There is an opinion among the population that the large weight of the fetus speaks of health and strength, but only mothers who have given birth to "heroes" and doctors know what difficulties they have to face during childbirth and after the birth of a child. According to the statistics, the birth big baby observed in 5 - 10% of all births.
Definition of concepts
They talk about a large fetus or macrosomia when its fetometric indicators prenatal development significantly exceed the established norm for a particular period of pregnancy, or the weight of the newborn is 4 kg or more. In addition to the weight of the child, his height is also taken into account, for example, in a normal baby, growth is in the range of 48 - 54 cm, while the length of a fetus with a large weight is 54 - 56 cm, and in some cases reaches 70 cm.
If the house has musical instruments, even toys, it's not too late to learn the sounds that can be produced with them - but let me be solitary, with a pause. Another appropriate period of play is to "walk" the toy from left to right and back slowly towards his face so that she turns on object tracking with her eyes and rolls her head. This game next month will help him in his attempts to reach and catch the toy with his hands.
Attempts to deny night time should be successful, and the child should sleep for a long time at noon at night. The second reception of these immunizations occurs in the third month, the third, last reception - in the fourth month. In the first month outside the maternity hospital, it is necessary to carry out immunization against hepatitis B, the second intake.
If the weight of the child at birth is 5 kg or more, then they speak of a giant fetus. The birth of giant children is less common than large ones, and has a ratio of 1/3000 births.
Causes
Why a child is born large is explained by many reasons, which can be due to both the characteristics of the woman's body and the individual characteristics of the baby developing in the uterus. These factors include:
During the tenth week of pregnancy, your baby's brain develops very quickly. For its proper development, it is mainly necessary to supply iron. Find out what foods you'll find in the gland and why it's so important to your child's future health.
What is going on inside your body?
Just like the week of pregnancy, your uterus is still growing steadily. It is now double the size of the pre-pregnancy period and about the size of a grapefruit. At the same time, the development of the placenta continues with the umbilical cord associated with the fetus. If you are expecting your first child, pregnancy is unlikely to be visible, but you may feel more tired than usual. Your heart rate increases and your metabolism speeds up. At the same time, you may experience fever and sweating.
genetic predisposition
It is noted that heredity also plays a role in the birth of a large child. Physically developed and tall parents have a greater opportunity to produce a large baby.
Increasing the duration of pregnancy
Normally, pregnancy lasts 38 - 41 weeks (see). If the gestational age exceeds the upper limit of the norm, they talk about over-pregnancy, which can be true and false. With true overwearing, a child is born with obvious signs of overwearing: dry, without original lubrication of the skin, its wrinkling, waters have a greenish or grayish tint, and their number is reduced. Such phenomena are explained by the aging of the placenta, the formation of multiple calcifications in it, and a decrease in its functions. The lack of oxygen and nutrients leads to the development of placental insufficiency, hypoxia and even fetal hypotrophy.
Your baby's development in the week of pregnancy
The head continues to evolve to make room for the brain and is still disproportionately large compared to other parts of the body. They can already see the baby's ear canals. Your child can also bend their elbows to help develop the muscles. It can also twist fingers that are already separated. If you could look inside, you could see how the baby's spine is clearly visible on the skin.
The baby is more active at this stage of the day and divides his stay in the mother's belly into sleep and wakefulness. Keep in mind the supply of high quality nutrients your baby receives during pregnancy as this will affect how her cells will be programmed in the future. This knowledge is the basis of nutrition programming in early age to tell you which foods and nutrition to focus on.
Diabetes in a woman
The birth of a large baby (or on ultrasound more than the gestational age) may be due to the presence of diabetes in the mother or its development during gestation (gestational diabetes). Children are born with a number of characteristic signs, which is called diabetic fetopathy. The large weight of the fetus is the result of hormonal storms and constant jumps in the level of glucose in the woman's blood. A characteristic sign of diabetic fetopathy is excessive weight gain in the baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy against the background of developing polyhydramnios. Accordingly, the child, although born large, is initially unhealthy. Pregnant women with diabetes are hospitalized no later than 32 weeks, examined and decide on the timing and methods of delivery.
How can you help your child to be healthy?
The main substance for proper development baby is a week pregnant. It is involved in the formation of hemoglobin, which forms red blood cells. They provide oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. iron plays important role for your child. If you don't have enough iron in your diet, you may be at risk of developing anemia, which is most common in the last third of pregnancy. Its symptoms manifest as fatigue, weakness, pallor, and the like. If you suffer from anemia and have not managed it, your baby may be born with a low birth weight.
Rh-conflict pregnancy
One of the reasons that determine the size of the fetus over the term is. This complication of gestation occurs when a child with a positive Rh factor is born by a woman who has a negative Rh factor. As a result, the unborn child develops a hemolytic disease, which is characterized by anemia and jaundice, and in extremely severe forms, swelling joins them, which is called the edematous form of hemolytic disease. At the same time, fluid accumulates in the fetal cavities (abdomen, chest), and the liver and spleen increase significantly in size. Massive edema and hepatosplenomegaly determine the large weight of the child.
