03.05.2011, 22:50
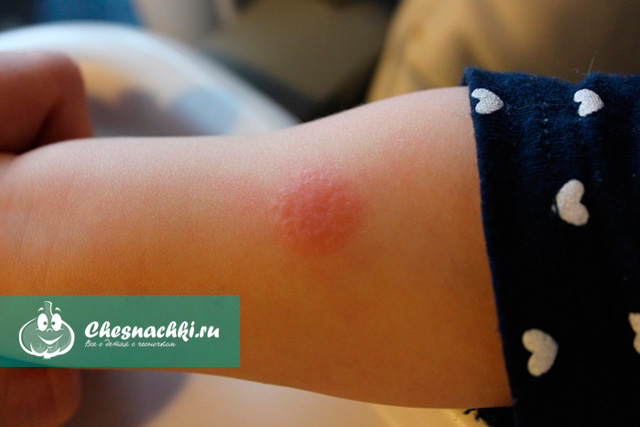
they did it today in the Mantoux kindergarten ... The child says that he didn’t wet it with water .. And for some reason, a swollen spot around the injection site with a diameter of 1.5-2 cm is approximately ...
I don’t remember something - so it was before, in previous years ...
Child 6 years old...
What is this reaction? maybe an allergic reaction? can give Zirtek or Suprastin? (child allergic)
Or is that the first day?
In some patients, radiation therapy is also used, especially if the lymphoma is in a limited area. Your doctor may test fluid around the brain, called cerebrospinal fluid, in certain cases during diagnosis and recommended treatments to prevent lymphoma from reaching the brain, called central prophylaxis. nervous system. Most of the time it starts in the lymph nodes, it is often lazy and grows very slowly. However, recent studies show that more than 85% of patients live at least 5 years after receiving a diagnosis of follicular lymphoma. In addition, 50% of patients are thought to live beyond 12 years. Or, they can be carefully monitored with watchful waiting and treated only when symptoms appear. Recent clinical studies show that patients with follicular lymphoma have lived longer in recent decades. Many new drugs are being evaluated for use as part of first-line treatment for follicular lymphoma. It is possible that stem cell transplantation, T-cell therapy with chimeric antigen receptors, and monoclonal antibody treatment may also be available treatment options, usually in clinical trials. It is most common in people over 60 and is much more common in men than women. Overall, it compromises the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, and digestive tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. The first approach to treat mantle cell lymphoma is to use a combination of chemotherapy with a monoclonal antibody. Most people with mantle cell lymphoma will have a recurrence of the disease after chemotherapy ends. As a result, physicians offer patients high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation at the end of treatment with initial chemotherapy; maintenance therapy with the monoclonal antibody rituximab is often given after transplantation. Physicians may offer maintenance therapy with rituximab or another monoclonal antibody for patients who are not being offered a stem cell transplant. If chemotherapy does not work, there are different opinions about the best way treatment of mantle cell lymphoma. This type of lymphoma is closely related to a disease called chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia. Or they may be under close supervision with watchful waiting. It is a large mass in the chest area. The mass can cause breathing problems or superior vena cava syndrome, a set of symptoms caused by blockage or partial compression of the superior vena cava. The superior vena cava is the main vein that carries blood from the head, neck, chest, and arms to the heart. Most often, doctors treat it with anthracycline and rituximab chemotherapy. A closely related lymphoma, called mediastinal gray area lymphoma, can also occur in the same age group. It is treated similarly to primary large B-cell mediastinal lymphoma. B-cell marginal zonal lymphoma. This type of lymphoma starts in the spleen and can also affect the blood. Usually their growth is slow and the therapeutic approach is usually watchful waiting. If the patient needs treatment, this type of lymphoma is usually treated similarly to follicular lymphoma. However, it can also occur in the lungs, skin, thyroid gland, salivary gland, or in the orbit of the eye and adjacent to it. Patients with this type of lymphoma often have a history of an autoimmune disease such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or Sjögren's syndrome. In other cases, the most common treatment plan is radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, or a combination of these procedures. Approximately 1% of people with lymphoma have this subtype. This form of lymphoma often affects the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. When this happens, the condition is known as Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. Treatment is similar to that of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or follicular lymphoma. Treatment may include the following: Expectant monitoring. Directed therapy with monoclonal antibodies. Combinations of chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies. The most common types of lymphoma are B-cell and T-cell lymphomas, which account for 85% and 15% of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
03.05.2011, 22:52
mantoux is measured after a strictly defined time
03.05.2011, 23:11
wait, it happens.
