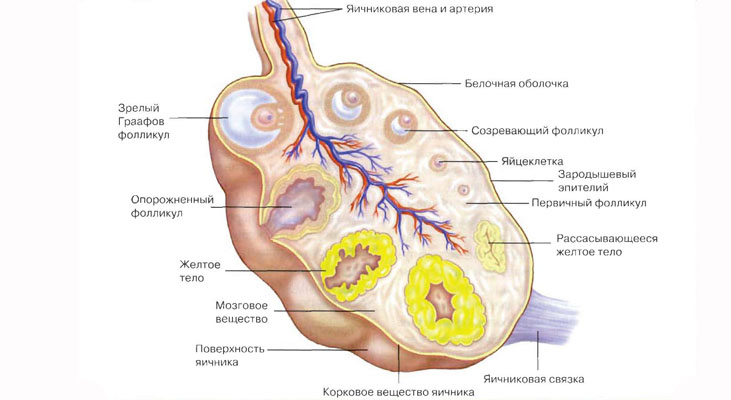 Cross section of a woman's ovary throughout a cycle
Cross section of a woman's ovary throughout a cycle Dimensions of the corpus luteum
The size of the corpus luteum in early pregnancy will depend on the amount of hormones produced. The larger the area of the gland, the higher the level of hormonal activity. In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the normal size of the gland is 18-20 mm, which means that it is fully ready for fertilization.
20-30 mm is the norm of the corpus luteum during pregnancy during the first trimester after conception. If such dimensions were found in the absence of pregnancy, it means that a liquid formation has formed in the follicle, which eventually regresses on its own.
A gland more than 30 mm already indicates the presence of a corpus luteum cyst in early pregnancy. This is a benign neoplasm that does not harm either the expectant mother or the child. In most cases, it resolves on its own by the middle of the second trimester of pregnancy. If the corpus luteum bothers or hurts in the early stages of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor to prescribe painkillers.
If, as a result of the diagnosis, the luteal gland was not detected, this does not mean at all that the size of the corpus luteum in early pregnancy is below normal. Perhaps the study was carried out on outdated equipment that does not have sufficient functionality to represent the real situation.
Diagnostics
When conducting an ultrasound of the ovaries, the corpus luteum is sighted in the following cases:
- monitoring the process of ovulation when planning a pregnancy;
- in the first trimester;
- with infertility;
- in the diagnosis of cystic corpus luteum.
The specialist necessarily measures the size of the gland, its volume, as well as density. All indicators are recorded in the form of expert ultrasound screening.
Pathology
The main pathology of the luteal gland is hypofunction of the corpus luteum. As noted above, this small endocrine organ produces two types of hormones - progesterone and estrogen.
 Thanks to the first, the muscle tissues covering the spiral arteries of the uterus atrophy. The uterus ceases to respond with contractions to various factors, chemical and physical changes in the body of a pregnant woman. As a result of these changes, blood flow to the placenta and embryo is maintained at a normal level. Estrogen helps the fertilized egg to firmly attach to the inner wall of the uterus. It prepares the uterine epithelium, makes it looser, reducing the risk of miscarriage in the early stages.
Thanks to the first, the muscle tissues covering the spiral arteries of the uterus atrophy. The uterus ceases to respond with contractions to various factors, chemical and physical changes in the body of a pregnant woman. As a result of these changes, blood flow to the placenta and embryo is maintained at a normal level. Estrogen helps the fertilized egg to firmly attach to the inner wall of the uterus. It prepares the uterine epithelium, makes it looser, reducing the risk of miscarriage in the early stages.
What threatens the hypofunction of the gland
With hypofunction of the gland, the process of hormone production is disrupted, as a result of which the body can perceive the fertilized egg as a foreign body and begin to reject it. Clinically, this manifests itself in placental insufficiency.
The negative consequences of gland hypofunction are:
- rejection of a fertilized egg;
- pregnant;
- puffiness;
- increased levels of protein in;
- premature birth.
To save the fetus, the attending physician prescribes progesterone replacement therapy.
yellow body at ectopic pregnancy produces much less hormones. This can be detected in the early stages after testing for hCG. By tracking the growth dynamics, you can calculate the risk of complications.
What to do if the corpus luteum has not formed
The course of pregnancy without a corpus luteum is also accompanied by hormonal therapy. For the full development of the embryo, you will need a full course of the hormone, or its plant analogue in the dosage form.
Some women complain that their corpus luteum hurts during pregnancy. Unpleasant sensations can occur during heavy physical exertion, as well as during sexual intercourse. In this case, it is recommended to reduce activity, otherwise the cyst may rupture.
In order to avoid pathologies associated with abnormal development or functioning of the corpus luteum, it is recommended to reduce activity and physical activity in the first three months of pregnancy.
A quiet, measured lifestyle will help you bear a healthy, beautiful and, most importantly, long-awaited child!