If you want to provide enough iron for your body, you must eat
Red meat fish and seafood Eggs Legumes Brewer's yeast Fruits Whole grains and wheat germ Vegetables Pumpkin and sunflower seeds Almonds Cacao. Then don't miss the next weeks of pregnancy. We will send them to you regularly, just enter your email.
Equally important is vitamin C, which helps the body absorb iron. Add a glass of orange juice or fresh fruits for your lunch or snacks. In a large amount of vitamin C, there are, for example, strawberries, blackcurrants, red peppers or broccoli. If you still have blood, it is likely that your doctor will recommend that you use an iron supplement.
Features of the placenta
The structural and functional features of the placenta can also provoke the formation of a large baby (see also). Often, at the birth of a child with a large body weight, a placenta of large size and thickness (5 cm or more) is noted. A thick and massive placenta promotes an intensive exchange of nutrients and microelements, which accelerates the development of the fetus. In addition to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and intensive blood supply to the child, there are bursts of placental hormones, which indirectly affect the metabolism in the mother's body and enhance the growth and development of the baby.
A normal pregnancy lasts 9 months, i.e. 38 to 42 weeks. This period is divided into three trimesters. The pregnancy calendar describes the course of pregnancy week by week. This allows the expectant mother to observe the development of the child and understand the changes that occur in her body.
Pregnancy is an extraordinary experience for every woman. During a woman's body, many changes occur. The first trimester of pregnancy, which lasts from fertilization to the week of pregnancy, has great importance for the proper development of the child. During this period, the mother may often be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as morning sickness, vomiting, and insomnia. The first three months of pregnancy is the time when all the internal organs of the baby are born, and the heart begins to work. At the end of the first trimester developing child begins to resemble a miniature person.
Subsequent pregnancies ending in childbirth
A directly proportional relationship was noted between the number of births and the body weight of children born. After the second, third, and so on, a large fetus is formed, which is about 30% larger than the size and weight of the firstborn. Doctors explain this fact in two ways.
- Firstly, the psychological factor matters, a woman, bearing a second / third child, is familiar with the processes of pregnancy and childbirth, is more balanced and calm.
- Secondly, the large size of the baby during subsequent pregnancies is due the best conditions intrauterine nutrition due to the developed circulatory network in the uterine wall.
- Also, the conditions for intrauterine growth and development of the second child are much better due to the greater extensibility of the uterus and slight resistance of the abdominal muscles.
The nature of the nutrition of a pregnant woman
An important role in the increase in the weight of the child is played by the nutrition and lifestyle of the woman, especially after the 20th week of pregnancy (see). Hypodynamia, a growing belly, a passion for high-calorie foods (consumption of muffins, sweets, pasta) leads not only to the accumulation of fatty tissue in future mother, but also provokes macrosomia in the fetus (see).
How is pregnancy in the first trimester, the most important period in a child's development?
It has a weight of about 14 grams and a height of about 6 centimeters. The week of pregnancy is supposed to start on the first day of the last menstrual cycle, so it is important for a woman to follow her menstrual calendar regularly. The week of pregnancy is the time when a woman's body is preparing for fertilization. During this period, ovulation occurs, which involves the release of an egg from Graaf's follicles, which is ready to be fertilized by sperm. During the week of pregnancy, the spermatozoa combine with the semen, which means that they are fertilized, but at this time a pregnancy test should not be performed - it is too early.
Obesity
Excessive weight of the expectant mother also plays a role. This is due not only to poor nutrition of the pregnant woman, but also to impaired lipid metabolism in her body, which provokes a violation of the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the fetus, intrauterine damage to the liver and pancreas, and activation of compensatory reactions in the placenta. All these factors contribute rapid growth and increased fetal weight. In the case of obesity of the 1st degree, a large fetus is born in 28% of pregnant women, with the 2nd degree, the probability of a large child increases to 32%, and with the 3rd degree, up to 35%.
Pregnancy is possible within a week when the hormone - placental gonadotropin reaches a detectable concentration in the woman's urine. Within a week, some women, especially during their first pregnancy, experience hormonal changes that take place in the body. There may be slight bleeding from the vagina, called implant bleeding, which is associated with the implantation of uterine embryos, reduced abdominal pain, fatigue, and irritability. Within a week, most women begin to suspect pregnancy, which signals a missed period and decides to perform a pregnancy test.
Taking medications
Uncontrolled consumption of certain drugs by a pregnant woman, which improve uteroplacental circulation and activate anabolic processes (for example, gestagens,) also contribute to weight gain.
Other factors
The age of a woman (under 20 or over 34 years old), the presence of inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system, can also affect the size.
In the brain and nervous system of the embryo, limbs, atria and ventricles develop and the face is formed. At the end of the week, the embryo reaches a body length of about 2 millimeters. The week of pregnancy is very important for developing child- at present it is especially vulnerable to various harmful factors. During this time, women often develop morning sickness. Make sure you drink plenty of water and avoid spicy and tasty foods.