03.05.2011, 23:57
don't panic, it happens. Then they check not by a spot, but by a button.
04.05.2011, 00:12
04.05.2011, 14:55
If it’s really 1.5 - 2 cm, then they will send you to the tube dispensary to do the Perque reaction ... They won’t even ask, they wetted it - they didn’t wet it: 008: They are obliged to send with such a reaction. Moreover, if this has not happened before, it means a turn. This year we have 16mm, they sent it to a tube dispensary, today we went, they did Perke (or Pirke - how right?: 008 :) They also said to bring a fluorography of all adults living with the child.
Maybe with a fright it seemed to you that 2 cm? Maybe less, well, there mm 14-15? Although it's still a lot ... The upper limit of the norm is 17 mm.
Antihistamine can be given, but now it will not help much ... Who is afraid of an allergic reaction (or knows for sure that there is an allergy to tuberculin) - they give antihistamines 2 days before Mantoux and then every day until the test.
They explained everything to us today in the dispensary ... If Mantou is big, they make Perke. If it's bad again - then Diaskintest (but not earlier than a month after Mantoux). And then on the basis of this they make a diagnosis. If it's just "tuberculosis" - then it's okay, tubercular infection is not a disease of tuberculosis, the child can simply be a carrier of the infection, but not get sick with tuberculosis (in the sense that treatment is required). We have 99% of the adult population TB-well, at least that's what they said in the dispensary.
And it could also be just an allergic reaction, then it won’t reach Diaskintest, Perke will show everything.
In general, do not worry, most likely - nothing to worry about. My allergy to tuberculin manifested itself at the age of 8 (before that, for some reason, I didn’t have it :))) Passed all the tests, recognized the allergy and fell behind. Although Mantoux was still regularly done at school, and the reaction was consistently great. And by the way, maybe my child will have the same thing now (we are 7 years old):)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma can be present at any age but occurs primarily in the elderly. This type of lymphoma usually starts as a rapidly growing mass of organs such as the intestines, bones, brain, spinal cord, or lymph node. Overall, approximately 75% of patients show no signs of disease after initial treatment, and about half of these patients are cured with treatment. Large cell mediastinal lymphoma is a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma but is characterized by more fibrosis. About 60% of patients with this lymphoma are women, most of whom are young people in their 30s. This lymphoma starts in the mediastinum and can cause breathing difficulties by pressing on the trachea and blocking the superior vena cava. Approximately half of patients can be cured. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma is a rare subtype, with lymphoma cells found only inside blood vessels. Follicular lymphoma - The term follicular means that cells tend to grow in circles in the lymph nodes. The median age of onset of this type of lymphoma is around 60 years old and is rare in very young people. Follicular lymphomas are often slow growing and respond well to treatment, but are difficult to cure. Patients are kept under medical supervision until the lymphoma begins to cause obvious changes. However, over time, about 30% of follicular lymphomas become diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. The lymphocytic cancer cells are mainly found in the lymph nodes and in the larynx. Mantle cell lymphoma is about 5% of this type of lymphoma, and their cells are small to medium. Recent treatments are more aggressive and may be more effective than those used in the past, giving a better chance of long-term survival. Marginal zonal B-cell lymphoma Marginal zonal lymphomas account for 5 to 10% of lymphomas. Patients are often elderly, male, and present with fatigue and discomfort caused by increased disease. As the disease slowly grows, treatment may not be needed unless symptoms become problematic. Burkitt's lymphoma - this type makes up 1% to 2% of all lymphomas, their cells are medium in size, and it is a very fast growing lymphoma. 90% of patients are men average age which is 30 years old. Although it is a rapidly growing lymphoma, more than half of patients can be cured with aggressive chemotherapy. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma - this type is not common and makes up only 1% to 2% of lymphoma, its cells are small and are mainly found in the bone marrow, lymph nodes and lungs. This lymphoma usually involves the brain, but can also be found in the spinal cord and tissues around the eyes. Most patients experience headaches, mental confusion, vision problems, paralysis of some facial muscles, and even seizures. It can be considered both lymphoma and leukemia, depending on which part of the bone marrow is involved. This lymphoma usually starts in the thymus and can progress to a large tumor in the mediastinum, which can cause respiratory problems or compress the superior vena cava. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma - This type of lymphoma develops from more mature forms of T-cells. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma - Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, also known as fungal mycoses, Sezari syndrome, and others, starts in the skin and accounts for about 5% of all lymphomas. Patients usually present with fever, weight loss, and skin rash and frequently develop infections. This lymphoma occurs in people with an intolerance to gluten, the main protein in wheat flour. The disease, called gluten-sensitive enteropathy, can progress to lymphoma, which usually invades the intestinal wall. This is a fast growing lymphoma, with a great chance of being cured with aggressive chemotherapy.