How to identify a large fetus during pregnancy
During the week of pregnancy, a woman may begin to gain weight, although not in every mother's future. In the body of the uterus, changes are taking place that are necessary to create an optimal environment for growth and development. During this period, the circulatory system mainly affects the internal organs, increasing blood flow. A woman may feel drowsiness, fatigue, sometimes fainting. During the week of pregnancy, the development of the mammary glands begins, therefore female breast may become sore and swollen. The child during this period has a length of about 2 centimeters.
Large fruit: signs and diagnosis
If a woman has a large belly during pregnancy, this is not necessarily evidence of a large child. Multiple pregnancy should be excluded and (many pregnant women neglect the passage of ultrasound during such an important period of life).
By 38 weeks of pregnancy, and sometimes even earlier, the clinical manifestations of a large fetus are objective data obtained during a visit to an obstetrician. At each appearance in the antenatal clinic, a pregnant woman is measured body weight, an increase of 500 grams. weekly, against the background of absent edema and other signs of gestosis, makes the doctor suspect a large weight in the baby.
Starting to develop arms and legs. week - the beginning of the third month of pregnancy. Lungs, liver, kidneys, blood and digestive tract of the child. The skeleton, made of gelatinous cartilage, is already fully formed. In the week of pregnancy, the baby reaches about 4 centimeters in length and has all the organs. Most women begin to experience nausea, nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness as the body adjusts to hormonal changes. During this period, the fetus may begin to move its arms and legs, but the movements are too weak to feel like a woman.
In the case of a large fetus during pregnancy, the signs are determined by the size of the woman's abdomen (circumference and height of the fundus of the uterus), evidence of this is the exceeding dimensions: The circumference of the abdomen is more than 100 cm, and the height of the fundus of the uterus is more than 40.
The estimated weight of the fetus is calculated by the formula: coolant is multiplied by VDM.
Since a baby with a large weight in utero takes up more space, the internal organs of a woman are subjected to greater compression and infringement and experience a significant load. As a result, the pregnant woman notes frequent urination, heartburn (reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus), constipation and shortness of breath. A large uterus presses on the inferior vena cava, which can provoke fainting in a horizontal position lying on your back. The load on the musculoskeletal system increases, which is manifested by pain in the legs, lower back, spine and ribs. Possible occurrence or worsening of the course of varicose veins of the legs. Also, there is a high probability of stretch marks on the abdomen and an increase in the tone of the uterus.
During pregnancy, the doctor of the pregnant woman must evaluate the anatomy of the fetus, its head, limbs, spine, heart, etc. the baby weighs about 8 grams and is 5 centimeters long. The risk of abnormal pregnancy, miscarriage and fetal death is greatly reduced during pregnancy. There is better mental and physical well-being.
The second trimester is the most enjoyable pregnancy for most pregnant women. The expectant mother has much better mood, because she has passed the first, most dangerous period of pregnancy for the child. At the same time, the fruits develop their senses. At the end of this trimester, the baby reaches about 40 centimeters and weighs about 1 kilogram.
Ultrasound is of great importance in the diagnosis of a large fetus, with a thorough measurement of the fetal data of the fetus and the determination of its estimated weight. The circumference of the head and abdomen, the length of the femur and humerus are measured. A large head and a significant size of the abdomen, an increase in the liver and spleen, the identification of fluid in the body cavities indicates an edematous form of hemolytic disease.
From the week of pregnancy, a woman begins to regularly gain weight. The child's body becomes sensitive to touch, and his movements are coordinated. At the week of pregnancy, the baby weighs about 75 grams and is 11 centimeters long, and some mothers can determine the sex of the baby. Women may experience increased vaginal discharge and mild pain in the lower abdomen.
The first movement of the baby begins to be felt by expectant mothers around the week of pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman should keep a close eye on her body, as pregnancy disorders such as gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced hypertension are common during this time. Within a week, the woman's stomach is already clearly rounded, and the mother's future clearly feels the movements of her child. In a week of pregnancy, the baby measures about 30 centimeters and weighs 45 grams. The next week of pregnancy may be associated with heartburn, frequent urination, constipation, or back pain.
The course of pregnancy
Pregnancy in women with a large fetus proceeds, as a rule, without complications. All the described complications (fainting, problems with the digestive tract and shortness of breath) develop by 38-40 weeks of pregnancy with a large fetus. There is a high probability of developing placental insufficiency and progressive hypoxia as a result of a discrepancy between the uteroplacental blood flow and the rapidly increasing weight of the child. Pregnancy features include:
Women, especially birthdays, are often accompanied by fears about the future. Stretch marks can develop on the abdomen, which are the result of cracking of the skin. It is advisable to use specialized stretch marks. During the third trimester, a woman may experience severe back pain. On many occasions I have calf cramps, swollen legs and varicose veins. The fetus is more like a newborn. During this period of intensive development of the brain. At the end of the third trimester, the child reaches a weight of 2.5 to 3.6 kg.
As he gets bigger and bigger, his movements become limited and therefore less frequent. During the last trimester of pregnancy, a woman may experience soreness in her ribs and difficulty breathing. In a week of pregnancy, the baby measures about 37 centimeters and weighs about 1.2 kilograms. During this time, the calming effect on the baby, whose quick movements and footwork can cause pain in the expectant mother, is relaxing music. The third trimester, especially its last weeks, can be very difficult for a woman.
- a thorough examination to exclude polyhydramnios and;
- exclude diabetes mellitus - conducting and consulting an endocrinologist;
- calculation according to ultrasound data and the size of the pregnant belly of the estimated weight of the fetus;
- physiotherapy;
- diet correction (exclude easily digestible carbohydrates and refractory fats);
- cancellation or restriction of taking drugs - anabolics.
The course of childbirth
“How to give birth if the fetus is large?” - expectant mothers ask a question. The answer is not the course of childbirth, which, with large sizes, have their own characteristics. Spontaneous childbirth of a child of considerable size is often complicated by the following circumstances:
Clinically narrow pelvis
This complication develops when the fetus has a large head, and even with full disclosure (10 cm) of the uterine os, it does not advance, which is called a mismatch in the size of the head to the woman's pelvis. It is characteristic that the size of the maternal pelvis may be within the normal range, but still, childbirth is difficult even with good and strong contractions. If there is also an anatomical narrowing of the pelvis (the size of the pelvis is shortened by 1-1.5 cm or more), the question of a caesarean section is raised.
Untimely outpouring of waters
Early discharge of water (before the opening of the pharynx by 8 cm) is due to the high standing of the baby's head, so due to its large size it cannot press against the entrance to the small pelvis and move forward, and there is no separation of water into the anterior (fetal bladder) and posterior ones. Early outflow of water is dangerous by prolapse of the umbilical cord or small parts of the child (leg, handle). In addition, this complication slows down the process of opening the uterine os, which lengthens the 1st period of labor and exhausts the woman in labor. If the anhydrous interval continues for 12 hours or more, the risk of the uterus is also high. If the umbilical cord or part of the fetus falls out, immediate operative delivery is indicated.
Anomalies of tribal forces
Childbirth with a fetus of large size is often complicated by anomalies of labor activity. A protracted course of childbirth leads to a decrease in the intensity and frequency of contractions (weakness of the birth forces develops, both primary and secondary). The child begins to suffer, intrauterine hypoxia increases (at first it becomes more frequent - tachycardia, then it slows down - bradycardia), which is also an indication for caesarean section.
Threat of uterine rupture
The straining period of childbirth with a large child is also fraught with danger. In the process of passing the fetal head through the birth canal, it is configured, that is, it acquires a shape that is convenient for overcoming the planes of the small pelvis (the bones of the skull "layer" on top of each other). With a disproportionate size of the baby's head and the mother's pelvis, the lower uterine segment is overstretched, which threatens to rupture it.
Fistula formation
Due to the prolonged standing of the baby's head in the same plane of the pelvis, the soft tissues of the birth canal (cervix and vagina) are compressed, but in addition to them, the bladder and urethra in front and the anus in the back are also compressed. This leads to impaired blood circulation in the tissues, ischemia, and then necrosis (necrosis). Necrotic tissues are shed after childbirth and genitourinary and/or rectovaginal fistulas are formed.
Rupture of the pubic joint
Difficult passage of the baby's head can damage the pubic articulation (rupture of the ligaments and divergence of the pubic bones), which often, especially in severe cases, requires surgical intervention after childbirth (see).
Shoulder dystocia
Childbirth with a fetus with a large weight can be complicated by difficult removal of the shoulders, which is typical for children with diabetic fetopathy (the size of the shoulder girdle is much larger than the size of the head). In this situation, special benefits are provided, which can result in fractures of the clavicle, humerus or cervical spine.
Cephalohematoma or cerebral hemorrhage in the fetus
The development of such complications is due to anomalies of the birth forces, disorder and subsequent. When the head is configured, there is an excessive displacement of the cranial bones and a sharp compression of them, which causes hemorrhage in the brain or under the periosteum.
Birth management
In the case of the diagnosis of a large fetus, what will be the delivery: operative (caesarean section) or through the natural birth canal (spontaneous birth) depends on many factors. Carrying out the planned:
- large size of the fetus in women under 18 and over 30 years of age;
- combination of breech presentation and a large child;
- prolongation of pregnancy with a large child;
- anatomical narrow pelvis, regardless of the shape and degree of narrowing, and the large weight of the child;
- anomalies in the development of the uterus, myomatous nodes and a large fetus;
- indications requiring the exclusion of the straining period (cardiovascular pathology, high myopia) and a large child;
- large fetal weight and aggravated obstetric history (birth of a dead child in the past, and the use of assisted reproductive technologies).
A caesarean section for emergency indications is performed for any complication during childbirth (threatening uterine rupture, improper insertion of the head, etc.).