- Although it is growing rapidly, it responds well to treatment.
- This type makes up 2% of all lymphomas.
- It is a rapidly growing lymphoma but generally responds well to treatment.
- This type of lymphoma does not require immediate treatment.
- Both are slow growing and handled in the same way.
- This type of lymphoma is more common in men with an average age of 60 years.
- When diagnosing lymphoma, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and lungs are found.
- Mantle cell lymphoma does not grow very quickly, but is difficult to treat.
- There are 3 types of marginal zone lymphoma.
- This lymphoma is slowly growing.
- Cellular leukemia - Despite the name, it is sometimes considered a type of lymphoma.
- They are commonly found in the bone marrow, bone marrow, and blood.
- Men, with an average age of 50, are more likely than women to develop this type of lymphoma.
- Lymphoma of the primary central nervous system.
- Lymphoma of the lymphoarea - Responsible for about 1% of all lymphomas.
- Patients are most often young people.
- They are rare and represent only a small fraction of all lymphomas.
- There are four subtypes: latent, chronic, acute, and lymphoma.
- Large anaplastic cell lymphoma is about 2% of this type of lymphoma.
- It usually starts in the lymph nodes and may spread to the skin.
what day is it measured?
04.05.2011, 14:58
What is Perk? where do they do it, in Helix do they do a blood test from a vein?
Today the spot is smaller, 1.5 cm.. and there is no swelling... can it go away?
what day is it measured?
Pirque reaction
Pirke reaction, Pirke test, skin allergic diagnostic test to detect hypersensitivity of a person to the causative agent of tuberculosis. Proposed by the Austrian pathologist and pediatrician K. Pirquet (S. Pirquet; 1907). A drop of tuberculin (a drug made from killed tuberculous mycobacteria) is applied to the skin of the forearm after a preliminary incision. The result is taken into account after 2-3 days, focusing on the amount of swelling at the incision site. Positive P. r. can be the result of both contact of the organism with the causative agent of tuberculosis (infectious allergy), and anti-tuberculosis vaccinations (post-vaccination allergy). The test is used to detect children infected with mycobacterium tuberculosis in preschool institutions and schools. Children with newly diagnosed positive Etc. referred to a phthisiatrician for examination. With widespread intradermal vaccinations against tuberculosis, the sample loses its diagnostic value. However, modified versions of the sample are used in phthisiology to determine the activity of the process. A more sensitive intradermal tuberculin test is used to select uninfected individuals for intradermal immunization.
Some of the children who attended the first parties have now become employees of the transport company. At the age of 72, but at the behest of a boy, José Pereira, he remembers the first editions of the festivities, which, he said, stemmed from the idea of thanking the population of the city, as well as God for achievements and even battles from day to day. We are blessed with health, what we overcome is the fruit of our work, and that is enough to be thankful to God. And we wanted to somehow show this gratitude. And nothing better than leaving a child's day happier, said the businessman.
Yes, wait for you to measure the result and stop winding yourself up.
Greetings, readers of my blog!
The Mantoux reaction is a well-known procedure carried out at school and in kindergarten. Any deviations in the results of the test cause a storm of parental emotions. Let's discuss today what it means if Mantoux is increased?