In the first 2 hours after childbirth (early postpartum period), there is a high risk of developing hypotonic uterine bleeding, which is due to prolonged labor and excessive uterine distension.
When drawing up a plan for childbirth through the birth canal, take into account:
- childbirth should be carried out under the monitoring control of the child's condition and;
- in childbirth, it is obligatory to maintain a partogram (drawing up a schedule taking into account the time of each period of childbirth, disclosure of the uterine os, intensity of contractions);
- during childbirth, re-measure the size of the pelvis;
- adequate and timely anesthesia and the introduction of antispasmodics;
- in the pushing period, prophylactic administration of reducing agents in order to prevent weakness of attempts;
- early diagnosis of a clinically narrow pelvis;
- prevention of bleeding in the afterbirth period and in the first 2 hours after childbirth.
Children born with a weight of 4 kg or more are at high risk for morbidity and mortality at an early neonatal age (up to 28 days of life), the development of birth injuries (cephalohematoma, cerebral hemorrhage, fractures of the shoulder, collarbone), the development of metabolic disorders and pathology of the central nervous system.
Question answer
Is hospitalization necessary before delivery when pregnant with a large fetus?
Yes, all women diagnosed with a large baby are advised to go to the hospital in advance, at 38-39 weeks. The doctor will carefully measure the size of the pelvis and abdomen, assess the condition of the pregnant woman (the presence of extragenital diseases and complications of pregnancy), the readiness of the cervix (maturity) and draw up a plan for the management of childbirth. And if there is evidence, the decision on the issue of a planned caesarean section and preparation for it.
How can the development of a large fetus be prevented?
First of all, it is necessary from the first days of pregnancy to adhere to rational nutrition. Food should contain the necessary amount for a pregnant woman of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The expectant mother should give up overeating, excessive passion for sweets, pastries, fatty and fried foods, and if the condition allows, do special exercises for pregnant women and avoid hypodynamia (frequent and prolonged lying and sitting).
This is my first pregnancy and I have a large fetus. Will I have to have a caesarean section?
No, it is not necessary at all, especially in the first childbirth of young women. Most often, pregnancy and the birth of a large fetus in young healthy women proceed without complications and end happily.
Obstetrician-gynecologist Anna Sozinova
Many believe that if the unborn child has a large weight, then this indicates that he will be born strong and healthy, but only doctors and "mothers" who gave birth to such heroes know how dangerous such childbirth can be and what difficulties can arise in the process of the birth of large fruits. According to statistics, the birth of a large child occurs in 5-10% of all cases of childbirth.
Definition of concepts
They say about macrosomia or a large fetus when there is a significant excess of its fetometric indicators, compared with the norms for each specific period of pregnancy, or when the mass born child is over 4 kilograms. In addition to the weight of the newborn, their height is also taken into account. So growth normal child is in the range from 48 to 54 centimeters, while the length of the fetus, which has a large weight, is 54-56 centimeters, in some cases children are born with a height of 70 centimeters.
If the mass of a newborn child is 5 kg or more, then we are talking about the giant fruit. The birth of giant children is much less common than large children and accounts for 1/3000 cases.
Causes
The birth of a large child can be explained by many reasons, among which an important role is played by the characteristics of the mother's body, as well as the individual characteristics of the child developing in the mother's uterus. Among these factors are:
genetic predisposition.
It is noted that essential role in the birth of a large child, heredity plays. Parents who are tall and physically well developed are more likely to reproduce a large baby.
Increase in the duration of pregnancy.
Pregnancy normally lasts from 38 to 41 weeks. Subject to an increase in the gestational age relative to the upper limit of the norm, doctors talk about overwearing, which can be both false and true. With a true prolongation of pregnancy, the child after birth has characteristic signs: wrinkling and dryness of the skin (lack of original lubrication), the amount of water is reduced, and their hue ranges from grayish to greenish. Such manifestations can be explained by the aging of the placenta, its multiple calcification, and decreased functions. Lack of nutrients and oxygen leads to the development of hypoxia, placental insufficiency, and in some cases even fetal hypotrophy.
The presence of diabetes in the mother.

The birth of a large baby (or the reflection of a larger fetus from the estimated gestational age during an ultrasound examination) may be caused by the presence of diabetes in the expectant mother or the development of diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes). In women diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, children are born with characteristic features, which in gynecology is called diabetic fetopathy. The large weight of the child comes from the presence of constant jumps in glucose levels and hormonal storms in the mother's body. A characteristic symptom of diabetic fetopathy is excess weight gain in the baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy, which occurs against the background of developing polyhydramnios. As is clear from the above, the child, although born large, is already unhealthy. Pregnant women with diabetes are hospitalized up to 32 weeks and after the examination they decide on the methods and timing of delivery.
Rh-conflict pregnancy.
One of the reasons for the appearance of a large fetus is the presence of an Rh-conflict pregnancy. Such a complication of pregnancy occurs when a child who has a Rh positive is born by a woman with a negative Rh. As a result, the child gets a hemolytic disease, with anemia, jaundice, characteristic of the pathology, and in especially severe cases, swelling also joins these symptoms. This is called the edematous form of hemolytic disease. In the cavities of the fetus (thorax, abdomen) there is an accumulation of fluid, and the spleen and liver of such children have a significant increase in size. Hepatosplenomegaly and massive edema determine the presence of a large weight in a child.
features of the placenta.

The presence of functional and structural features of the placenta can become the cause of the formation and birth of a large child. Often the birth of a baby with a large weight coincides with the presence of a thick (more than 5 centimeters) and large placenta. A massive and thick placenta increases the intensity of the metabolism of microelements and nutrients, which leads to accelerated development of the fetus. In addition to an increase in the intensity of the child's blood supply and the volume of circulating blood, there are bursts of placental hormones that indirectly affect the metabolism in the mother's body and enhance the development and growth of the baby.
Subsequent pregnancies that end in childbirth.
Celebrate right proportional dependence on the number of births and the weight of children born. After the second and third births, as well as further, the formation of a large fetus occurs, which is approximately 30% larger than the weight and size of the firstborn. Doctors explain this fact by the presence of such moments:
firstly, there is a psychological factor, a woman who is carrying a second, third, and so on child is already well acquainted with all the features of pregnancy and, accordingly, is more calm and balanced;
secondly, the large size of the fetus during subsequent pregnancies may be due to improved intrauterine nutrition, since the circulatory network of the uterus after the first birth is more developed;
also, more favorable conditions for the development of a second child can be explained by the fact that the uterus is in a more stretched state, and the abdominal muscles have little resistance.
The nature of the nutrition of a woman in position.

A significant role in the process of increasing the weight of the child is also played by the lifestyle of a woman and the nature of her diet, this is especially true after the 20th week of gestation. Hypodynamia, abdominal growth and the use of a large number of high-calorie foods (pasta, sweets, muffins) leads to the accumulation of fatty tissue, and also provokes the development of macrosomia in an unborn child.
Obesity.
Excessive weight of a woman during and before pregnancy also plays a role. This may be due not only to the lack proper nutrition, but also caused by a violation of lipid metabolism in the body, respectively, this leads to a violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the fetus, intrauterine damage to the pancreas and liver occurs, and the compensatory functions of the placenta are activated. These factors together contribute to weight gain and fetal growth. If a woman has obesity of the first degree, then the birth of a large fetus is observed in 28%, in the presence of a second degree of obesity, this figure rises to 32%, and if there is obesity of the third degree, the probability of having a large child is 35%.
Reception medicines.
![]()
Uncontrolled use of certain drugs by a pregnant woman, which activate anabolic processes and improve uteroplacental circulation (for example, Actovegin, Gestagens) can cause an increase in fetal weight.
Other factors.
The age of the expectant mother (under 20 years old or over 34 years old), cycle disorders, the presence of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system and genital organs can also cause an increase in the size and weight of the fetus.
Large fetus: diagnosis and signs
If a woman has a large belly during pregnancy, this is not necessarily evidence of a large fetus. In such cases, it is necessary to exclude the presence of multiple pregnancy and such a feature of gestation as polyhydramnios (a large percentage of women neglect ultrasound even in such an important period of their lives).
By the beginning of the 38th week of pregnancy, and in some cases even earlier, signs of the presence of a fetus big size are objective data that are recorded during regular visits to the antenatal clinic. The main indicators include weight measurement, weight gain of 500 grams per week; in the absence of edema and other manifestations of gestosis, they are a reason for suspicion of the presence of a large fetus.
With a large fetus during pregnancy, the signs are determined on the basis of measurements of the woman's abdomen (bottom height and uterine circumference), confirmation of suspicions for a large fetus are indicators: the height of the fundus of the uterus is more than 40 and the abdominal circumference is more than 100 cm.
Since a fetus with a large weight in utero takes up much more space (compared to a normal fetus), the internal organs of a woman are subjected to infringement and compression, and the load on these organs increases. This leads to the occurrence of such phenomena as shortness of breath, constipation, heartburn (due to the reflux of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus), and frequent urination. Due to the increase in the size of the uterus, additional pressure appears on the inferior vena cava, as a result, the likelihood of developing fainting conditions while lying on your back in a horizontal position increases. The load on the musculoskeletal system increases, this load is manifested by pain in the ribs, spine, lower back, legs. The course of varicose veins of the lower extremities may occur or be aggravated. There is also a high probability of an increase in the tone of the uterus and the appearance of stretch marks on the abdomen.
A huge role in diagnosing the presence of a large fetus in a woman is played by ultrasound diagnostics, which allows you to carefully measure the fetometric data of the embryo and establish its estimated weight. Measure the length of the humerus and femur, the circumference of the abdomen and head. The significant size of the abdomen and a large head, enlargement of the spleen and liver, the presence of fluid in the body cavities of the child indicate the presence of an edematous form of hemolytic disease in the fetus.