The Mantoux reaction is an annual procedure carried out by children in schools. This is how the presence of the causative agent of tuberculosis in the baby's body is checked. The Mantoux test is a regular vaccination, after which a papule appears on the second or third day - a small reddish elevation. In fact, this is not a vaccine, but really a test.
The more pathogens in the baby's body, the wider the seal will be. Depending on the size of the papule, the result is determined:
- negative - if the papule is absent or does not exceed 1 mm;
- doubtful - the size of the papule is from 2 to 4 mm;
- positive - the size of the papule is up to 5 to 16 mm (depending on the degree of infection);
- hyperergic - diameter more than 17 mm. This means that the child is infected and the disease is acute.
However, dear readers, it should be remembered that there can always be a false positive result when contraindications to Mantoux, the presence of an allergy to tuberculin in the baby, and recent infections were not taken into account.
Before raising a panic, you need to find out the reasons for the increase in Mantoux, and they may not be related to the disease in any way.
Why is the papule enlarged?
Unfortunately, there are many subjective factors that make Mantoux's results untrue:
Allergy
If the child is prone to allergies, then the probability that the papule will be increased is 80%. Allergy can manifest itself not only to tuberculin, but also to other irritants. If the doctor was not warned about this in advance, he may think that the baby has a positive reaction.
Poor quality vaccine
Unfortunately, in our enlightened age, this also occurs, and quite often. Improper storage of the vaccine and an attempt by manufacturers to save money leads to a decrease in the quality of medical products.
What to do in this case, it is difficult to advise. The only way out is to make Mantoux after a while in another clinic.
Human factor
It happens that the doctor, due to fatigue or inexperience, took the wrong measurements. It does not make sense to double-check on your own: this should be done by a person with a medical education, since the procedure is not as simple as it seems.
If the child was checked by Mantoux at school, take him to the pediatrician at the clinic and ask him to take a measurement.
Individual characteristics of the organism
If the child eats a lot of protein foods (eggs, milk, meat), or has a hereditary reaction to tuberculin, the result may be positive. In this regard, on the eve of vaccination, protein products should be excluded from the diet.
Tuberculosis
This is the worst option when your baby is really sick or is a wand carrier. It may not manifest itself in any way until a certain point, but such a child is registered in a tuberculosis dispensary, and parents should carefully monitor his health, lifestyle and nutrition.
The frequency of false positive results also increases due to the negligent attitude of the school's medical staff themselves. As a rule, they do not warn parents that tomorrow or in a few days the child will undergo a Mantoux reaction.
Moreover, they are not always interested in what the baby was sick recently, whether he has a runny nose, how he feels. Vaccinations are given to everyone in a row, fearing that parents will write refusals. Hence, there are so many problems with unexpected results in perfectly healthy children.
Hike to the phthisiatrician
Parents go into a real panic when a child is found to be positive and sent to a tuberculosis dispensary for examination by a phthisiatrician. There is no need to be afraid of this, because sometimes a more experienced specialist, after a careful examination, can determine that the increase in the papule was false.
What threatens a trip to a phthisiatrician will become clear if you stop worrying and prepare for this meeting with all responsibility. Prepare the following documents:
- an extract from the child's outpatient card, which indicates vaccinations, including BCG;
- take blood and urine tests in advance and take the results with you;
- whether it is necessary to do an x-ray, each parent decides on his own, but the phthisiatrician will most likely send the child for fluorography, therefore, if it has not been done within a year, it is better to immediately take a referral;
- the results of fluorography of all family members who live with the child.
What can a phthisiatrician do?
- Conduct an inspection;
- Collect anamnesis;
- Check the tests you brought, x-rays;
- It will measure the Mantoux reaction (in order for the measurement to be accurate, it is better to go to the phthisiatrician within 6 days after vaccination).
This is a diagnostic minimum, on the basis of which it is possible to draw a conclusion about the health of the child. If everything is fine, you will be allowed to go home.
In the case of a positive result in the absence of pronounced symptoms, but the carriage of the wand, the baby is registered in the tuberculosis dispensary, he is closely monitored, isoniazid is prescribed, as well as appropriate treatment.
Parents should remember one thing: an enlarged papule after Mantoux is not a sentence, but an occasion to carefully consider the health of the child.