The course of pregnancy
The course of pregnancy in women with a large fetus usually passes without significant complications. The complications described above (shortness of breath, problems with the digestive tract, fainting) occur at 38-40 weeks during pregnancy with a large fetus. There is also a high probability of progressive hypoxia and placental insufficiency against the background of a discrepancy between the rapidly increasing fetal weight and the rate of uteroplacental blood flow. Features of conducting such a pregnancy include:
limiting or canceling the use of anabolic drugs;
diet correction (exclusion of refractory fats and easily digestible carbohydrates);
physiotherapy;
calculation according to the size of the belly of the pregnant woman and the ultrasound data of the estimated weight of the child;
consultations with an endocrinologist and a glucose tolerance test to exclude diabetes mellitus;
a thorough examination to exclude multiple pregnancy and polyhydramnios.
The course of childbirth
Many expectant mothers ask themselves: “How to give birth if the fetus is large?”. The answer to this question is the nature of the course of childbirth, which, in the presence of a large fetus, has its own characteristics. Spontaneous childbirth in the presence of a large fetus is often complicated by such circumstances:
Clinically narrow pelvis.
Such a complication occurs when the fetus has a large head, and even if the cervix is fully opened (10 cm), it does not advance. This complication is called a discrepancy between the size of the baby's head and the pelvis of the expectant mother. characteristic feature is that the parameters of the mother's pelvis may be normal, but childbirth is significantly hampered even if there are strong and good contractions. If there is an anatomically narrowed pelvis (the dimensions of the pelvis are shortened by 1-1.5 or more centimeters), then the issue of performing a caesarean section is discussed.
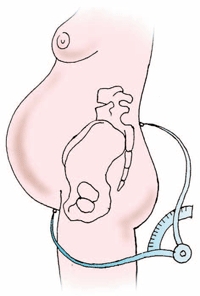
Untimely outpouring of water.
The discharge of amniotic fluid before the opening of the pharynx by 8 cm (early) may be due to the high position of the head of the child, due to its large size, it cannot normally press against the entrance of the small pelvis and move forward, respectively, there is no differentiation of the amnion into the posterior and anterior. Early discharge of amniotic fluid threatens to fall out of small parts of the child (handle, leg) or umbilical cord. In addition, a complication can slow down the process of opening the cervix of the uterus, which leads to a lengthening of the first stage of labor and significantly weakens the woman in labor. In case of loss of part of the fetus or umbilical cord, immediate delivery through surgery is indicated.
Anomalies of tribal forces.
The birth of a large fetus is quite often complicated by anomalies of the birth forces. A protracted labor process leads to a decrease in the frequency and intensity of contractions (weak labor activity appears, primary or secondary). The child suffers in such cases, as intrauterine hypoxia increases (first, tachycardia is heard in the fetal heartbeat, and then slowing down - bradycardia). Such signs are also an indication for operative delivery.
Threat of uterine rupture.
The pushing period at the birth of a large child is also dangerous. During the passage of the fetal head through the birth canal, it changes shape, acquiring the most suitable configuration for overcoming the planes of the small pelvis (the bones of the skull seem to overlap one another). If the size of the baby's head and the mother's pelvis are disproportionate, overstretching of the lower segment of the uterus occurs, which can cause it to rupture.
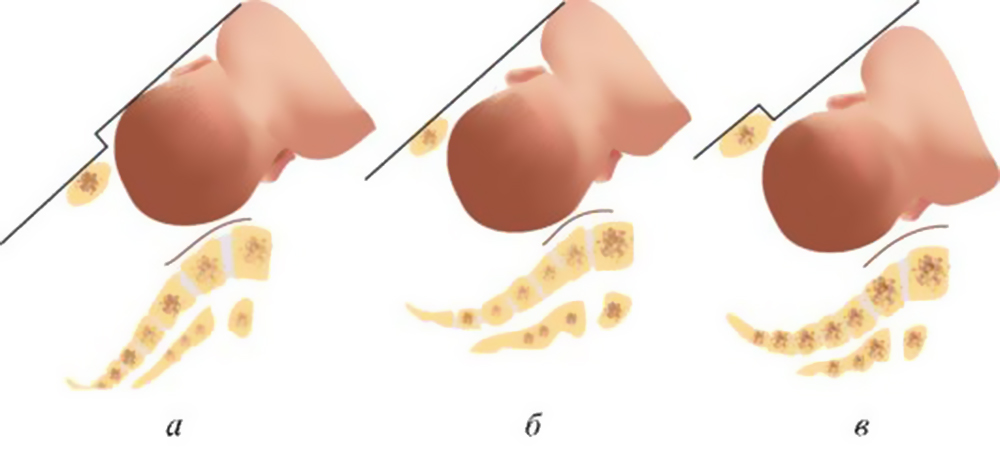
Fistula formation.
Prolonged standing of the baby's head in one of the planes of the pelvis leads to compression of the soft tissues of the birth canal (vagina and cervix), the bladder is also compressed in a pair with the urethra in front and the anus, respectively, in the back. Such pressure leads to a violation of blood circulation in the tissues, ischemia occurs, followed by the death of fiber (tissue necrosis). Dead tissues after childbirth are rejected by the body, which leads to the appearance of rectovaginal and genitourinary fistulas.
Rupture of the articulation of the womb.
Severe passage of the baby's head can cause damage to the pubic joint (divergence of the pubic bones, rupture of the ligaments), often such injuries, especially severe ones, require exclusively surgical treatment.
Shoulder dystocia.
Childbirth with large sizes can be complicated during the passage of the shoulders, this complication is especially typical for children with diabetic phenopathy (the size of the head is much smaller than the size of the shoulder girdle). In such situations, additional assistance is provided during the passage, which often ends in fractures of the cervical spine, humerus or collarbone.
Cerebral hemorrhage or cephalohematoma in the fetus.
The development of such a complication occurs against the background of a disorder of the uteroplacental blood flow, followed by hypoxia of the child, anomalies of the birth forces. During a change in the configuration of the head, there is a strong displacement of the bones and their excessive compression, which ends in hemorrhage into the periosteum or brain.
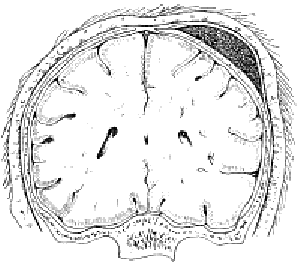
Birth management
If a woman is diagnosed with a large fetus, then the nature of delivery: through the natural birth canal (normal birth) or through surgery (caesarean section) depends on many factors. Planned operative delivery is required for the following indications:
large fetus in women over 30 and under 18;
myomatous nodes and a large fetus, anomalies in the development of the uterus;
anatomically narrow pelvis with a large weight of the child;
a large child and re-carrying of pregnancy;
the totality of a large fetus and its breech presentation;
large fetal weight with an aggravating obstetric history (use of assisted reproductive technologies for infertility, recurrent miscarriage, stillbirth in the past);
indications that require the exclusion of a tight period (high myopia, cardiovascular pathology) in combination with a large child.
Cesarean section in the event of emergency indications is performed in any case of complications in childbirth (incorrect insertion of the head, the threat of uterine rupture, weakness of contractions).
In the first couple of hours after delivery (early postpartum period) there is a high risk of developing hypotonic uterine bleeding, which is caused by excessive distension of the uterus and prolonged labor.
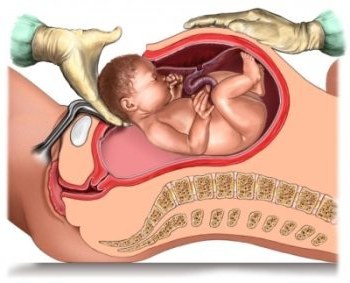
In the course of drawing up a plan for delivery through the natural birth canal, it is necessary to take into account:
childbirth should take place under the monitor control of contractions and the condition of the child;
it is obligatory to maintain a partogram (a schedule taking into account the time of each of the periods of labor, the intensity of contractions, the opening of the uterine os);
in childbirth, a re-measurement of the parameters of the pelvis should be carried out;
timely and adequate pain relief, as well as the introduction of antispasmodics;
prophylactic administration of reducing agents in the pushing period in order to prevent weakness of attempts;
early diagnosis of a narrow (clinically) pelvis;
prevention of possible bleeding in the first 2 hours after childbirth and in the postpartum period.
Children who are born with a weight of four or more kilograms are at high risk of pathologies of the central nervous system, the development of metabolic disorders, asphyxia, the development of birth injuries (fractures of the collarbone, shoulder, cerebral hemorrhage, cephalohematomas), general morbidity and mortality in early neonatal age (the first 28 days of life).
Question answer
Is hospitalization required before childbirth, in case of pregnancy with a large fetus?
Yes, all women diagnosed with a large fetus should go to the hospital a little earlier than the due date, at about 38-39 weeks. During this time, the doctor will perform a thorough diagnosis, assess the condition of the expectant mother (presence of pregnancy complications, extragenital diseases), carefully measure the size of the abdomen and pelvis of the woman in labor, draw up a plan for conducting the birth process. If there are indications for a planned caesarean section, then an operation plan will be drawn up.
How to prevent the development of a large fetus?
First of all, from the moment of pregnancy, you need to adhere to proper nutrition. The diet should consist of food rich in carbohydrates, fats and proteins. You should give up the habit of overeating, as well as the passion for fried, fatty foods and pastries with sweets. If the state of health allows, it is necessary to perform exercises for pregnant women in order to avoid hypodynamia (prolonged sitting or lying down).

During my first pregnancy, I was diagnosed with a large fetus. Is it necessary to perform a caesarean section?
No, operative delivery is not a mandatory algorithm for childbirth, especially in the first childbirth in young women. In most cases, in young healthy women, the process of pregnancy and childbirth takes place without significant complications and with a favorable outcome.
